TL;DR: WeChat messages and conversations should not encrypted end-to-end, which means the app’s servers can decrypt and skim each message. Nonetheless, customers of the favored messaging app may be involved to study that there are vulnerabilities within the encryption protocol that might go away the service open to assault, in accordance with a brand new examine.
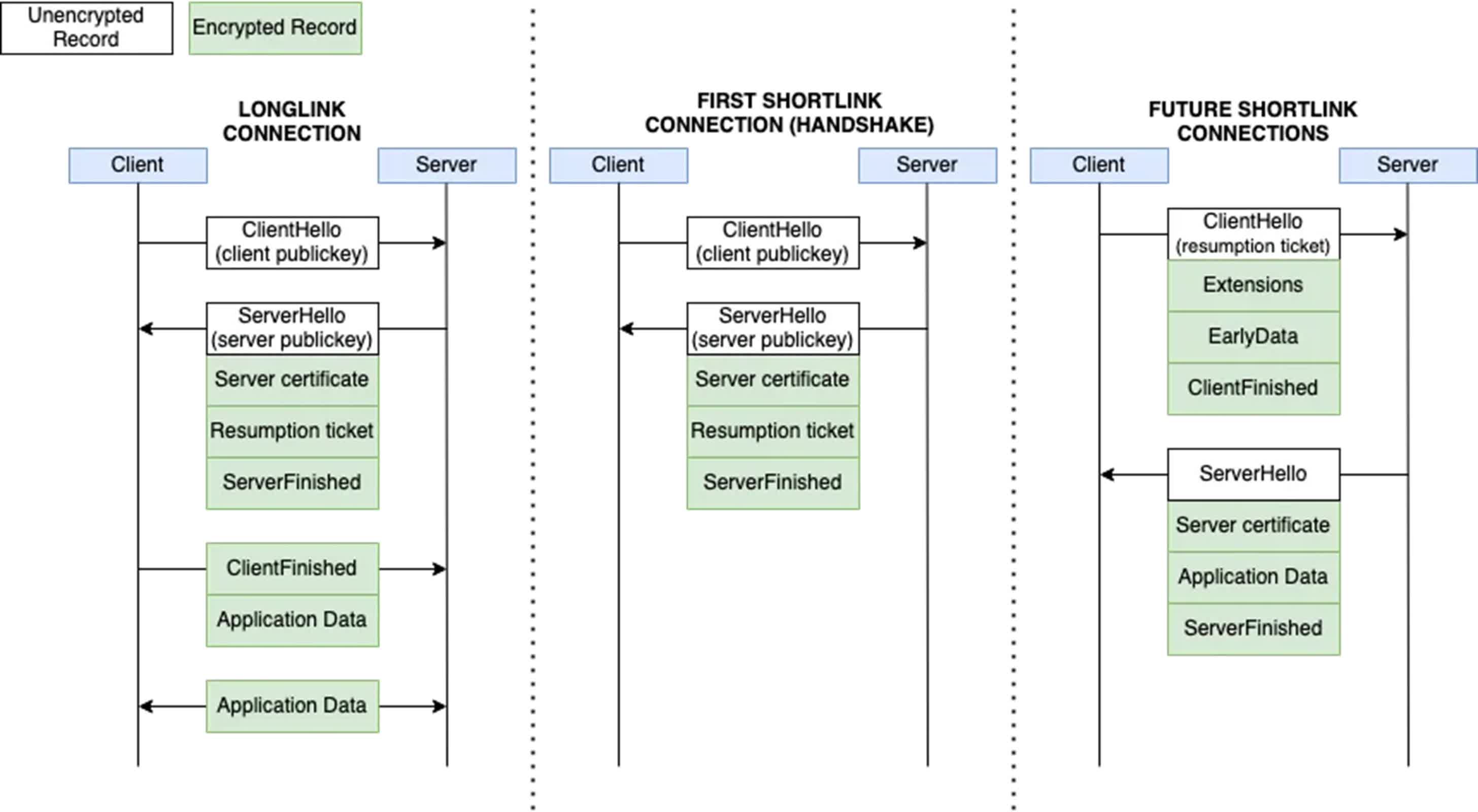
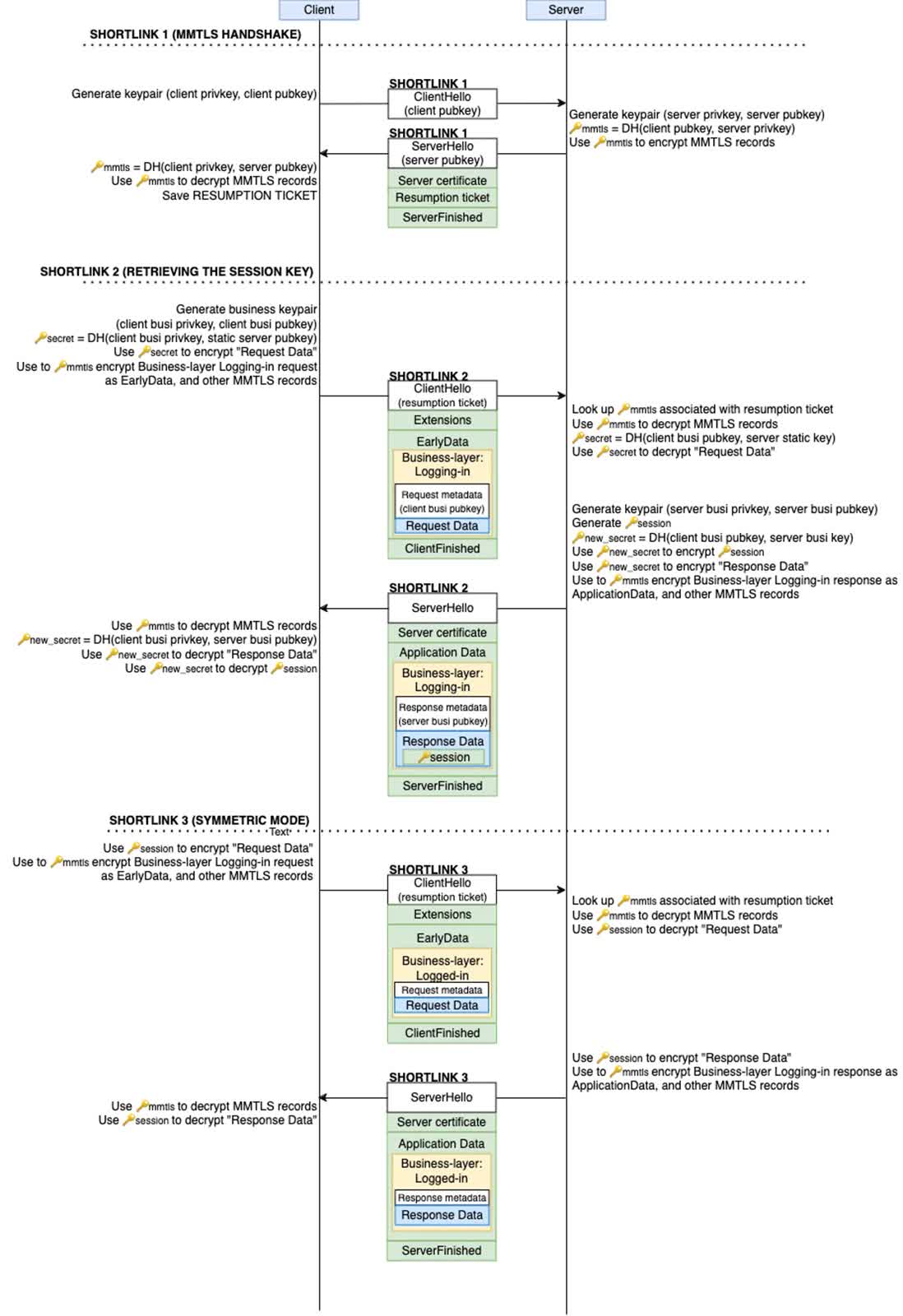
A latest investigation by the College of Toronto’s Citizen Lab has uncovered potential safety weaknesses in WeChat’s customized encryption protocol. These weaknesses come up as a result of the builders of WeChat, which boasts over a billion month-to-month energetic customers, have modified the Transport Layer Safety (TLS) 1.3 protocol, making a model referred to as MMTLS.
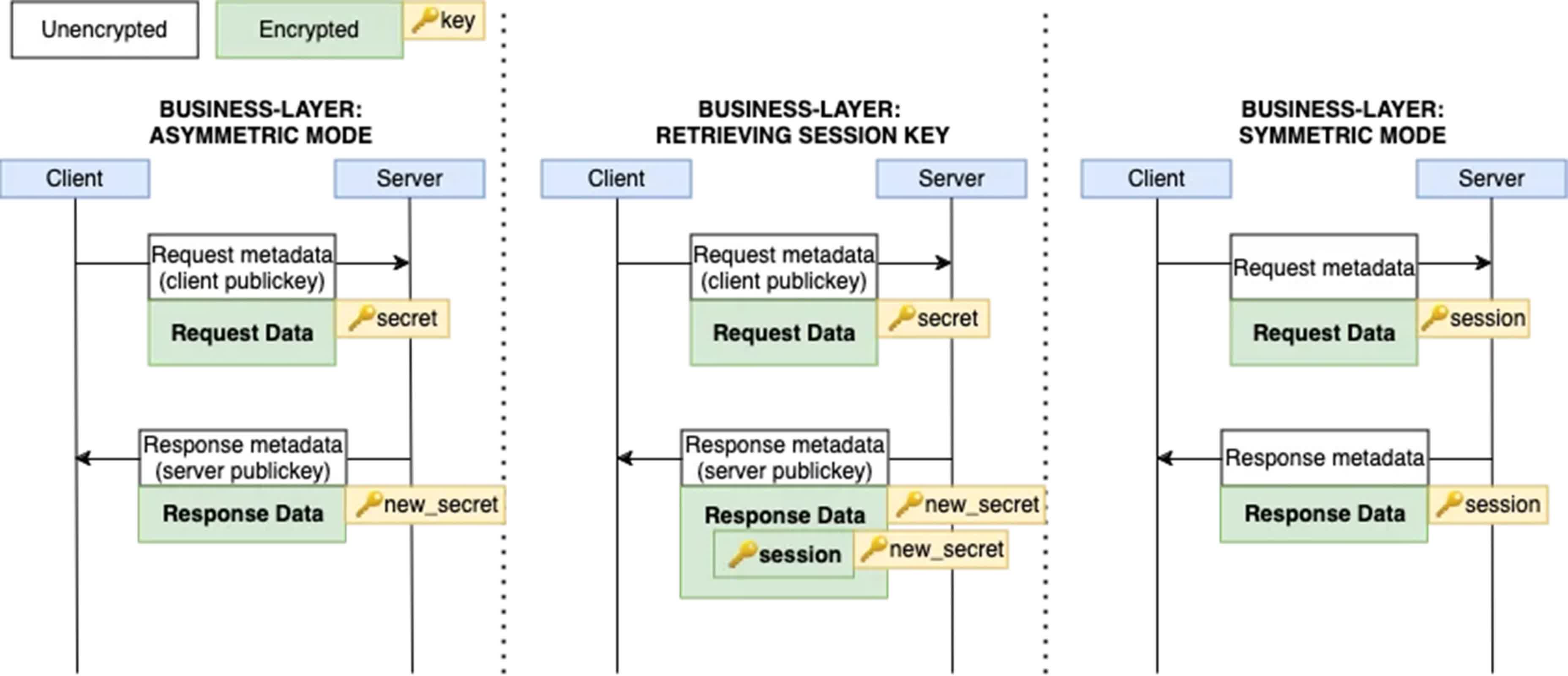
WeChat makes use of a two-layer encryption system. First, the internal layer, often known as “Enterprise-layer encryption,” encrypts the plaintext content material. This encrypted content material is then additional encrypted with MMTLS earlier than being transmitted.
Whereas this dual-layer encryption gives some safety, a number of regarding points have been recognized. The Enterprise-layer encryption fails to safe delicate metadata, reminiscent of person IDs and request URIs. Moreover, MMTLS makes use of deterministic initialization vectors (IVs), which contradict fashionable cryptographic greatest practices. Moreover, the encryption lacks ahead secrecy, an important characteristic for long-term safety.
Earlier than 2016, WeChat relied solely on Enterprise-layer encryption for community requests. The introduction of MMTLS seems to be an try to deal with the shortcomings of the earlier system.
To some extent, this has been efficient. The researchers have been unable to efficiently assault WeChat’s encryption on this examine as a result of the weak Enterprise-layer encryption is now protected by the MMTLS layer. In earlier variations of WeChat, which lacked MMTLS, the Enterprise-layer encryption was uncovered and probably vulnerable to sure assaults. The addition of MMTLS has considerably improved WeChat’s general safety by shielding the internal encryption layer from direct assaults.
Nonetheless, the researchers famous that WeChat’s implementation falls in need of the cryptographic requirements anticipated for an app of its scale. Moreover, different “minor” points recognized by the researchers should not current in the usual, unmodified model of TLS.
The researchers additionally identified that it’s a distinctive apply in China for safety builders to create their very own customized cryptographic methods slightly than utilizing established requirements. These homegrown options typically don’t match the effectiveness of extensively used protocols like TLS 1.3 or QUIC. Citizen Lab described this as “a rising, regarding development distinctive to the Chinese language safety panorama.”
As an illustration, some Chinese language apps implement customized area decision strategies to fight DNS hijacking by ISPs. Moreover, many Chinese language apps, together with WeChat, use open-source infrastructure elements like Tencent Mars, which can lack correct documentation and safety steerage.
Maybe not surprisingly, the important thing advice by Citizen Lab researchers was that WeChat’s father or mother firm Tencent undertake normal TLS or a mixture of QUIC and TLS to boost app safety.