As not too long ago introduced at this yr’s Knowledge and AI Summit, Databricks AI/BI democratizes enterprise intelligence and analytics throughout your group with extremely visible and interactive low-code AI/BI Dashboards and no-code conversational analytics powered by AI/BI Genie. On this weblog, we’re excited to showcase various new options that improve the efficiency and interactivity of AI/BI Dashboards.
Extremely interactive (or clickable) enterprise intelligence dashboards are desk stakes as of late. They’re important as a result of they allow dashboard customers to discover knowledge dynamically, customizing insights with each click on. This enables them to ask follow-up questions of their knowledge and make extra knowledgeable choices a lot sooner, not like static dashboards that restrict exploration and problem-solving by analytics.
Key enhancements that we are going to cowl on this weblog embody:
- Cross-Filtering: Now you can click on on attention-grabbing knowledge factors in a visualization to filter your dashboard and see the influence on different key metrics and visuals. This helps you discover your knowledge to grasp relationships and correlations that uncover new insights.
- Static Widget Parameters: Create a number of filtered visualizations that spotlight totally different points of your knowledge. For instance, construct two charts specializing in gross sales, one from the present yr and one from the earlier yr. With static widget parameters, you’ll be able to construct visualizations from a single parameterized dataset without having to create a customized dataset per visualization.
- Filter Default Values: Focus viewers on particular knowledge or context inside a dashboard by setting default filter values that apply on preliminary load.
- Improved Efficiency: No one likes dashboards that lock up or inform you to “please wait” each time you open them or click on on an attention-grabbing knowledge level. To that finish, now we have added a number of efficiency enhancements to make sure customers get lightning-fast interactive dashboards to allow them to ask follow-on questions of their knowledge with out operating extra SQL queries.
- Question-Based mostly Parameters: Dashboard authors ought to be capable to create expressive experiences with each discipline and parameter filters. By permitting the mix of parameters and fields in a single filter, we have enabled new capabilities, reminiscent of dynamically populating a parameter dropdown with question outcomes.
Cross-Filtering
When exploring a dashboard, particular knowledge factors in a visualization could stand out for additional investigation. Whereas some filters could already be in place, they could not anticipate each viewer’s wants.
With cross-filtering, each chart can now be used to filter your knowledge. Merely click on on visualizations to filter the dashboard and discover the information extra deeply. Cross-filtering is routinely enabled for all visualizations that share the identical dataset, which means you’ll be able to click on on one a part of a visualization (like a bar in a bar chart) to filter the information throughout all associated visualizations within the dashboard.

Slice by your knowledge and focus your evaluation by clicking on outliers, reminiscent of visually distinct marks in a heatmap.

Navigate hierarchical knowledge by drilling down by aggregated visualizations. For instance, click on on yearly knowledge to limit different charts to that yr’s knowledge. Click on on bars in month-level and week-level charts to proceed drilling down.
At present obtainable for bar charts, heatmaps, pie charts, and scatter plots, cross-filtering enhances current discipline and parameter filters. Help for added visualizations, together with histograms, line charts, space charts, combo charts, and multi-value choice, is coming quickly.
Static Widget Parameters
Constructing dashboards is simpler with fewer datasets. Cloning a dataset simply so as to add one other filter or mixture for a selected visualization introduces litter and friction
Static widget parameters simplify this course of by permitting you to customise filters for every visualization with out creating separate filtered datasets. This function enhances the prevailing skill to outline per-visualization aggregates and bins.
For instance, to focus on temperature metrics for various places utilizing a single dataset, you’ll be able to increase it with a situation like:
/*
This filter permits for the show of grand totals when the viewer selects 'All'.
- If a selected location is chosen, the filter matches information for that location.
- If 'All' is chosen, the filter situation all the time returns true, together with all places within the outcomes.
Learn extra particulars about this sample right here
*/
WHERE location = :location OR :location = 'All'Subsequent, merely set a unique static parameter worth for every new visualization. Within the instance beneath, you’ll be able to see three charts: one for all places, one for Seattle and one for New York. Every chart makes use of the identical dataset, however totally different static values are utilized to filter the information accordingly.
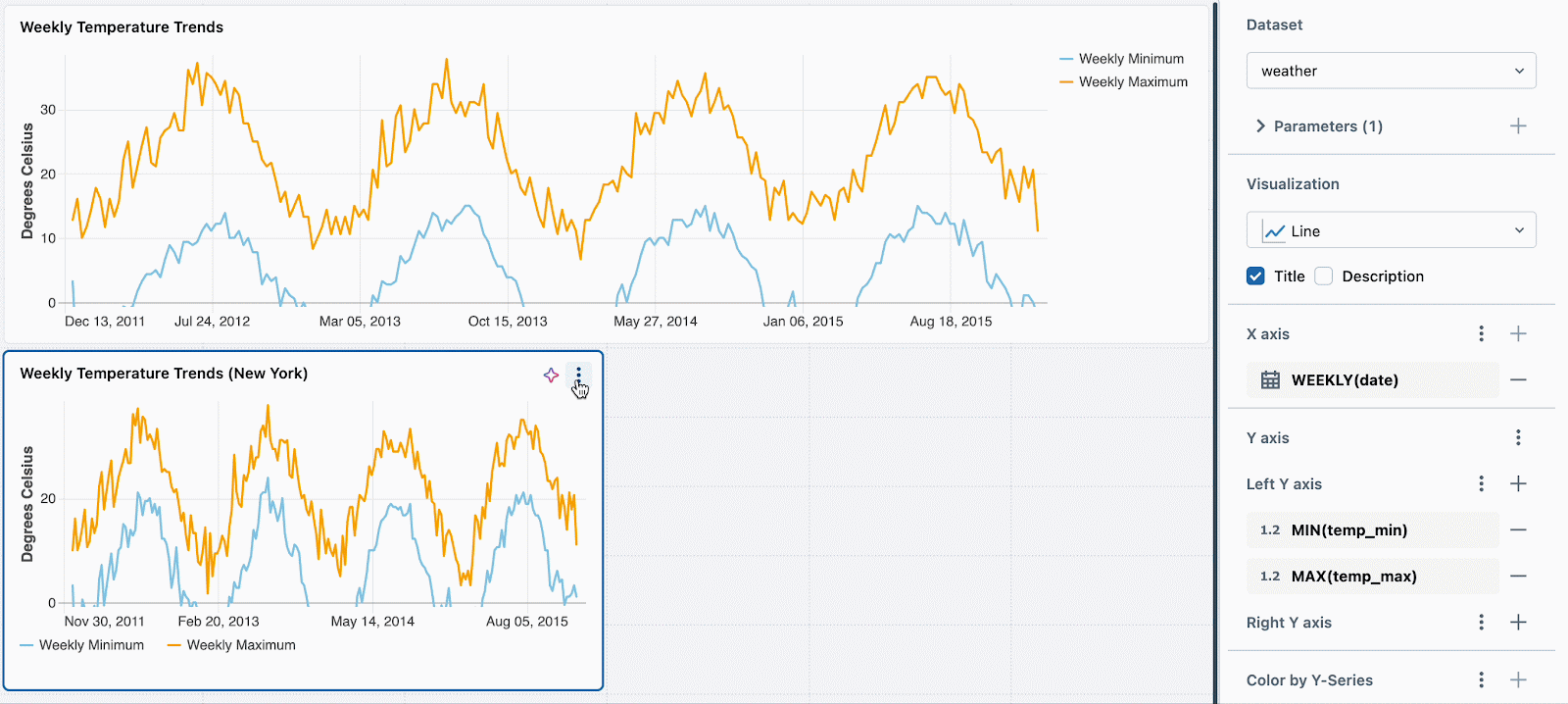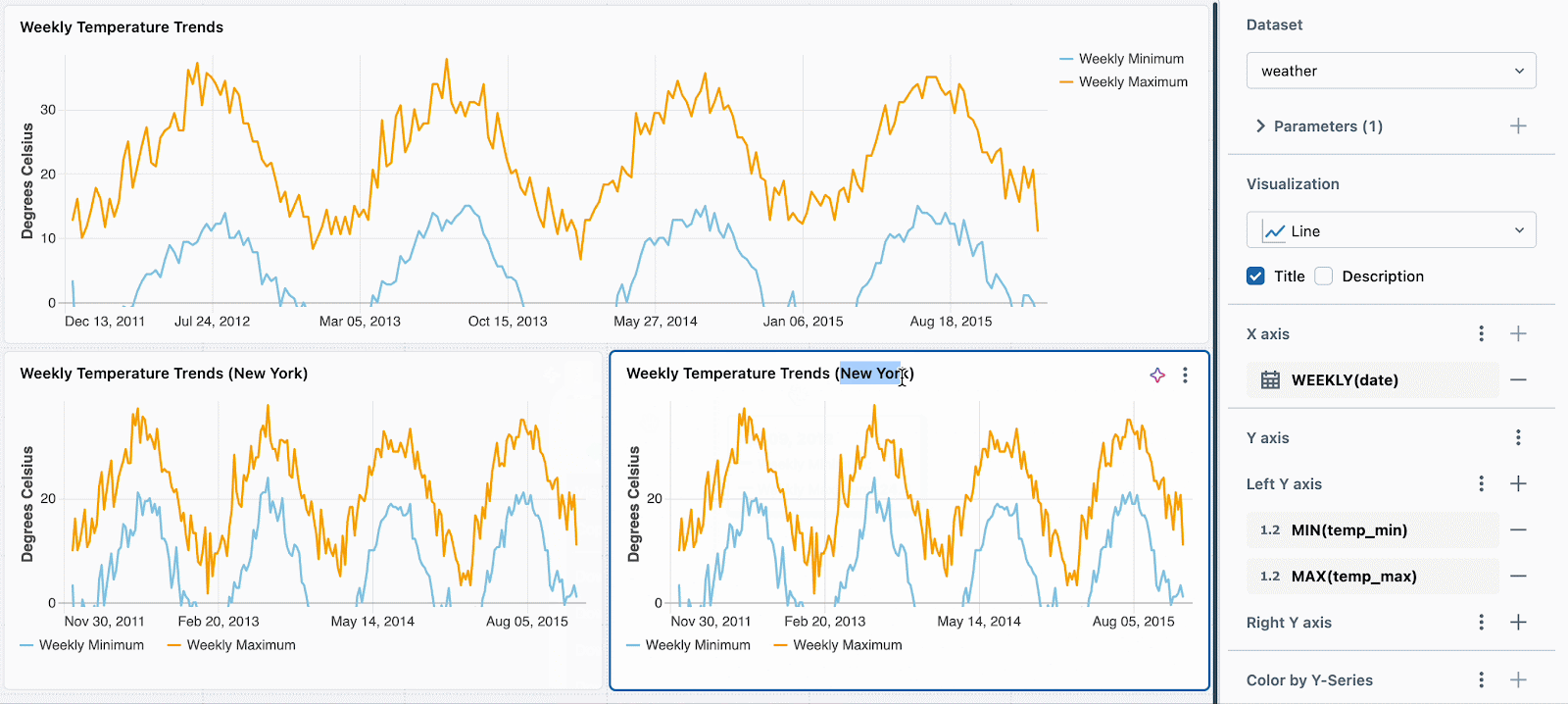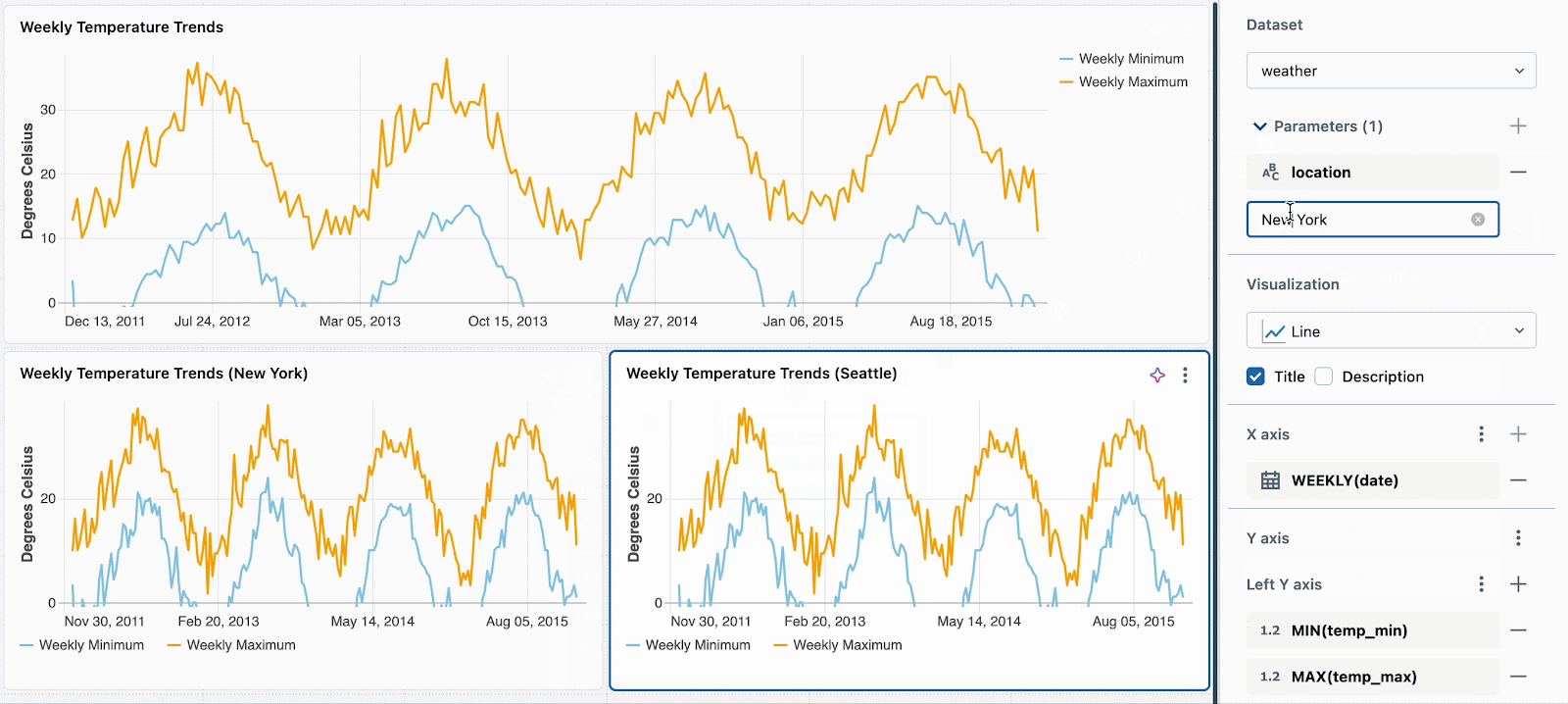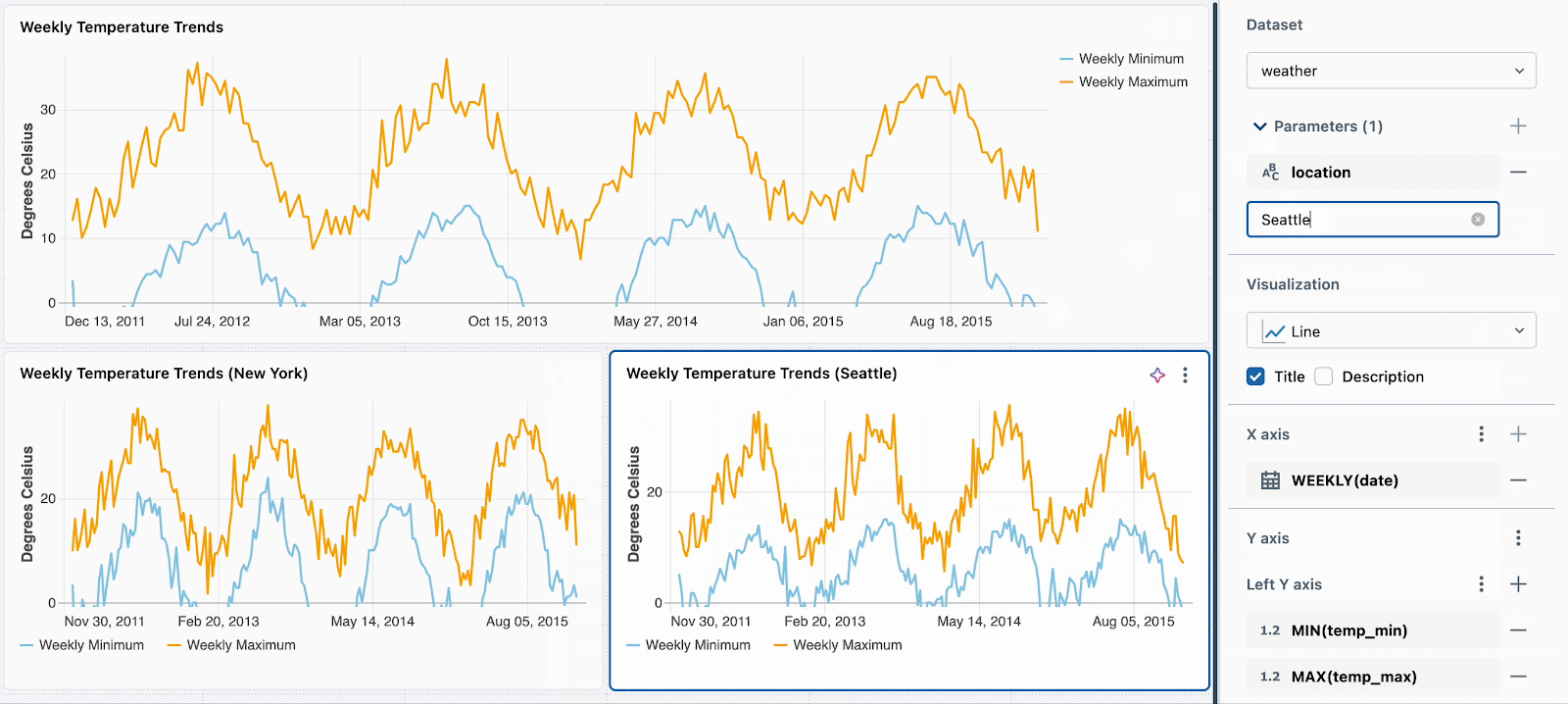
We’re engaged on extending this performance to help per-widget filtering utilizing fields. For instance, you might filter every chart on the situation discipline without having to parameterize the underlying dataset.
Default Values
As a dashboard writer, you may need to information viewers to a selected knowledge slice, reminiscent of a selected date vary or location.
With default values, you’ll be able to set particular filter values that apply on preliminary dashboard load or when alternatives are reset. This ensures that viewers deal with the important thing knowledge factors from the beginning. Default values complement the prevailing skill to protect dashboard filter alternatives by sharing a URL of your present view.
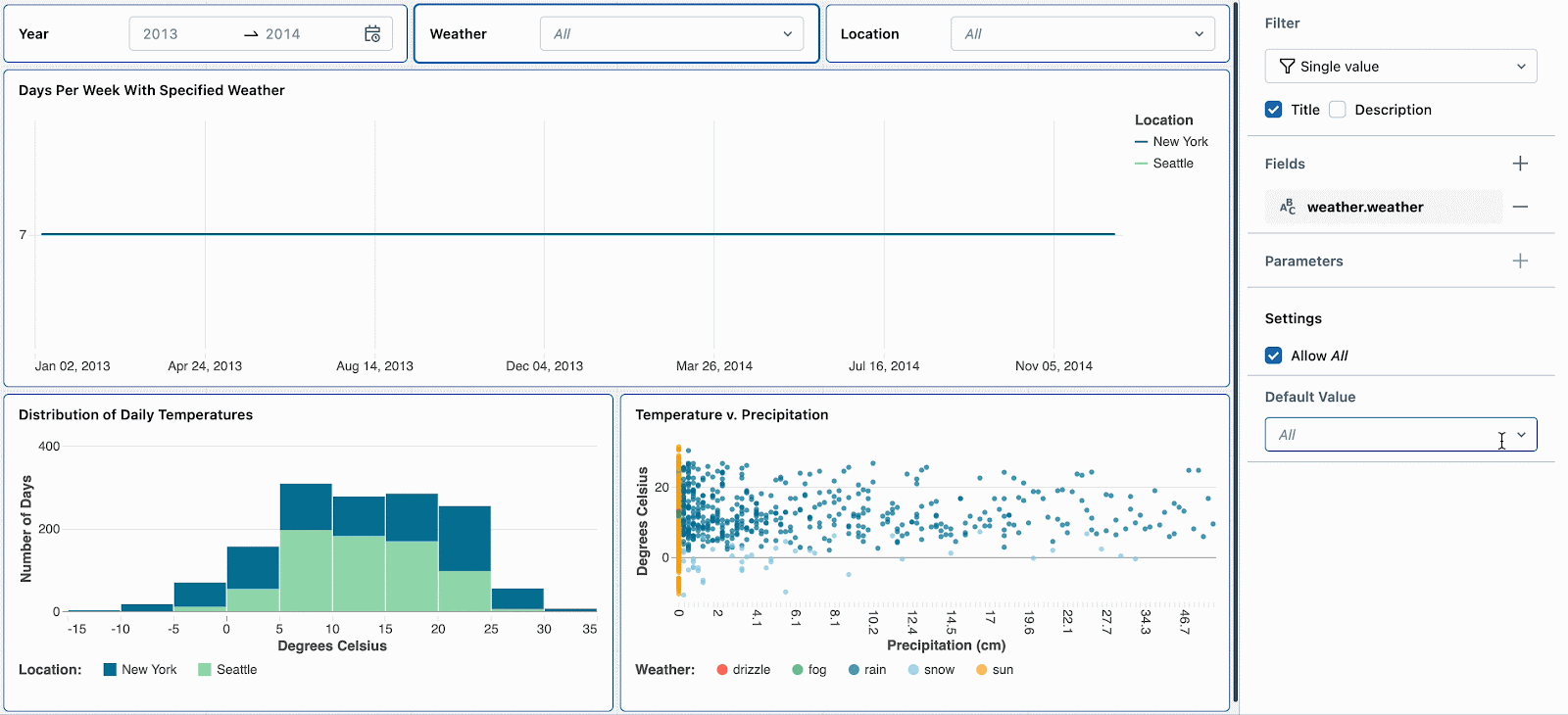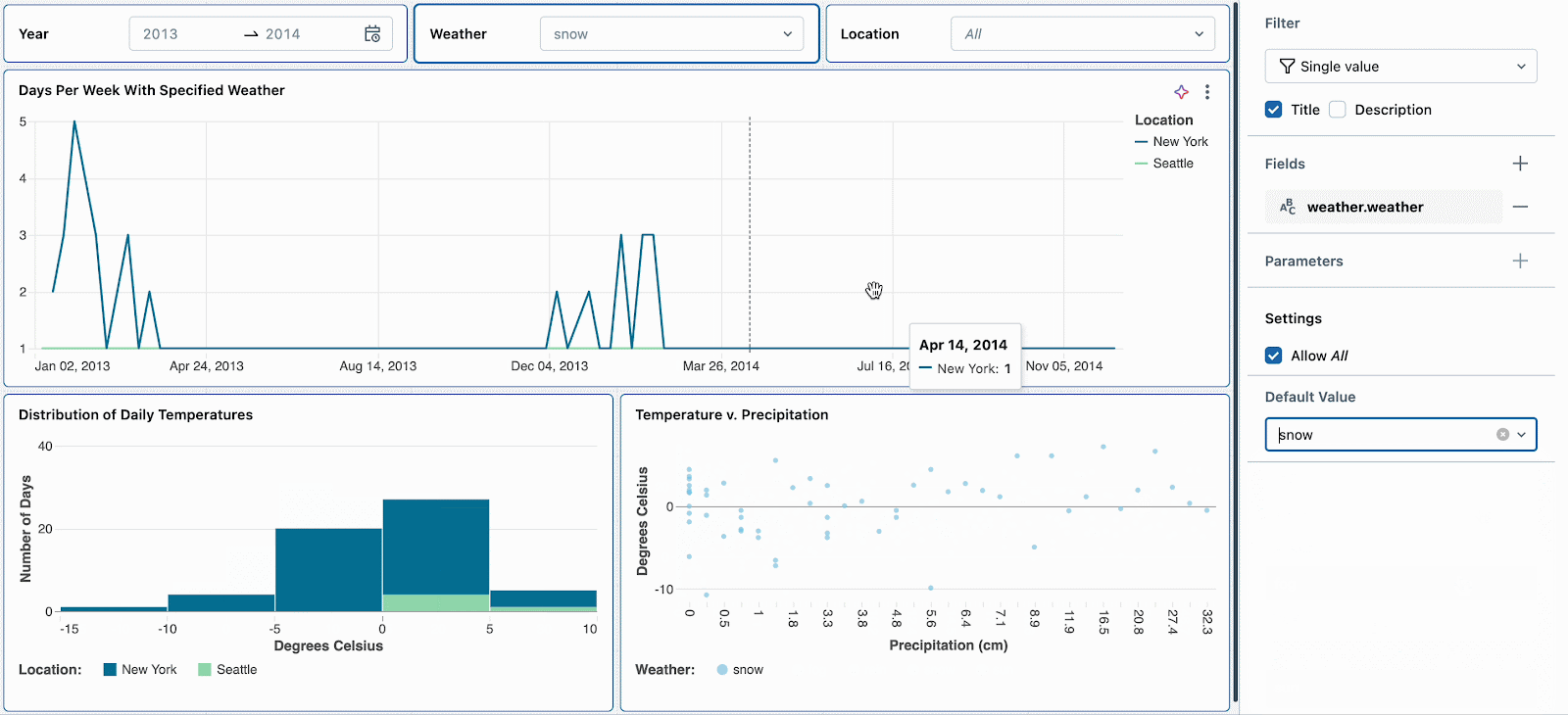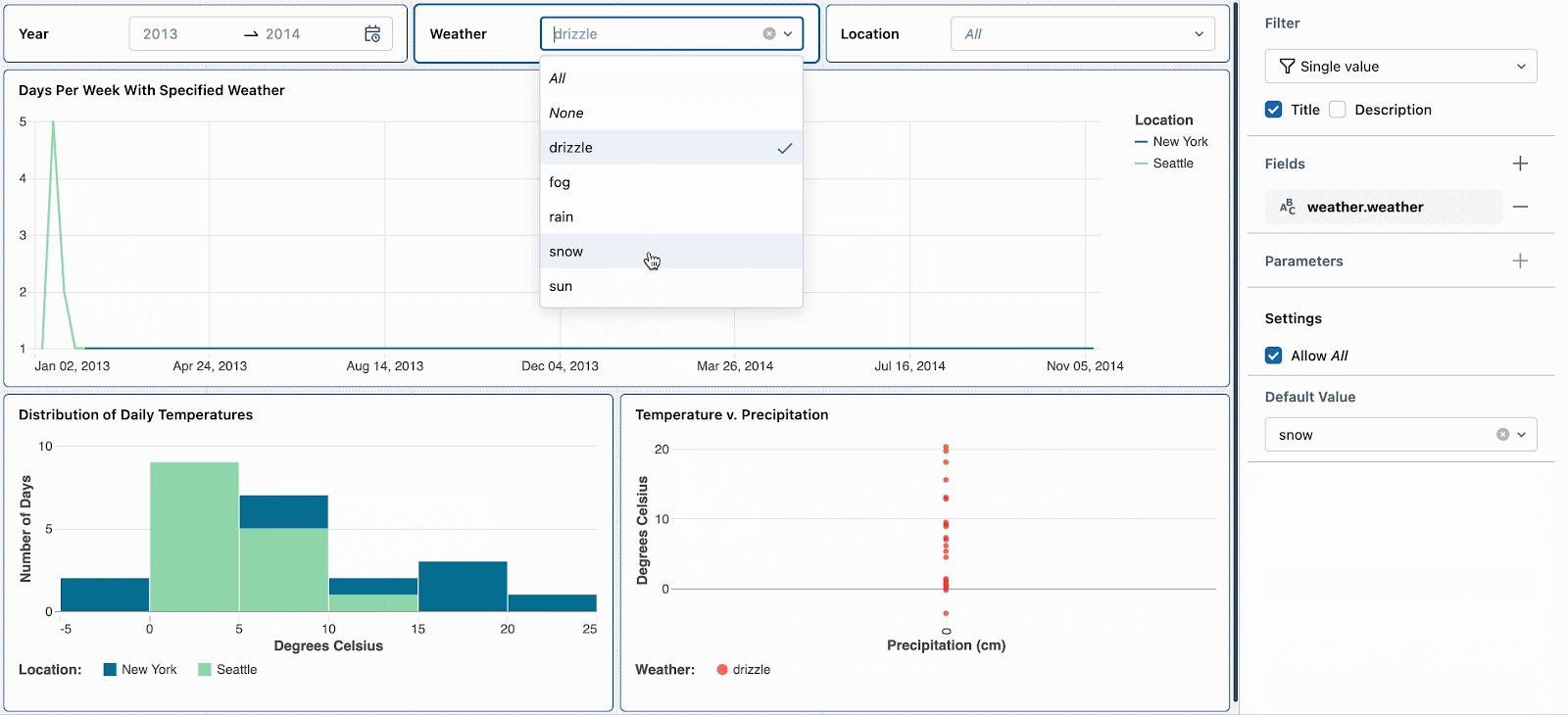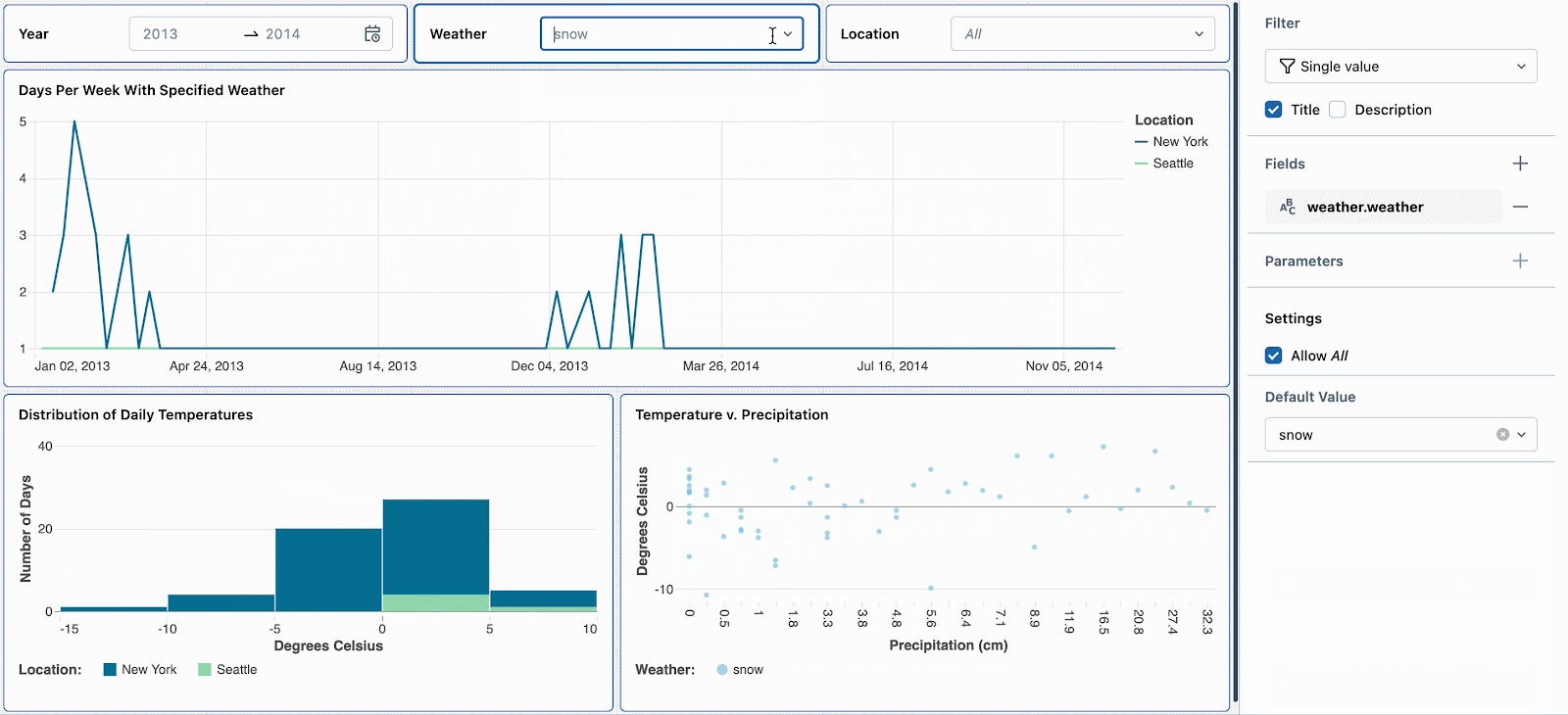
For instance, snow days are attention-grabbing as a result of they’ve excessive temperatures and excessive precipitation. Setting the default climate filter to ‘snow’ will encourage new dashboard viewers to discover this climate sort first. After reviewing different climate developments, they’ll reset the filter to proceed their deep dive into snow days.
Improved Efficiency
For an interactive dashboard to really be pleasant, it should be quick. Ready for queries to run with every filter utility can disrupt the stream of study.
AI/BI Dashboards are optimized for top efficiency, even with giant knowledge, by methods like question caching and deep platform integration. Question caching routinely shops the question outcomes for twenty-four hours, guaranteeing sooner efficiency by leveraging beforehand executed queries. You may as well proactively populate the cache by schedules.
Along with delivering quick preliminary load, AI/BI Dashboards present near-instant interactivity for smaller datasets by evaluating filters within the browser slightly than re-executing queries on each change.
We not too long ago elevated the client-side filter analysis restrict to 100K rows. Which means that for datasets inside this restrict, all the dataset is queried as soon as, and all subsequent filtering is dealt with client-side, eliminating the necessity for added server-side queries. Even with giant tables, methods like pre-aggregation with materialized views can create smaller, faster-filtering datasets.
We typically advocate filtering on fields slightly than parameters, which all the time require server-side queries. Parameters are finest suited to circumstances that filtering on fields cannot but deal with, like filtering in subqueries or defining datasets with advanced aggregates.
We proceed to discover extra optimizations reminiscent of additional rising the client-side filter restrict. Upcoming options reminiscent of visualization-level calculations will enhance the variety of use circumstances that may be totally achieved by filtering on fields.
Question-Based mostly Parameters
Parameters are a robust instrument as a result of they are often launched wherever in a dataset’s SQL, providing most flexibility when defining filters. Though parameters are placeholders for literals in SQL, they need to act like every other discipline, permitting authors to populate dropdowns and different filters used to configure their values.
By enabling the blending of parameters and fields, we’ve added the power to populate parameter filters with values from different datasets. This method to query-based parameter values unlocks superior evaluation capabilities, reminiscent of dynamically altering date granularities.
For instance, you’ll be able to allow drilling down by totally different date granularities by parameterizing the DATE_TRUNC perform used for aggregation. The ensuing dataset and metrics are aggregated, which implies that including an extra climate filter additionally requires parameterizing the question.
SELECT
DATE_TRUNC(:date_granularity, date) as date,
avg(wind) as average_wind_speed,
sum(precipitation) as total_precipitation
FROM
climate
WHERE
:climate = 'All' or climate = :climate
GROUP BY ALLDashboard viewers ought to be capable to simply select legitimate values of their filter dropdowns. For instance, they need to not must guess if “YEAR” or “YEARLY” is the proper literal for date truncation. To populate the dropdowns accurately, create the next two datasets
--Dataset 1: Generate a static checklist of legitimate date granularities
SELECT * FROM VALUES ('day'), ('week'), ('month'), ('yr') AS t(date_granularity)--Dataset 2: Select the distinct climate classes from the underlying desk
SELECT DISTINCT climate FROM climate UNION ALL SELECT DISTINCT 'All' AS ClimateModify the date granularity and climate parameter filters to reference the fields in these dataset to populate the dropdowns and begin drilling down by dates.

Combining fields and parameters in a single widget additionally helps you to use one filter to regulate a number of datasets, no matter whether or not these datasets use parameters or discipline filters.
We’re trying ahead to offering much more flexibility in discipline and parameter filtering with upcoming options like date vary parameters and multi-value parameters.
Be taught Extra About AI/BI Dashboards
As we have demonstrated, AI/BI Dashboards are a big space of funding for Databricks, with interactivity being a key focus. We encourage you to discover these new options and see how they’ll elevate your individual dashboards. Try the Databricks documentation round AI/BI Dashboards, together with deep dives on parameters and filters.
Your suggestions is invaluable as we proceed to refine and increase our AI/BI Dashboards. We look ahead to listening to your ideas and options!
