Optical networking is a expertise that makes use of gentle indicators to transmit knowledge by means of fiber-optic cables. It encompasses a system of parts, together with optical transmitters, optical amplifiers, and fiber-optic infrastructure to facilitate high-speed communication over lengthy distances.
This expertise helps the transmission of huge quantities of knowledge with excessive bandwidth, enabling sooner and extra environment friendly communication in comparison with conventional copper-based networks.
Foremost parts of optical networking
The principle parts of optical networking embrace fiber optic cables, optical transmitters, optical amplifiers, optical receivers, transceivers, wavelength division multiplexing (WDM), optical switches and routers, optical cross-connects (OXCs), and optical add-drop multiplexers (OADMs).
Fiber optic cables
Fiber optic cables are a sort of high-capacity transmission medium with glass or plastic strands often called optical fibers.
These fibers carry gentle indicators over lengthy distances with minimal sign loss and excessive knowledge switch charges. A cladding materials surrounds the core of every fiber, reflecting the sunshine indicators again into the core for environment friendly transmission.
Fiber optic cables are broadly utilized in telecommunications and networking purposes as a result of immunity to electromagnetic interference and lowered sign attenuation in comparison with conventional copper cables.
Optical transmitters
Optical transmitters convert electrical indicators into optical indicators for transmission over fiber optic cables. Their major perform is to modulate a lightweight supply, often a laser diode or light-emitting diode (LED), in response to electrical indicators representing knowledge.
Optical amplifiers
Strategically positioned alongside the optical fiber community, optical amplifiers increase the optical indicators to take care of sign power over prolonged distances. This element compensates for sign attenuation and permits the space indicators to journey with out costly and complicated optical-to-electrical sign conversion.
The first sorts of optical amplifiers embrace:
- Erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA): EDFAs make use of erbium-doped optical fiber. When uncovered to gentle at a particular wavelength, erbium ions throughout the fiber soak up and re-emit photons, amplifying the optical sign. Usually used within the 1550 nm vary, EDFA is a key element for long-haul communication.
- Semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA): SOAs amplify optical indicators by means of semiconductor supplies. Incoming optical indicators induce stimulated emission throughout the semiconductor, leading to sign enchancment. SOAs concentrate on short-range and entry community situations.
- Raman amplifier: Raman amplifiers use the Raman scattering impact in optical fibers. Pump gentle at a distinct wavelength interacts with the optical sign, transferring vitality and intensifying it. The sort of amplifier is flexible and may function at numerous wavelengths, together with the generally used 1550 nm vary.
Optical receivers
On the reception finish of the optical hyperlink, optical receivers remodel incoming optical indicators again into electrical indicators.
Transceivers
Transceivers, brief for transmitter-receiver, are multifunctional gadgets that mix the functionalities of each optical transmitters and receivers right into a single unit, facilitating bidirectional communication over optical fiber hyperlinks. They flip electrical indicators into optical indicators for transmission, and convert acquired optical indicators again into electrical indicators.
Wavelength division multiplexing (WDM)
Wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) permits the simultaneous transmission of a number of knowledge streams over a single optical fiber. The basic precept of WDM is to make use of totally different wavelengths of sunshine to hold unbiased knowledge indicators, supporting elevated knowledge capability and efficient utilization of the optical spectrum.
WDM is broadly utilized in long-haul and metro optical networks, offering a scalable and cost-effective resolution for assembly the rising demand for high-speed and high-capacity knowledge transmission.
Optical add-drop multiplexers (OADMs)
Optical add-drop multiplexers (OADMs) are main parts in WDM optical networks, providing the aptitude to selectively add (inject) or drop (extract) particular wavelengths of sunshine indicators at community nodes. OADMs assist refine the information movement throughout the community.
Optical switches and routers
Each optical switches and routers contribute to the event of superior optical networks with options for high-capacity, low-latency, and scalable communication methods that may meet the altering calls for of recent knowledge transmission.
- Optical switches selectively route optical indicators from one enter port to a number of output ports. They’re necessary in establishing communication paths inside optical networks. These gadgets work by controlling the course of optical indicators with out changing them into electrical indicators.
- Optical routers, however, direct knowledge packets on the community layer based mostly on their vacation spot addresses. They function within the optical area, sustaining the integrity of the optical indicators with out changing them into electrical kind.
Optical cross-connects (OXCs)
Optical cross-connects (OXCs) allow the reconfiguration of optical connections by selectively routing indicators from enter fibers to desired output fibers. By streamlining wavelength-specific routing and fast reconfiguration, OXCs contribute to the pliability and low-latency traits of superior optical communication methods.
How optical networking works
Optical networking features by harnessing gentle indicators to transmit knowledge by means of fiber-optic cables, making a fast communication framework. The method includes gentle sign era, gentle transmission, knowledge encoding, gentle propagation, sign reception and integration, and knowledge processing.
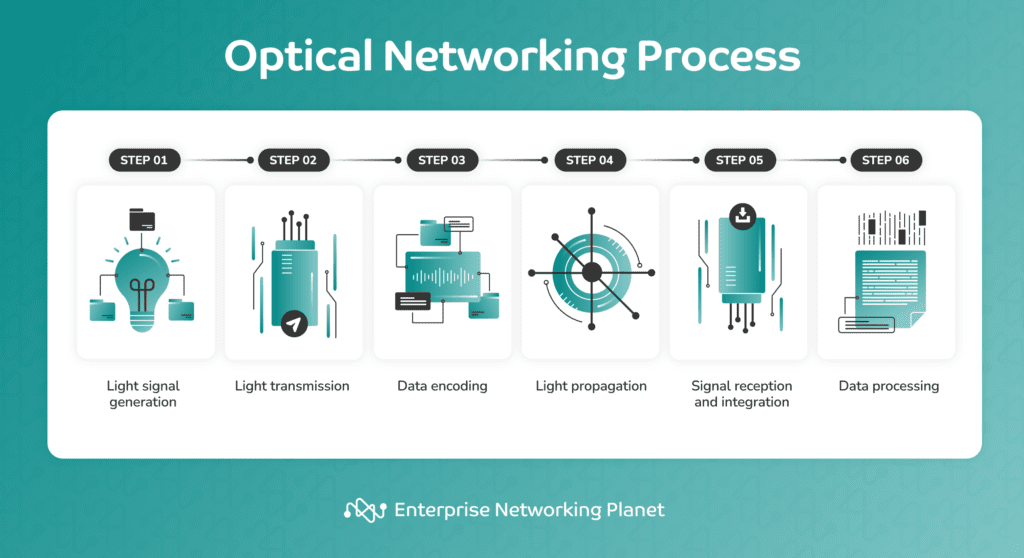

1. Gentle sign era
The optical networking course of begins by changing knowledge into gentle pulses. This conversion is often achieved utilizing laser sources to safe the profitable illustration of knowledge.
2. Gentle transmission
The system sends gentle pulses carrying knowledge by means of a fiber optic cable throughout this section. The sunshine travels throughout the cable’s core, bouncing off the encompassing cladding layer as a result of whole inside reflection. This lets the sunshine journey nice distances with minimal loss.
3. Information encoding
Information is then encoded onto the sunshine pulses, introducing variations in both the sunshine’s depth or wavelength. This course of is tailor-made to satisfy the wants of enterprise purposes, guaranteeing a seamless integration into the optical networking framework.
4. Gentle propagation
The sunshine pulses propagate by means of the fiber-optic cables, delivering high-speed and dependable connectivity throughout the community. This ends in the swift and safe transmission of necessary info between totally different areas.
5. Sign reception and integration
On the receiving finish of the community, photosensitive gadgets, like photodiodes, detect the incoming gentle indicators. The photodiodes then convert these gentle pulses again into electrical indicators, bettering optical networking integration.
6. Information processing
{The electrical} indicators endure additional processing and interpretation by digital gadgets. This stage consists of decoding, error correction, and different operations obligatory to ensure the information transmission accuracy. The processed knowledge is used for numerous operations, supporting key features, reminiscent of communication, collaboration, and data-driven decision-making.
8 sorts of optical networks
There are various various kinds of optical networks serving numerous functions. Probably the most generally used ones are mesh networks, passive optical community (PON), free-space optical communication networks (FSO), wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) networks, synchronous optical networking (SONET) and synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH), optical transport community (OTN), fiber to the house (FTTH)/fiber to the premises (FTTP), and optical cross-connect (OXC).
1. Mesh networks
Optical mesh networks interconnect nodes by means of a number of fiber hyperlinks. This offers redundancy and permits for dynamic rerouting of visitors in case of hyperlink failures, enhancing the community’s reliability.
- Typical use: Typically utilized in large-scale, mission-critical purposes the place community resilience and redundancy are important, reminiscent of in knowledge facilities or core spine networks.
2. Passive optical community (PON)
PON is a fiber-optic community structure that brings optical cabling and indicators to the tip consumer. It makes use of unpowered optical splitters to distribute indicators to a number of customers, making it passive.
- Typical use: “Final-mile” connectivity, offering high-speed broadband entry to residential and enterprise customers.
3. Free-space optical communication (FSO)
FSO makes use of free house to transmit optical indicators between two factors.
- Typical use: Excessive-speed communication in environments the place it’s impractical or difficult to put optical fibers, reminiscent of city areas or navy functions.
4. Wavelength division multiplexing (WDM)
WDM makes use of totally different wavelengths of sunshine for every sign, permitting for elevated knowledge capability. Sub-types of WDM embrace coarse wavelength division multiplexing (CWDM) and dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM).
- Typical use: CWDM is used for short-distance, metro-area networks, whereas DWDM is for long-haul and high-capacity communication.
5. Synchronous optical networking (SONET)/synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH)
SONET and SDH are standardized protocols for transmitting massive quantities of knowledge over lengthy distances utilizing fiber-optic cables. North America extra generally makes use of SONET, whereas worldwide industries use SDH.
- Typical use: SONET and SDH are designed for high-speed, long-distance transmission of voice, knowledge, and video. They provide a synchronous and dependable transport infrastructure utilized in telecommunications backbones and service networks.
6. Optical transport community (OTN)
OTN transports digital indicators within the optical layer of communication networks. It comes with features like error detection, efficiency monitoring, and fault administration options.
- Typical use: Used along with WDM to maximise the resilience of long-haul transmissions.
7. Fiber to the house (FTTH)/fiber to the premises (FTTP)
FTTH and FTTP consult with the deployment of optical fiber on to residential or enterprise premises, offering high-speed web entry.
- Typical use: FTTH and FTTP assist bandwidth-intensive purposes like video streaming, on-line gaming, and different broadband companies.
8. Optical cross-connect (OXC)
OXC facilitates the switching of optical indicators with out changing them to electrical indicators.
- Typical use: Principally utilized in large-scale optical networks by telecommunication carriers to handle visitors.
How optical networking is used right now
Varied industries and domains right now use optical networking for high-speed and environment friendly knowledge transmission. These embrace telecommunications, healthcare, monetary organizations, knowledge facilities, web service suppliers (ISPs), enterprise networks, 5G networks, video streaming companies, and cloud computing.
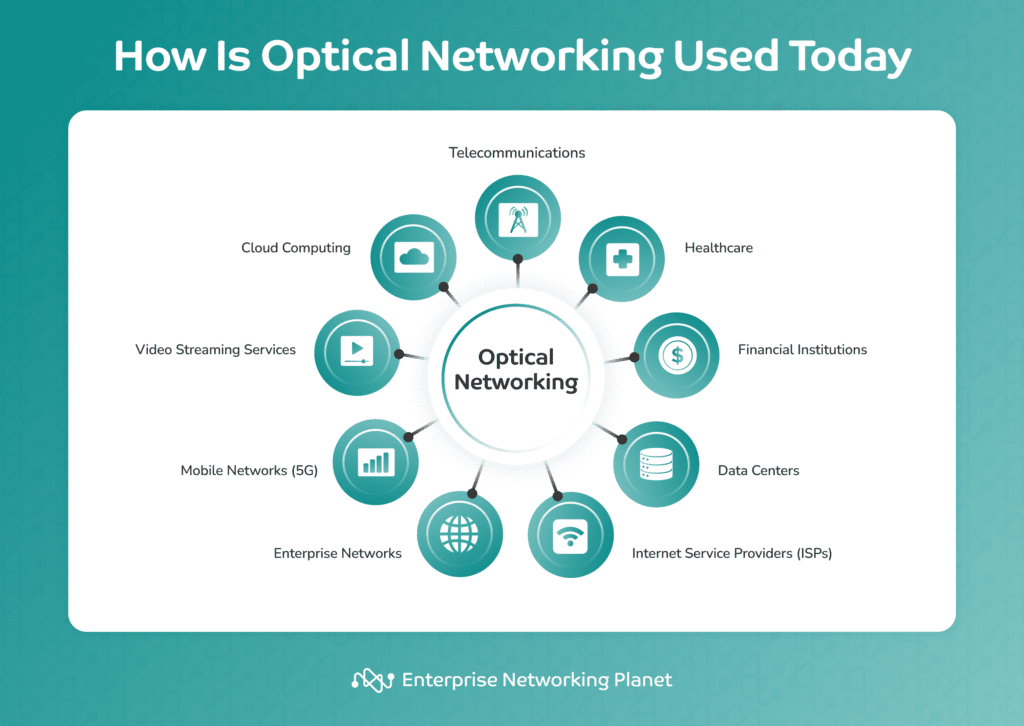

Telecommunications
Optical networking is the muse of cellphone and web methods. In the present day, optical networking stays pivotal in telecommunications, connecting cell websites, guaranteeing excessive availability by means of dynamic visitors rerouting, and enabling high-speed broadband in metropolitan areas and long-distance networks.
Healthcare
For healthcare, optical networking ensures fast and safe transmission of medical knowledge, expediting distant diagnostics and telemedicine companies.
Monetary organizations
Monetary organizations use this expertise for quick and protected knowledge transmission, which is indispensable for actions like high-frequency buying and selling and connecting branches seamlessly.
Information facilities
Optical networking in knowledge facilities hyperlinks servers and storage models, providing a high-bandwidth and low-latency infrastructure for dependable knowledge communication.
Web service suppliers (ISPs)
Web service suppliers (ISPs) make use of optical networking to supply broadband companies, utilizing fiber-optic connections for faster web entry.
Enterprise networks
Giant companies use inside optical networking to attach workplaces and knowledge facilities, sustaining high-speed and scalable communication inside their infrastructure.
Cellular networks (5G)
For 5G cell networks, optical networking permits for elevated knowledge charges and low-latency necessities. Fiber-optic connections hyperlink 5G cell websites to the core community, bringing bandwidth for numerous purposes.
Video streaming companies
Optical networks allow clean knowledge transmission to ship high-quality video content material through streaming platforms for a extra optimistic viewing expertise.
Cloud computing
Cloud service suppliers depend on optical networking to interconnect knowledge facilities to present scalable and high-performance cloud-based companies.
Historical past of optical networking
The collaborative efforts of a number of optical networking corporations and distinguished people have considerably formed the optical networking panorama as we all know it right now.
- 1792: French inventor Claude Chappe invented the optical semaphore telegraph, one of many earliest examples of an optical communication system.
- 1880: Alexander Graham Bell patented the Photophone, an optical phone system. Nonetheless, his first invention, the phone, was deemed to be extra sensible.
- 1966: Sir Charles Okay. Kao and George A. Hockham proposed that fibers product of ultra-pure glass may transmit gentle for distances of kilometers with no whole lack of sign.
- 1996: The primary commercially accessible 16-channel DWDM system was launched by Ciena Company.
- Nineties: Organizations started to use fiber optics in enterprise native space networks (LANs) to attach Ethernet switches and IP routers.
- Speedy growth of optical networks to assist the rising demand pushed by the web increase.
- Organizations started to make use of optical amplification to lower the necessity for repeaters, and extra companies applied WDM to spice up knowledge capability. This marked the beginning of optical networking, as WDM grew to become the expertise of alternative for increasing the bandwidth of fiber-optic methods.
- 2009: The time period software-defined networking (SDN) was first coined in an MIT evaluate article.
- Current: 5G began changing into accessible in 2020.
- Analysis and growth for photonic applied sciences continues. Photonics options have extra reliable laser capabilities and may switch gentle at historic speeds, letting gadget producers unlock broader purposes and put together next-generation merchandise.
Tendencies in optical networking
Tendencies in optical networking, reminiscent of 5G integration, elastic optical networks, optical community safety, interconnects in knowledge facilities, and inexperienced networking spotlight the continuing evolution of the expertise to satisfy the calls for of latest applied sciences and purposes.
5G integration
Optical networking permits the mandatory high-speed, low-latency connections to deal with the information calls for of 5G purposes. 5G integration makes certain that you just get quick and dependable connectivity for actions reminiscent of streaming, gaming, and rising applied sciences like augmented actuality (AR) and digital actuality (VR).
Coherent optics developments
Ongoing developments in coherent optics expertise contribute to larger knowledge charges, longer transmission distances, and elevated capability over optical networks. That is important for accommodating the rising quantity of knowledge visitors and supporting purposes that want excessive bandwidth.
Edge computing
Integration of optical networking with edge computing reduces latency and elevates the efficiency of purposes and companies that decision for real-time processing. That is crucial for apps and companies needing real-time responsiveness, reminiscent of autonomous automobiles, distant medical procedures, and industrial automation.
Software program-defined networking (SDN) and community perform virtualization (NFV)
Adopting SDN and NFV in optical networking results in higher flexibility, scalability, and efficient useful resource use. This lets operators dynamically allocate sources, optimize community efficiency, and reply shortly to altering calls for, bettering general community effectivity.
Elastic optical networks
Elastic optical networks permit for dynamic changes to the spectrum and capability of optical channels based mostly on visitors calls for. This promotes optimum useful resource use and minimizes the chance of congestion throughout peak utilization intervals.
Optical community safety
Specializing in bolstering the safety of optical networks, together with encryption strategies, is necessary for safeguarding delicate knowledge and communications. As cyberthreats turn into extra refined, safeguarding your networks turns into paramount, particularly when transmitting delicate info.
Optical interconnects in knowledge facilities
The rising demand for high-speed optical interconnects in knowledge facilities is pushed by the necessities of cloud computing, large knowledge processing, and synthetic intelligence purposes. Optical interconnects have the bandwidth to deal with massive volumes of knowledge inside knowledge middle environments.
Inexperienced networking
Efforts to make optical networks extra energy-efficient and environmentally-friendly align with broader sustainability targets. Inexperienced networking practices play a key position in lowering the environmental influence of telecommunications infrastructure, making it extra sustainable in the long term.
Backside line: Optical networking is right here to remain
The development of optical networking has been instrumental in shaping the historical past of laptop networking. As the necessity for sooner knowledge transmission strategies grew with the event of laptop networks, optical networking offered an answer. By utilizing gentle for knowledge transmission, this expertise enabled the creation of high-speed networks that we use right now.
Because it grows, optical networking is doing extra than simply offering sooner web speeds. Optical community safety, as an example, can defend your group towards rising cyberthreats, whereas tendencies like inexperienced networking could make your telecommunication infrastructure extra sustainable over time.
Learn our information on high optical networking corporations and get to know the main optical networking options you’ll be able to think about for your small business.
