US Sanctions Backfire: Huawei’s AI Chips Speed up China’s Self-Reliance
Huawei Applied sciences is getting ready to mass-ship a pair of superior synthetic intelligence chips – the Ascend 910C and upcoming Ascend 920 – marking an enormous second within the international AI {hardware} area. These new chips are poised to fill a void left by U.S. export restrictions which have curbed China’s entry to top-tier AI accelerators from U.S. corporations like Nvidia.
Huawei’s transfer not solely underscores China’s dedication to forge forward in semiconductor self-reliance, but in addition foreshadows a possible reordering of the worldwide AI provide chain. In a local weather of U.S.-China tech tensions, the corporate’s chip ambitions are set to reverberate far past its home market, hinting at an rising bifurcation on the planet’s AI growth ecosystems.
Huawei’s Ascend Chips Purpose to Fill the Nvidia Void
In accordance with sources cited by Reuters, Huawei will start mass shipments of its Ascend 910C AI chip to Chinese language prospects as early as Could. Preliminary deliveries have reportedly already occurred, signaling Huawei’s readiness to step into the breach created by U.S. bans on Nvidia’s high-end GPUs.
The 910C is a cutting-edge AI processor designed to match the efficiency of Nvidia’s flagship H100 accelerator by an ingenious means: it packages two of Huawei’s previous-generation 910B chips into one module. This chiplet integration successfully doubles the computing energy and reminiscence, yielding efficiency corresponding to Nvidia’s H100, which has been barred from China since 2022
The Ascend 910C just isn’t a completely new structure however somewhat an evolutionary improve, leveraging Huawei’s proprietary Da Vinci structure. With roughly 780–800 TFLOPS of AI efficiency (in BF16/FP16 precision), it achieves about 60% of the Nvidia H100’s efficiency on sure duties – a major feat given China’s present manufacturing constraints.
The chip helps mainstream AI frameworks (like TensorFlow and PyTorch) along with Huawei’s personal MindSpore, making it comparatively sensible for Chinese language firms to undertake. By providing a home various with excessive efficiency, Huawei is successfully filling the hole left by Nvidia’s absence. The timing is opportune: simply weeks in the past the U.S. authorities tightened export guidelines, blocking Nvidia’s China-only “H20” AI chips and not using a license. With Nvidia’s superior silicon abruptly off-limits, Huawei’s 910C arrives as a lifeline for China’s tech trade – one developed by itself phrases. This transfer ensures that China’s AI labs and information facilities can proceed coaching massive AI fashions and deploying superior analytics, albeit on homegrown {hardware}. Briefly, Huawei’s new chip shipments sign that Chinese language corporations gained’t be left stranded by geopolitics; as an alternative, they’re pivoting to home options to maintain their AI ambitions on monitor.

Ascend 910 (Huawei)
U.S. Sanctions Spur China’s Tech Self-Reliance
Huawei’s push into high-end AI chips is going on in opposition to the backdrop of an intensifying tech “chilly conflict” between the USA and China. Washington has imposed successive rounds of export controls to restrict China’s entry to cutting-edge semiconductors, citing nationwide safety considerations.
These embody the late-2022 ban on Nvidia’s A100/H100 GPUs for China, prolonged in 2023/24 to cowl even pared-down variations (like Nvidia’s A800, H800, and the H20), in addition to related curbs on superior processors from AMD (MI300 sequence). The intent is to hamper China’s progress in AI and supercomputing, however an unintended consequence is turning into obvious: the restrictions are galvanizing China’s drive for semiconductor self-sufficiency. Beijing has poured large investments into its chip sector (together with a state-backed $47.5 billion “Massive Fund” for semiconductors), and corporations like Huawei are the tip of the spear for these efforts.
Constructing world-class AI chips below sanctions isn’t any straightforward activity. Huawei should navigate round a U.S. expertise blockade that minimize off its entry to prime silicon fabrication and IP. The Ascend 910C gives a case examine in resourcefulness. A part of the chip is reportedly fabricated by China’s main foundry, SMIC, on a 7-nanometer course of. As well as, Huawei has needed to get artistic in sourcing elements: some 910C models might incorporate chips initially made by TSMC for a third-party (Sophgo) that had been acquired by way of intermediaries. U.S. regulators are reportedly investigating such workarounds, underscoring how carefully Washington is awaiting any sanction evasion.
Huawei denies utilizing illicit elements, and TSMC asserts it now not immediately provides Huawei. In the meantime, essential reminiscence like HBM (high-bandwidth reminiscence) for these AI boards may additionally be procured by way of middlemen, on condition that main reminiscence makers are additionally topic to U.S. strain. All of this illustrates the advanced cat-and-mouse dynamic at play: China’s tech giants are pressured to innovate and improvise to beat obstacles, and in doing so they’re step by step chipping away on the nation’s reliance on Western expertise.
Removed from halting China’s AI growth, the strain from sanctions seems to be accelerating it. Within the absence of U.S. chips, a cadre of Chinese language firms is speeding to fill the void. Huawei’s Ascend sequence is joined by a rising lineup of home AI chips from gamers like Baidu (Kunlun chips), Alibaba (T-Head division), startup Biren Know-how, and others. Even comparatively younger corporations are actually coming into a market lengthy dominated by Nvidia.
This surge of innovation means that China is set to regulate its personal future within the AI age. Chinese language authorities have even informally suggested native tech firms to prioritize home chips over overseas alternate options, making certain a built-in buyer base for made-in-China silicon. The fast payoff of this technique is continuity – Chinese language firms can maintain coaching AI fashions with out interruption. The longer-term payoff could possibly be a strong, homegrown semiconductor ecosystem that’s far much less susceptible to exterior shocks. In essence, the U.S.-China tech rivalry has entered a brand new section: one the place export controls and expertise bans are met with an equal and reverse power of home innovation. Huawei’s new chips are a tangible results of that dynamic.
Nvidia’s Market Dominance Faces a New Problem
For years, Nvidia has loved an virtually unassailable lead within the AI chip market worldwide, with its GPUs serving because the workhorses for machine studying in each trade and analysis. That dominance has translated into booming enterprise – till now. With the Chinese language market successfully fenced off by U.S. coverage, Nvidia is bracing for the monetary fallout.
Within the wake of the newest restrictions, Nvidia’s inventory took a noticeable hit (dropping practically 7% on the information) amid investor fears of misplaced gross sales. The corporate even warned it could have to put in writing off as much as $5.5 billion in stock constructed for China that may now not be bought freely. Analysts have estimated that if the U.S. continues to tighten chip exports, Nvidia may ultimately forfeit tens of billions of {dollars} in potential income from the China market. For a corporation that in 2024 briefly reached a $1 trillion market capitalization on the again of AI enthusiasm, shedding entry to one of many world’s largest tech markets is a critical setback.
Huawei’s emergence as a viable GPU competitor thus poses a twofold problem to Nvidia. First, it threatens to erode Nvidia’s share in China, the second-largest financial system, which had been a key supply of progress. Chinese language tech giants and cloud suppliers that when purchased Nvidia chips by the hundreds are actually strongly incentivized – by necessity and coverage – to modify to home alternate options. This price benefit, mixed with geopolitical tailwinds, means Nvidia may see a good portion of its Chinese language buyer base migrate to homegrown chips.
Second, a profitable rollout of Huawei’s AI chips may ultimately encourage confidence (and capital) in different markets for non-Nvidia options. Whereas Western firms are unlikely to interchange Nvidia {hardware} with Chinese language chips anytime quickly as a consequence of commerce restrictions and safety considerations, the mere existence of a reputable various underscores that Nvidia’s technological lead just isn’t insurmountable.
That mentioned, Nvidia’s international dominance just isn’t toppling in a single day. The corporate’s GPUs nonetheless set the gold normal for AI efficiency and have a deeply entrenched software program ecosystem that Huawei and others should compete with. Exterior of China, Nvidia stays the default alternative for AI infrastructure, and even inside China, Nvidia’s prior generations (like GPUs equal to the A100) are nonetheless in use the place accessible. Huawei’s 910C, spectacular as it’s, operates at maybe ~60–70% of the efficiency of Nvidia’s newest flagship in lots of situations. Furthermore, Huawei might want to display that it might probably manufacture these chips in quantity and help them with software program and developer communities.
Nvidia’s market place within the West is safe for now, bolstered by exploding AI demand globally (from Silicon Valley to Europe to India) that far exceeds provide. The true check shall be whether or not Huawei’s subsequent chip era can slim the hole additional. If Huawei can ship on that promise, it is going to cement the corporate’s function as a critical long-term rival in AI silicon, a minimum of inside its sphere of affect.

(Unite AI/Alex McFarland)
Towards a Bifurcated AI Ecosystem?
Huawei’s newest strikes spotlight a broader development: the potential bifurcation of the worldwide AI ecosystem into two parallel tracks. On one aspect, the U.S. and its allies proceed to advance with chips from firms like Nvidia, AMD, and Intel, together with specialised AI accelerators from Google (TPUs) and others. On the opposite aspect, China is quickly constructing its personal stack of AI {hardware} and software program – from chips just like the Ascend sequence to frameworks like MindSpore – largely incompatible with or remoted from Western provide chains. If this development continues, we may witness a world the place AI growth in China is constructed on Chinese language processors working in Chinese language information facilities, whereas the remainder of the world runs on Western chips.
Beijing’s encouragement for corporations to make use of home tech and Washington’s bans on chip exports are collectively driving this wedge deeper. The worldwide AI race, in impact, might splinter into separate lanes: both sides racing with its personal expertise, guidelines, and requirements.
Such a divide carries profound implications. Within the close to time period, China’s pivot to self-reliant AI {hardware} ensures it might probably pursue cutting-edge AI analysis (from massive language fashions to superior pc imaginative and prescient) with out begging Silicon Valley for instruments. That is important for China’s aspirations to guide in AI by 2030 – a purpose enshrined in its nationwide technique.
In the long run, nonetheless, a decoupling of AI ecosystems may result in diminished interoperability and information alternate between East and West. As we speak, a machine studying mannequin developed in a single nation can usually be shared and run elsewhere, assuming the {hardware} is obtainable; tomorrow’s bifurcated panorama would possibly complicate that stream. As an illustration, engineers proficient in Nvidia’s software program might not simply transition to programming Huawei’s Ascend chips, and vice versa. Firms and researchers might should specialize for one ecosystem, doubtlessly limiting collaboration.
On the flip aspect, competitors between two AI superpowers can spur innovation: both sides shall be pushed to outdo the opposite, probably accelerating developments in chip design and AI capabilities at a blistering tempo. We would see divergent approaches to AI computing emerge – maybe novel architectures or optimizations in China that differ from these within the West – enriching the worldwide innovation pool, but in addition creating technical obstacles between the 2 spheres.
For the worldwide provide chain, this break up means adaptation. Producers, cloud service suppliers, and even smaller nations will face decisions about which ecosystem to align with, or learn how to bridge each. It may result in duplicate funding in parallel infrastructures – expensive, however seen as crucial for strategic autonomy. Nations in Europe or Asia-Pacific circuitously concerned within the U.S.-China standoff might attempt to keep impartial or help requirements that enable some interoperability, however they too might ultimately lean a technique or one other for crucial applied sciences.
In essence, Huawei’s new AI chips are a strategic assertion. They sign that the steadiness of energy in AI computing is starting to shift, nonetheless step by step, and that we’re coming into an period the place technological energy is extra distributed. The approaching years will reveal whether or not this marks the beginning of a very divided tech world or just a extra aggressive one. Both manner, Huawei’s Ascend chips have ensured that the worldwide AI race won’t be a one-horse race – and that geopolitics will stay intertwined with who leads in AI. The world shall be watching as these chips roll out, for what they imply not just for China’s tech trajectory however for the longer term form of AI innovation in every single place.
Redwire boosts space-based pharma tech with new crystallizer and gold nanoparticle check
Redwire boosts space-based pharma tech with new crystallizer and gold nanoparticle check
by Clarence Oxford
Los Angeles CA (SPX) Apr 23, 2025
Redwire Company (NYSE: RDW), a distinguished drive in house infrastructure innovation, has expanded its pharmaceutical analysis efforts in orbit with the deployment of latest crystallization expertise and a groundbreaking cancer-detection experiment aboard the Worldwide House Station (ISS).
Constructing on the success of its PIL-BOX platform, Redwire has launched a high-volume Industrial Crystallizer designed to course of samples as much as 200 occasions bigger than these beforehand accommodated. This development helps the corporate’s imaginative and prescient of scaling in-space drug growth into commercially viable manufacturing. The objective is to transform microgravity-based insights into manufacturable supplies that serve terrestrial medical and industrial markets.
A key element of the enlargement is the “Golden Balls” experiment, which goals to create gold nanospheres in microgravity for the primary time. These nanoparticles have potential makes use of in medical diagnostics and focused most cancers therapies. Redwire expects space-grown nanospheres to exhibit enhanced dimension uniformity and floor integrity, attributes that might enhance their effectiveness in biomedical functions.
“Gold nanospheres may result in early testing and analysis of most cancers and different illnesses, focused drug supply, and enhanced radiation and photothermal remedy, providing a promising strategy to most cancers administration,” mentioned John Vellinger, Redwire’s President of In-House Industries.
The brand new Industrial Crystallizer and the Golden Balls experiment had been launched aboard SpaceX’s thirty second business resupply mission to the ISS on April twenty first.
Associated Hyperlinks
Uncompromised Ethernet – AI/ML cloth benchmark
Immediately, we’re exploring how Ethernet stacks up in opposition to InfiniBand in AI/ML environments, specializing in how Cisco Silicon One™ manages community congestion and enhances efficiency for AI/ML workloads. This publish emphasizes the significance of benchmarking and KPI metrics in evaluating community options, showcasing the Cisco Zeus Cluster geared up with 128 NVIDIA® H100 GPUs and cutting-edge congestion administration applied sciences like dynamic load balancing and packet spray.
Networking requirements to satisfy the wants of AI/ML workloads
AI/ML coaching workloads generate repetitive micro-congestion, stressing community buffers considerably. The east-to-west GPU-to-GPU site visitors throughout mannequin coaching calls for a low-latency, lossless community cloth. InfiniBand has been a dominant expertise within the high-performance computing (HPC) surroundings and currently within the AI/ML surroundings.
Ethernet is a mature various, with superior options that may tackle the rigorous calls for of the AI/ML coaching workloads and Cisco Silicon One can successfully execute load balancing and handle congestion. We got down to benchmark and examine Cisco Silicon One versus NVIDIA Spectrum-X™ and InfiniBand.
Analysis of community cloth options for AI/ML
Community site visitors patterns differ primarily based on mannequin dimension, structure, and parallelization strategies utilized in accelerated coaching. To guage AI/ML community cloth options, we recognized related benchmarks and key efficiency indicator (KPI) metrics for each AI/ML workload and infrastructure groups, as a result of they view efficiency by means of completely different lenses.
We established complete exams to measure efficiency and generate metrics particular to AI/ML workload and infrastructure groups. For these exams, we used the Zeus Cluster, that includes devoted backend and storage with a normal 3-stage leaf-spine Clos cloth community, constructed with Cisco Silicon One–primarily based platforms and 128 NVIDIA H100 GPUs. (See Determine 1.)

We developed benchmarking suites utilizing open-source and industry-standard instruments contributed by NVIDIA and others. Our benchmarking suites included the next (see additionally Desk 1):
- Distant Direct Reminiscence Entry (RDMA) benchmarks—constructed utilizing IBPerf utilities—to judge community efficiency throughout congestion created by incast
- NVIDIA Collective Communication Library (NCCL) benchmarks, which consider software throughput throughout coaching and inference communication section amongst GPUs
- MLCommons MLPerf set of benchmarks, which evaluates probably the most understood metrics, job completion time (JCT) and tokens per second by the workload groups

Legend:
JCT = Job Completion Time
Bus BW = Bus bandwidth
ECN/PFC = Express Congestion Notification and Precedence Move Management
NCCL benchmarking in opposition to congestion avoidance options
Congestion builds up throughout the again propagation stage of the coaching course of, the place a gradient sync is required amongst all of the GPUs taking part in coaching. Because the mannequin dimension will increase, so does the gradient dimension and the variety of GPUs. This creates large micro-congestion within the community cloth. Determine 2 exhibits outcomes of the JCT and site visitors distribution benchmarking. Notice how Cisco Silicon One helps a set of superior options for congestion avoidance, reminiscent of dynamic load balancing (DLB) and packet spray strategies, and Information Middle Quantized Congestion Notification (DCQCN) for congestion administration.

Determine 2 illustrates how the NCCL benchmarks stack up in opposition to completely different congestion avoidance options. We examined the most typical collectives with a number of completely different message sizes to focus on these metrics. The outcomes present that JCT improves with DLB and packet spray for All-to-All, which causes probably the most congestion because of the nature of communication. Though JCT is probably the most understood metric from an software’s perspective, JCT doesn’t present how successfully the community is utilized—one thing the infrastructure crew must know. This data might assist them to:
- Enhance the community utilization to get higher JCT
- Know what number of workloads can share the community cloth with out adversely impacting JCT
- Plan for capability as use circumstances enhance
To gauge community cloth utilization, we calculated Jain’s Equity Index, the place LinkTxᵢ is the quantity of transmitted site visitors on cloth hyperlink:

The index worth ranges from 0.0 to 1.0, with greater values being higher. A price of 1.0 represents the proper distribution. The Site visitors Distribution on Cloth Hyperlinks chart in Determine 2 exhibits how DLB and packet spray algorithms create a near-perfect Jain’s Equity Index, so site visitors distribution throughout the community cloth is sort of good. ECMP makes use of static hashing, and relying on move entropy, it will possibly result in site visitors polarization, inflicting micro-congestion and negatively affecting JCT.
Silicon One versus NVIDIA Spectrum-X and InfiniBand
The NCCL Benchmark – Aggressive Evaluation (Determine 3) exhibits how Cisco Silicon One performs in opposition to NVIDIA Spectrum-X and InfiniBand applied sciences. The information for NVIDIA was taken from the SemiAnalysis publication. Notice that Cisco doesn’t understand how these exams have been carried out, however we do know that the cluster dimension and GPU to community cloth connectivity is just like the Cisco Zeus Cluster.

Bus Bandwidth (Bus BW) benchmarks the efficiency of collective communication by measuring the velocity of operations involving a number of GPUs. Every collective has a particular mathematical equation reported throughout benchmarking. Determine 3 exhibits that Cisco Silicon One – All Cut back performs comparably to NVIDIA Spectrum-X and InfiniBand throughout varied message sizes.
Community cloth efficiency evaluation
The IBPerf Benchmark compares RDMA efficiency in opposition to ECMP, DLB, and packet spray, that are essential for assessing community cloth efficiency. Incast situations, the place a number of GPUs ship information to at least one GPU, usually trigger congestion. We simulated these circumstances utilizing IBPerf instruments.

Determine 4 exhibits how Aggregated Session Throughput and JCT reply to completely different congestion avoidance algorithms: ECMP, DLB, and packet spray. DLB and packet spray attain Hyperlink Bandwidth, enhancing JCT. It additionally illustrates how DCQCN handles micro-congestions, with PFC and ECN ratios enhancing with DLB and considerably dropping with packet spray. Though JCT improves barely from DLB to packet spray, the ECN ratio drops dramatically resulting from packet spray’s very best site visitors distribution.
Coaching and inference benchmark
The MLPerf Benchmark – Coaching and Inference, printed by the MLCommons group, goals to allow truthful comparability of AI/ML techniques and options.

We centered on AI/ML information middle options by executing coaching and inference benchmarks. To realize optimum outcomes, we extensively tuned throughout compute, storage, and networking elements utilizing congestion administration options of Cisco Silicon One. Determine 5 exhibits comparable efficiency throughout varied platform distributors. Cisco Silicon One with Ethernet performs like different vendor options for Ethernet.
Conclusion
Our deep dive into Ethernet and InfiniBand inside AI/ML environments highlights the exceptional prowess of Cisco Silicon One in tackling congestion and boosting efficiency. These modern developments showcase the unwavering dedication of Cisco to supply strong, high-performance networking options that meet the rigorous calls for of immediately’s AI/ML functions.
Many because of Vijay Tapaskar, Will Eatherton, and Kevin Wollenweber for his or her assist on this benchmarking course of.
Discover safe AI infrastructure
Uncover safe, scalable, and high-performance AI infrastructure you should develop, deploy, and handle AI workloads securely once you select Cisco Safe AI Manufacturing facility with NVIDIA.
Share:
Authorized Implications in Outsourcing Initiatives
Over the past 2-3 years, synthetic intelligence (AI) brokers have change into extra embedded within the software program improvement course of. In accordance with Statista, three out of 4 builders, or round 75%, use GitHub Copilot, OpenAI Codex, ChatGPT, and different generative AI of their day by day chores.
Nonetheless, whereas AI exhibits promise in directing software program improvement duties, it creates a wave of authorized uncertainty.
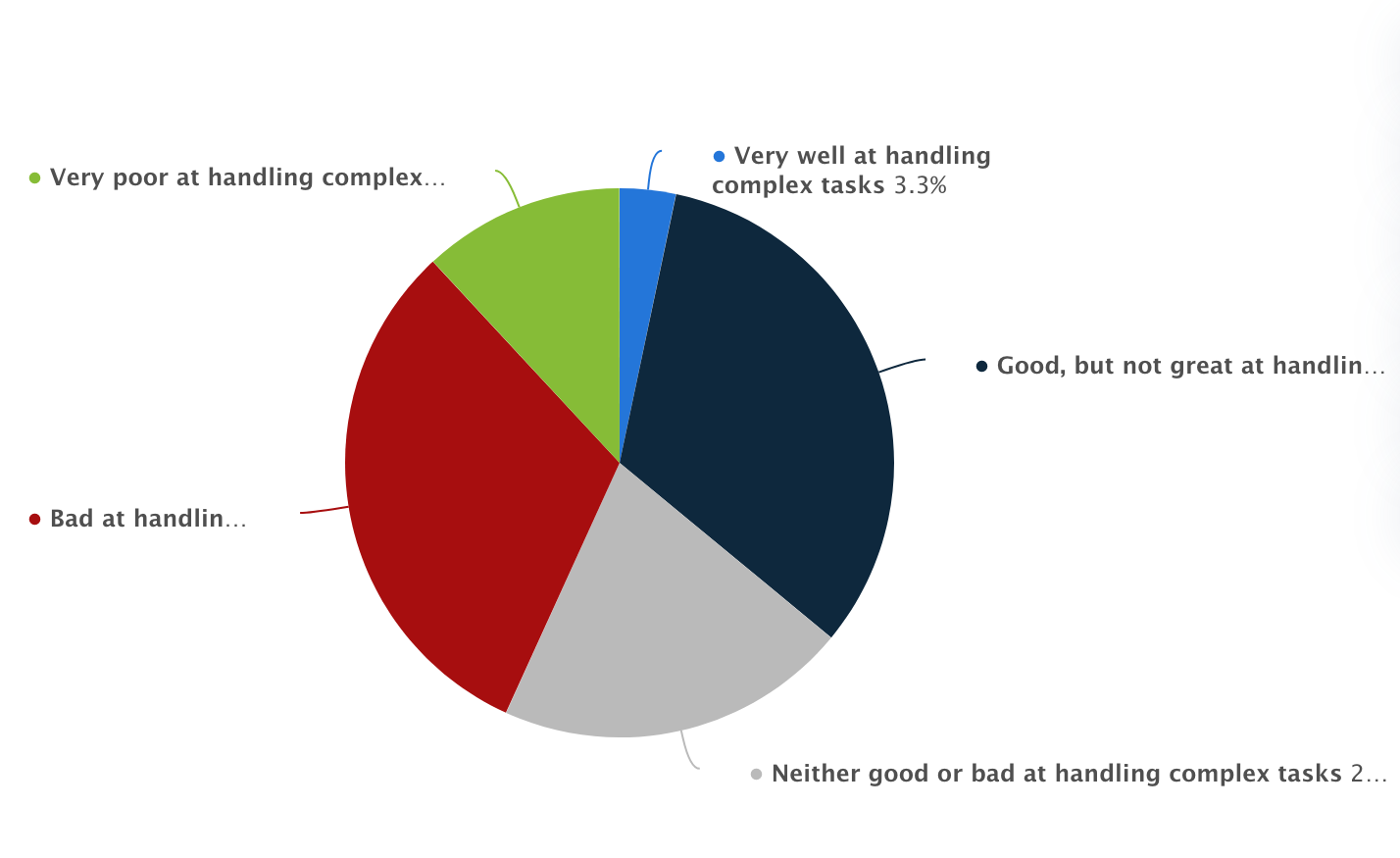
Capacity of Synthetic Intelligence in Managing Complicated Duties, Statista
Who owns the code written by an AI? What occurs if AI-made code infringes on another person’s mental property? And what are the privateness dangers when industrial information is processed by way of AI fashions?
To reply all these burning questions, we’ll clarify how AI improvement is regarded from the authorized facet, particularly in outsourcing instances, and dive into all issues firms ought to perceive earlier than permitting these instruments to combine into their workflows.
What Is AI in Customized Software program Improvement?
The marketplace for AI applied sciences is huge, amounting to round $244 billion in 2025. Usually, AI is split into machine studying and deep studying and additional into pure language processing, pc imaginative and prescient, and extra.
In software program improvement, AI instruments discuss with clever techniques that may help or automate components of the programming course of. They will recommend strains of code, full features, and even generate complete modules relying on context or prompts supplied by the developer.
Within the context of outsourcing tasks—the place velocity is not any much less essential than high quality—AI applied sciences are rapidly turning into staples in improvement environments.
They increase productiveness by taking redundant duties, lower the time spent on boilerplate code, and help builders who could also be working in unfamiliar frameworks or languages.
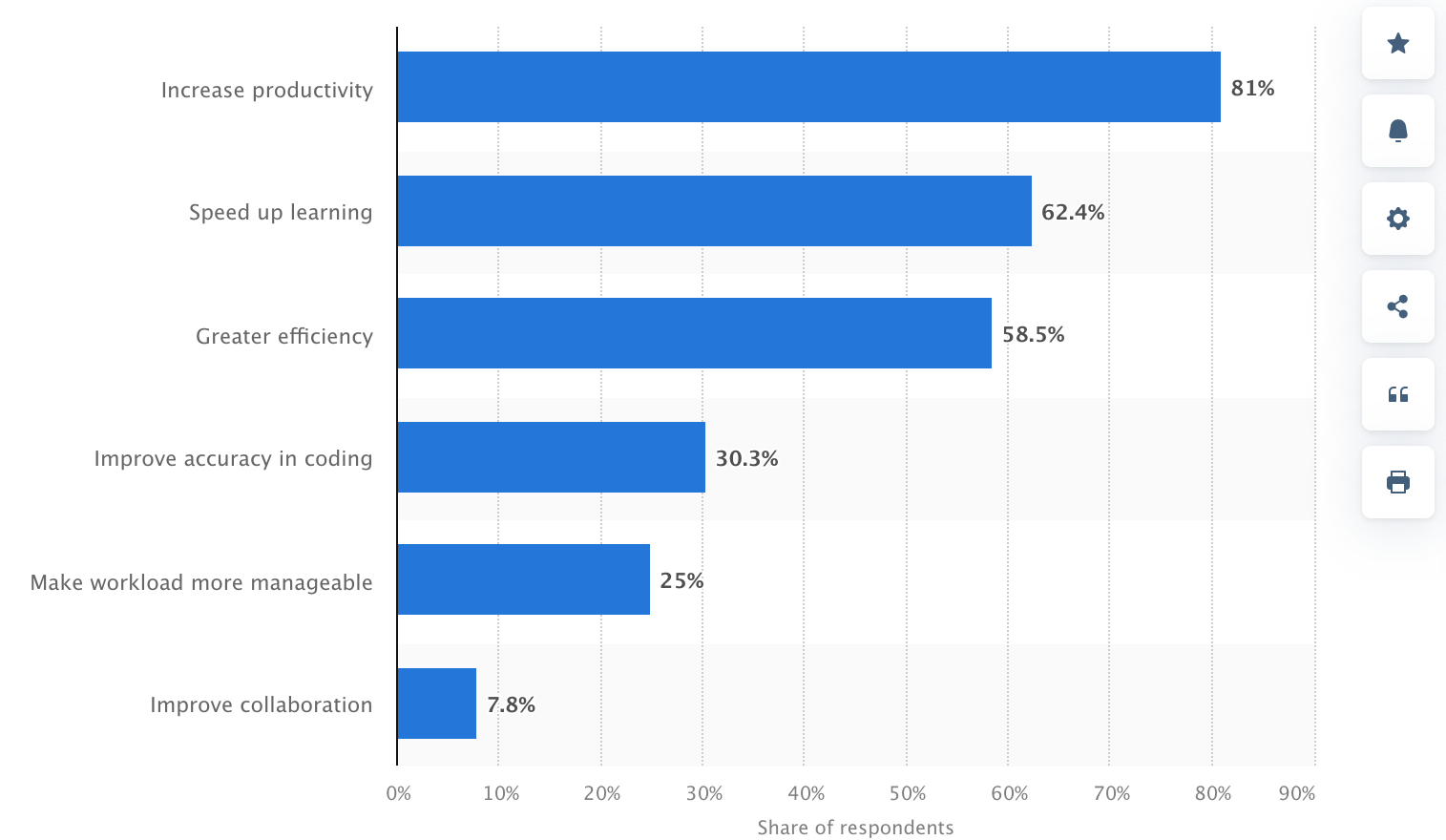
Advantages of Utilizing Synthetic Intelligence, Statista
How AI Instruments Can Be Built-in in Outsourcing Initiatives
Synthetic intelligence in 2025 has change into the specified ability for practically all technical professions.
Whereas the uncommon bartender or plumber might not require AI mastery to the identical stage, it has change into clear that including an AI ability to a software program developer’s arsenal is a should as a result of within the context of software program improvement outsourcing, AI instruments can be utilized in some ways:
- Code Technology: GitHub Copilot and different AI instruments help outsourced builders in coding by making hints or auto-filling features as they code.
- Bug Detection: As an alternative of ready for human verification in software program testing, AI can flag errors or dangerous code so groups can repair flaws earlier than they change into irreversible points.
- Writing Assessments: AI can independently generate take a look at instances from the code, thus the testing turns into faster and extra exhaustive.
- Documentation Assist: AI can depart feedback and draw up documentation explaining what the code does.
- Multi-language Assist: If the challenge wants to change programming languages, AI may also help translate or re-write segments of code with a purpose to decrease the necessity for specialised information for each programming language.
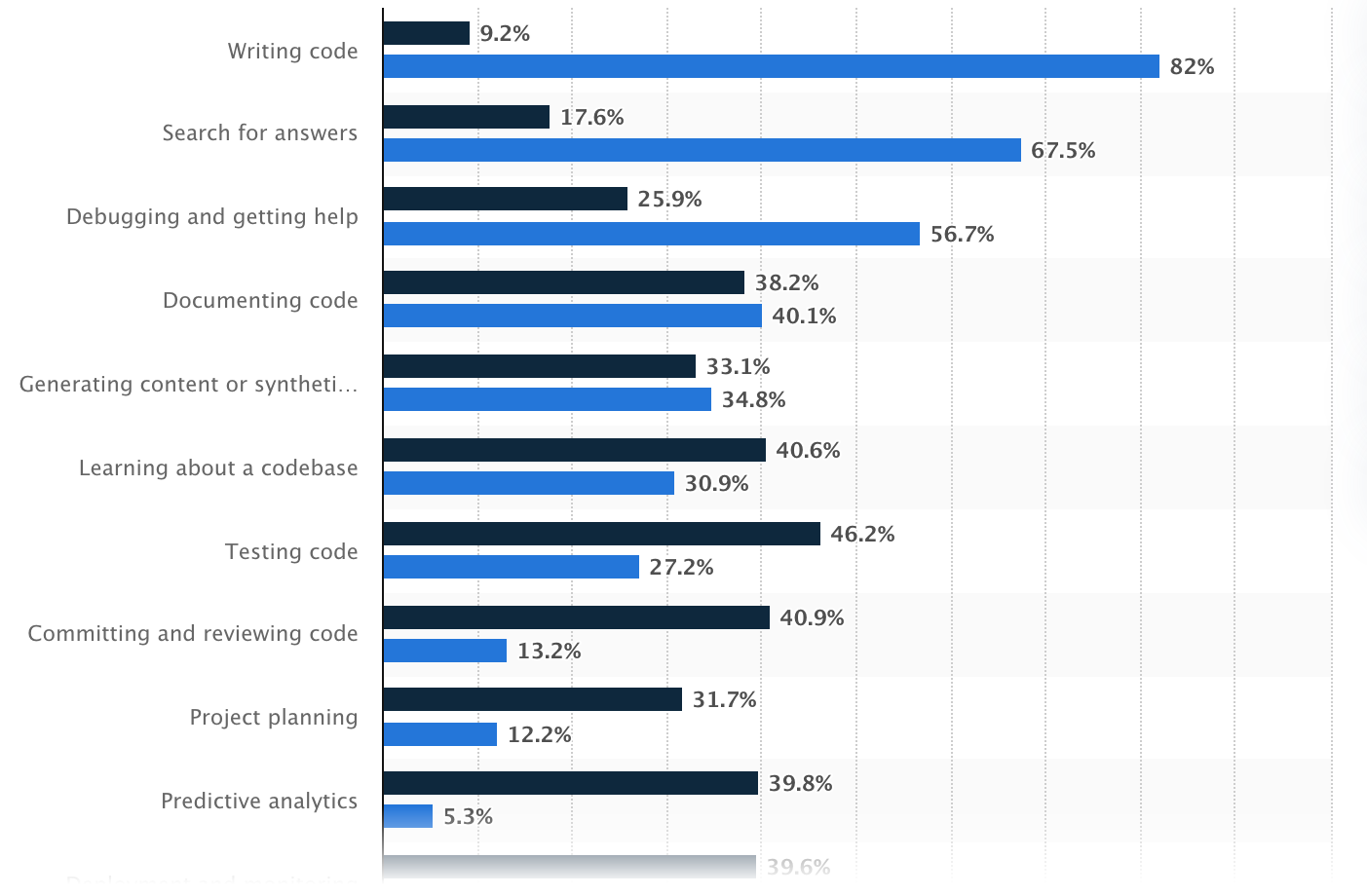
Hottest makes use of of AI within the improvement, Statista
Authorized Implications of Utilizing AI in Customized Software program Improvement
AI instruments might be extremely useful in software program improvement, particularly when outsourcing. However utilizing them additionally raises some authorized questions companies want to pay attention to, primarily round possession, privateness, and accountability.
Mental Property (IP) Points
When builders use AI instruments like GitHub Copilot, ChatGPT, or different code-writing assistants, it’s pure to ask: Who truly owns the code that will get written? This is among the trickiest authorized questions proper now.
At the moment, there’s no clear international settlement. Normally, AI doesn’t personal something, and the developer who makes use of the software is taken into account the “writer,” nonetheless, this may occasionally range.
The catch is that AI instruments study from tons of present code on the web. Generally, they generate code that’s very related (and even an identical) to the code they had been educated on, together with open-source tasks.
If that code is copied too intently, and it’s beneath a strict open-source license, you would run into authorized issues, particularly in the event you didn’t notice it or comply with the license guidelines.
Outsourcing could make it much more problematic. For those who’re working with an outsourcing group they usually use AI instruments throughout improvement, you have to be further clear in your contracts:
- Who owns the ultimate code?
- What occurs if the AI software unintentionally reuses licensed code?
- Is the outsourced group allowed to make use of AI instruments in any respect?
To 100% keep on the protected facet, you may:
- Be sure that contracts clearly state who owns the code.
- Double-check that the code doesn’t violate any licenses.
- Think about using instruments that run regionally or restrict what the AI sees to keep away from leaking or copying restricted content material.
Knowledge Safety and Privateness
When utilizing AI instruments in software program improvement, particularly in outsourcing, one other main consideration is information privateness and safety. So what’s the danger?

The vast majority of AI instruments like ChatGPT, Copilot, and others usually run within the cloud, which implies the knowledge builders put into them could also be transmitted to outer servers.
If builders copy and paste proprietary code, login credentials, or industrial information into these instruments, that data may very well be retained, reused, and later revealed. The state of affairs turns into even worse if:
- You’re giving confidential enterprise data
- Your challenge issues buyer or person particulars
- You’re in a regulated trade akin to healthcare or finance
So what does the regulation say concerning it? Certainly, totally different international locations have totally different laws, however essentially the most noticeable are:
- GDPR (Europe): In easy phrases, GDPR protects private information. For those who collect information from folks within the EU, you must clarify what you’re amassing, why you want it, and get their permission first. Folks can ask to see their information, rectify something unsuitable, or have it deleted.
- HIPAA (US, healthcare): HIPAA covers non-public well being data and medical data. Submitting to HIPAA, you may’t simply paste something associated to affected person paperwork into an AI software or chatbot—particularly one which runs on-line. Additionally, in the event you work with different firms (outsourcing groups or software program distributors), they should comply with the identical decrees and signal a particular settlement to make all of it authorized.
- CCPA (California): CCPA is a privateness regulation that provides folks extra management over their private information. If your small business collects information from California residents, you must allow them to know what you’re gathering and why. Folks can ask to see their information, have it deleted, or cease you from sharing or promoting it. Even when your organization is predicated some other place, you continue to must comply with CCPA in the event you’re processing information from folks in California.
The obvious and logical query right here is how one can defend information. First, don’t put something delicate (passwords, buyer information, or non-public firm information) into public AI instruments until you’re certain they’re protected.
For tasks that concern confidential data, it’s higher to make use of AI assistants that run on native computer systems and don’t ship something to the web.
Additionally, take a great take a look at the contracts with any outsourcing companions to ensure they’re following the correct practices for protecting information protected.
Accountability and Duty
AI instruments can perform many duties however they don’t take accountability when one thing goes unsuitable. The blame nonetheless falls on folks: the builders, the outsourcing group, and the enterprise that owns the challenge.
If the code has a flaw, creates a security hole, or causes injury, it’s not the AI’s guilt—it’s the folks utilizing it who’re accountable. If nobody takes possession, small compromises can flip into massive (and costly) points.
To keep away from this case, companies want clear instructions and human oversight:
- At all times evaluate AI-generated code. It’s simply a place to begin, not a completed product. Builders nonetheless must probe, debug, and confirm each single half.
- Assign accountability. Be it an in-house group or an outsourced accomplice, ensure somebody is clearly accountable for high quality management.
- Embody AI in your contracts. Your settlement with an outsourcing supplier ought to say:
- Whether or not they can apply AI instruments.
- Who’s accountable for reviewing the AI’s work.
- Who pays for fixes if one thing goes unsuitable due to AI-generated code.
- Preserve a report of AI utilization. Doc when and the way AI instruments are utilized, particularly for main code contributions. That means, if issues emerge, you may hint again what occurred.
Case Research and Examples
AI in software program improvement is already a standard observe utilized by many tech giants although statistically, smaller firms with fewer workers are extra probably to make use of synthetic intelligence than bigger firms.
Beneath, we have now compiled some real-world examples that present how totally different companies are making use of AI and the teachings they’re studying alongside the best way.
Nabla (Healthcare AI Startup)
Nabla, a French healthtech firm, built-in GPT-3 (by way of OpenAI) to help medical doctors with writing medical notes and summaries throughout consultations.

How they use it:
- AI listens to patient-doctor conversations and creates structured notes.
- The time medical doctors spend on admin work visibly shrinks.
Authorized & privateness actions:
- As a result of they function in a healthcare setting, Nabla deliberately selected to not use OpenAI’s API straight resulting from issues about information privateness and GDPR compliance.
- As an alternative, they constructed their very own safe infrastructure utilizing open-source fashions like GPT-J, hosted regionally, to make sure no affected person information leaves their servers.
Lesson realized: In privacy-sensitive industries, utilizing self-hosted or non-public AI fashions is usually a safer path than counting on industrial cloud-based APIs.
Replit and Ghostwriter
Replit, a collaborative on-line coding platform, developed Ghostwriter, its personal AI assistant just like Copilot.
The way it’s used:
- Ghostwriter helps customers (together with newcomers) write and full code proper within the browser.
- It’s built-in throughout Replit’s improvement platform, usually utilized in training and startups.
Problem:
- Replit has to stability ease of use with license compliance and transparency.
- The corporate offers disclaimers encouraging customers to evaluate and edit the generated code, underlining it is just a tip.
Lesson realized: AI-generated code is highly effective however not all the time protected to make use of “as is.” Even platforms that construct AI instruments themselves push for human evaluate and warning.
Amazon’s Inner AI Coding Instruments
Amazon has developed its personal inside AI-powered instruments, just like Copilot, to help its builders.

How they use it:
- AI helps builders write and evaluate code throughout a number of groups and companies.
- It’s used internally to enhance developer productiveness and velocity up supply.
Why they don’t use exterior instruments like Copilot:
- Amazon has strict inside insurance policies round mental property and information privateness.
- They like to construct and host instruments internally to sidestep authorized dangers and defend proprietary code.
Lesson realized: Giant enterprises usually keep away from third-party AI instruments resulting from issues about IP leakage and lack of management over prone information.
How one can Safely Use AI Instruments in Outsourcing Initiatives: Basic Suggestions
Utilizing AI instruments in outsourced improvement can deliver sooner supply, decrease prices, and coding productiveness. However to do it safely, firms must arrange the correct processes and protections from the beginning.
First, it’s essential to make AI utilization expectations clear in contracts with outsourcing companions. Agreements ought to specify whether or not AI instruments can be utilized, beneath what circumstances, and who’s accountable for reviewing and validating AI-generated code.
These contracts also needs to embrace robust mental property clauses, spelling out who owns the ultimate code and what occurs if AI unintentionally introduces open-source or third-party licensed content material.
Knowledge safety is one other important concern. If builders use AI instruments that ship information to the cloud, they have to by no means enter delicate or proprietary data until the software complies with GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA.
In extremely regulated industries, it’s all the time safer to make use of self-hosted AI fashions or variations that run in a managed surroundings to reduce the danger of information openness.
To keep away from authorized and high quality points, firms also needs to implement human oversight at each stage. AI instruments are nice for recommendation, however they don’t perceive enterprise context or authorized necessities.
Builders should nonetheless take a look at, audit, and reanalyze all code earlier than it goes stay. Establishing a code evaluate workflow the place senior engineers double-check AI output ensures security and accountability.
It’s additionally clever to doc when and the way AI instruments are used within the improvement course of. Holding a report helps hint again the supply of any future defects or authorized issues and exhibits good religion in regulatory audits.

Lastly, ensure your group (or your outsourcing accomplice’s group) receives primary coaching in AI finest practices. Builders ought to perceive the restrictions of AI strategies, how one can detect licensing dangers, and why it’s essential to validate code earlier than delivery it.
FAQ
Q: Who owns the code generated by AI instruments?
Possession often goes to the corporate commissioning the software program—however provided that that’s clearly acknowledged in your settlement. The complication comes when AI instruments generate code that resembles open-source materials. If that content material is beneath a license, and it’s not attributed correctly, it might increase mental property points. So, clear contracts and guide checks are key.
Q: Is AI-generated code protected to make use of as-is?
Not all the time. AI instruments can unintentionally reproduce licensed or copyrighted code, particularly in the event that they had been educated on public codebases. Whereas the strategies are helpful, they need to be handled as beginning factors—builders nonetheless must evaluate, edit, and confirm the code earlier than it’s used.
Q: Is it protected to enter delicate information into AI instruments like ChatGPT?
Often, no. Until you’re utilizing a non-public or enterprise model of the AI that ensures information privateness, you shouldn’t enter any confidential or proprietary data. Public instruments course of information within the cloud, which might expose it to privateness dangers and regulatory violations.
Q: What information safety legal guidelines ought to we contemplate?
This is determined by the place you use and what sort of information you deal with. In Europe, the GDPR requires consent and transparency when utilizing private information. Within the U.S., HIPAA protects medical information, whereas CCPA in California offers customers management over how their private data is collected and deleted. In case your AI instruments contact delicate information, they have to adjust to these laws.
Q: Who’s accountable if AI-generated code causes an issue?
Finally, the accountability falls on the event group—not the AI software. Meaning whether or not your group is in-house or outsourced, somebody must validate the code earlier than it goes stay. AI can velocity issues up, however it will probably’t take accountability for errors.
Q: How can we safely use AI instruments in outsourced tasks?
Begin by placing the whole lot in writing: your contracts ought to cowl AI utilization, IP possession, and evaluate processes. Solely use trusted instruments, keep away from feeding in delicate information, and ensure builders are educated to make use of AI responsibly. Most significantly, hold a human within the loop for high quality assurance.
Q: Does SCAND use AI for software program improvement?
Sure, however supplied that the consumer agrees. If public AI instruments are licensed, we use Microsoft Copilot in VSCode and Cursor IDE, with fashions like ChatGPT 4o, Claude Sonnet, DeepSeek, and Qwen. If a consumer requests a non-public setup, we use native AI assistants in VSCode, Ollama, LM Studio, and llama.cpp, with the whole lot saved on safe machines.
Q: Does SCAND use AI to check software program?
Sure, however with permission from the consumer. We use AI instruments like ChatGPT 4o and Qwen Imaginative and prescient for automated testing and Playwright and Selenium for browser testing. When required, we robotically generate unit exams utilizing AI fashions in Copilot, Cursor, or regionally accessible instruments like Llama, DeepSeek, Qwen, and Starcoder.




