The state of DMARC e mail authentication and safety commonplace regarded so promising in the beginning of 2024.
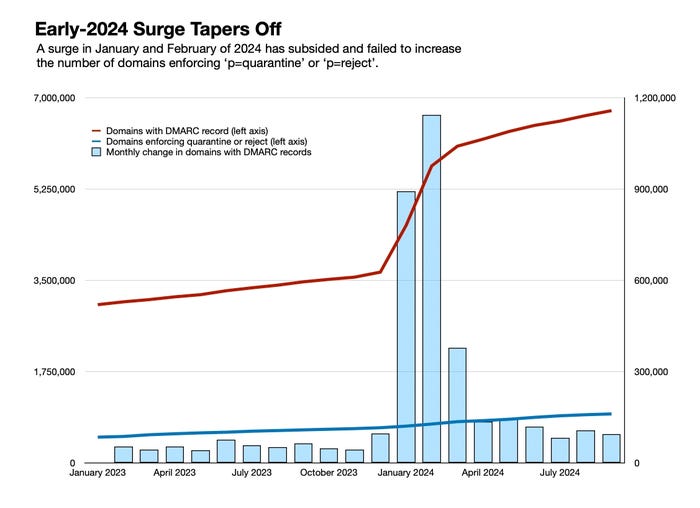
Google and Yahoo had set a deadline of February 2024 for bulk e mail senders to undertake a Area-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance (DMARC) coverage, and as corporations scrambled to fulfill the deadline, the variety of e mail domains with a sound DMARC report jumped 60% in two months. As of September, practically 6.8 million domains have e mail sender authentication configured.
Even with that surge earlier within the 12 months, the truth is that companies proceed to be gradual in organising e mail authentication on their domains. The adoption lag is very pronounced in making the change from DMARC’s minimum-baseline coverage of ‘p=none‘ to extra stringent insurance policies. Enforcement means non-authenticated emails get quarantined or rejected. The share of DMARC-enabled domains with an enforced coverage has really gone down from a excessive of 18% a 12 months in the past, to lower than 14% right now.
Whereas Google’s and Yahoo’s actions compelled many corporations to undertake DMARC, most of them — spurred by considerations about blocking professional messages — have not adopted the quarantine or reject insurance policies, says Seth Clean, chief know-how officer at Valimail, a supplier of e mail safety companies.
“Google and Yahoo put the necessities out, the ecosystem bought a shot within the arm, and the message was closely about safety — so the individuals who cared about safety did one thing,” Clean says. “There’s nonetheless a big a part of this market that has not moved, hasn’t taken any steps, even this naked minimal that we’re seeing right here.”
The DMARC protocol goals so as to add authentication to the Web’s e mail infrastructure, requiring that e mail senders undertake two verification applied sciences — Sender Coverage Framework (SPF) and DomainKeys Recognized Mail (DKIM) — and specify a coverage for a way different servers ought to deal with mail from a sender not a part of a certified area. In October 2023, Google and Yahoo required that e mail entrepreneurs — anybody sending greater than 5,000 emails day by day by means of the companies — arrange DMARC. The transfer resulted in a major discount in non-authenticated emails, with Google seeing two-thirds much less (65%) unauthenticated messages despatched to Gmail customers and 265 billion fewer unauthenticated message despatched to date this 12 months, in keeping with firm information launched final week.
Worry, Uncertainty, and DMARC
The adoption fee of DMARC has roughly doubled over the previous 12 months — from about 55,000 domains including new DMARC data every month in 2023, to 110,000 domains per thirty days in Q3 2024, in keeping with Valimail information. But, even at that fee, it could nonetheless take practically 15 extra years for the highest 25 million domains to get on board.
Supply: Writer, with information from Valimail
Furthermore, DMARC adoption has been spotty. Whereas greater than 60% of the organizations in some industries, similar to manufacturing and healthcare, have adopted DMARC, just one in 5 have really moved from the bottom safety coverage (‘p=none‘) to the best (‘p=reject,’) in keeping with information from EasyDMARC, an email-authentication companies agency. Some sectors, similar to non-profits and charity organizations, have elevated adoption over the 12 months, however fewer than 8% of domains are utilizing DMARC.
As a result of e mail is important to enterprise operations, organizations fear that stricter enforcement will lead to misplaced messages, particularly as a result of DMARC shouldn’t be vital a straightforward know-how to implement and keep, says Kelly Molloy, director of community growth for DomainTools, an web intelligence agency.
“The worry is, particularly in case you are an organization who is determined by leads by way of e mail, is that you will miss messages from events — from prospects and potential prospects — when you begin doing [strict enforcement],” she says, including: “Quite a lot of corporations are being conservative and should not going farther than they really want to … as a result of it does take sources.”
Ready for the Different Shoe to Drop
The stalled adoption cycle will doubtless appeal to one other main transfer by Google, Yahoo and different massive client e mail companies, says Hagop Khatchoian, technical companies group lead at EasyDMARC.
“They [Google and Yahoo] are simply forcing everybody to have at the very least ‘p=none‘ … to simply have a fundamental coverage with none enforcement — we foresee that might be modified within the subsequent few years,” he says. “However you’ll be able to’t simply go on and inform everybody, ‘Hey, you want ‘p=reject,‘ … as a result of when you’ve got a small misconfiguration in your e mail ecosystem, and you’ve got an enforced coverage, then your personal professional emails might be blocked as effectively.”
Valimail’s Clean agrees, noting that the most important e mail companies — Google, Microsoft and Yahoo, in addition to main e mail suppliers in different nations — are unlikely to attend lengthy earlier than once more turning the screws on unauthenticated e mail.
“The sending neighborhood or the receiving neighborhood will mandate the subsequent steps, as a result of they know [authentication] is the only most vital enter into their system — with the ability to know who despatched an e mail with much more certainty,” he says. “We will see extra motion there … and it’ll take years, nevertheless it’s not going to be 5 to 10 years. It is in all probability two, three, possibly 4.”
None’s Not Nothing, However Near It
With one other DMARC-push within the playing cards from main e mail companies, organizations ought to plan to shift their DMARC coverage from ‘none’ to the next stage of enforcement.
The three ranges of enforcement are:
-
p=none — Mail that fails authentication checks are nonetheless delivered.
-
p=quarantine — Any authentication failure ends in e mail being quarantined, probably delivered to a person’s spam folder or to a company’s quarantine storage.
-
p=reject — Authentication failure results in the e-mail being discarded, though some service suppliers could as an alternative quarantine the e-mail in a separate folder.
Each enforcement stage can produce experiences, and firms ought to monitor the experiences to test for points and anomalies, says Valimail’s Clean.
“DMARC at ‘p=none‘ with no reporting is syntactically equal to not having DMARC in any respect,” he says. “The worth of DMARC comes from reporting and dealing in the direction of a coverage that’s not ‘none.’ If in case you have ‘p=none‘, and you are not getting experiences, there may be nothing you are able to do, there may be nothing you’ll be able to see, there may be nothing you’ll be able to repair.”
Getting experiences from the DMARC infrastructure is vital stage of visibility for corporations as they pursue higher e mail safety. Massive corporations should not the one organizations to see important abuse of e mail, so any companies that sends e mail ought to monitor their DMARC experiences, he says.
