Rockset is a schemaless SQL knowledge platform. It’s designed to help SQL on uncooked knowledge. Whereas most SQL databases are strongly and statically typed, knowledge inside Rockset is strongly however dynamically typed. Dynamic typing makes it tough for us to undertake off-the-shelf SQL question optimizers since they’re designed for statically typed knowledge the place the forms of the columns are recognized forward of time. Most of Rockset’s operational analytics use instances execute a whole lot of concurrent queries, and every question wants to finish inside a number of milliseconds. Given our distinctive challenges and efficiency necessities, constructing our personal SQL question engine from scratch appeared like the best selection.
This weblog put up provides you a sneak peek at what occurs underneath the hood of our SQL question engine once you subject a SQL question to Rockset.
Broadly talking, a SQL question goes by 3 important levels as proven in Determine 1:
- Planning
- Optimization
- Execution
Within the strategy planning stage, a set of steps that must be executed to finish the question is produced. This set of steps is named a question plan.
A question plan is additional categorized into the next sorts:
- Logical Question Plan: It’s an algebraic illustration of the question.
- Bodily Question Plan: It consists of operators that execute components of the question. For instance, the logical question plan might comprise a “Assortment” node that signifies that knowledge have to be retrieved from a selected assortment, whereas the bodily plan comprises a “ColumnScan” or “IndexFilter” operator that truly retrieves the information utilizing a selected entry technique from the index.
A number of question plans may be produced for a similar question from which the question optimizer then chooses essentially the most environment friendly question plan for execution. The ultimate question plan chosen for execution is named the execution plan.
With the intention to inspire our design decisions for the question planner we first want to know the question optimization stage. Particularly, we have to perceive how an optimizer chooses an execution plan. Within the subsequent part, we take a look at the two important classes of question optimization strategies.
Rule Based mostly Optimization vs. Value Based mostly Optimization
A question optimizer is entrusted with the job of choosing essentially the most environment friendly execution plan for a specific question.
The Rule Based mostly Optimizer (RBO) makes use of a set of predetermined guidelines based mostly on a heuristic to infer essentially the most environment friendly execution plan. For instance, you would have a rule that chooses a unique entry technique to fetch the information from the index based mostly on the character of the filter clause within the question. We index all fields, so predicates that evaluate a subject worth with a continuing (resembling “a < 10”) may be pushed into the index. However predicates that evaluate a subject with one other subject (resembling “a < b”) can’t be pushed into the index. You can select the entry technique that scans the inverted index for under these paperwork that fulfill the predicate (IndexFilter) for queries which have predicates that may be pushed down into the index, versus a full columnar scan adopted by a filter within the case the place the predicates can’t be pushed down. That is illustrated in Determine 2.
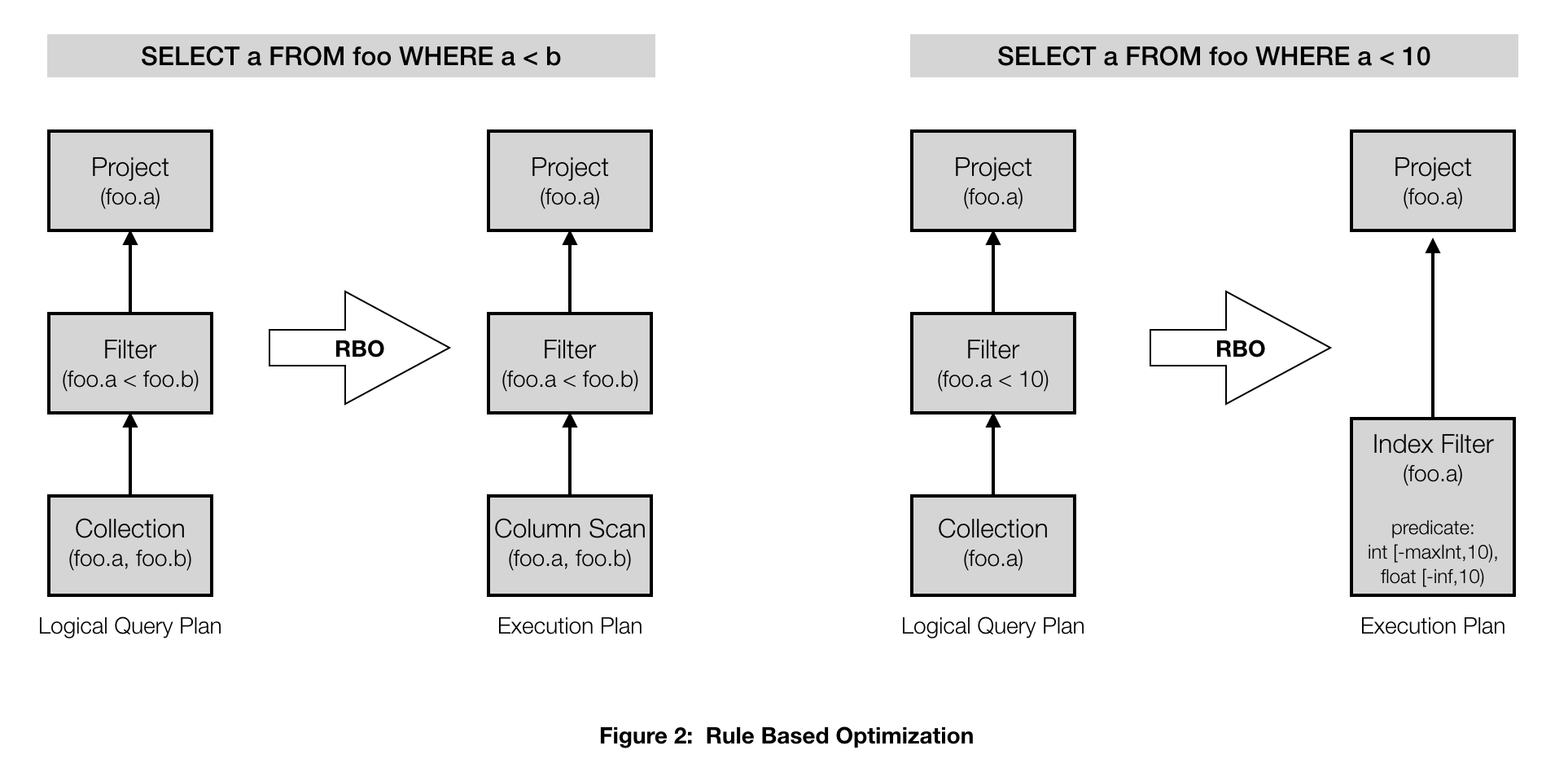
Or you might have a rule that chooses a unique be part of technique relying on whether or not the be part of is an equijoin or not. An RBO doesn’t at all times produce essentially the most environment friendly execution plan, however in most conditions it’s adequate.
Alternatively, a Value Based mostly Optimizer (CBO) begins with all attainable question plans in its search area. It evaluates them by assigning a rating to each plan. This rating is a operate of the compute, reminiscence, and time required to execute that plan. The ultimate value of the plan is memoized by breaking the question plan into easier sub-plans and scoring every of them as you go alongside. The fee mannequin may be designed based mostly on the necessities of the system. It additionally makes use of different details about the information resembling row selectivity and distribution of values to infer essentially the most environment friendly execution plan extra precisely. Provided that the search area of plan alternate options can develop exponentially, a superb CBO must steadiness exploration (which grows the search area) with exploitation (scoring the already-explored plans and pruning those that won’t be optimum).
The primary question optimizer for Rockset was rule based mostly. Whereas it labored nicely for easier queries with fewer knobs to show, for extra complicated queries it quickly developed right into a reasonably gnarly mesh of specialised guidelines providing little or no flexibility to seize different subtleties. Particular care needed to be taken to make sure that these guidelines didn’t step on one another. Additional, it was nearly inconceivable to exhaustively cowl all of the optimizations, typically leading to clunky tweaks to present guidelines after a helpful heuristic was found as an afterthought. Our rule based mostly optimizer quickly developed into an enormous home of playing cards with guidelines precariously balanced collectively.
Provided that the first use case for Rockset is operational analytics queries with low latency and excessive concurrency necessities, there was an growing emphasis on question efficiency. The RBO supplied a reasonably brittle strategy in the direction of question optimization and we quickly realized that we would have liked one thing that was extensible, secure, and dependable. After surveying some analysis literature, we got here throughout Orca, which is a state-of-the-art value based mostly question optimizer particularly designed for heavy operational workloads. We determined to maneuver in the direction of a price based mostly optimizer that will assist us higher meet our necessities. Within the course of, we determined to rewrite our question planner to help value based mostly optimization. Our question planning structure is closely impressed by Orca[1] in addition to CockroachLabs[2].
Now that we perceive at a excessive degree how a question optimizer operates, allow us to transfer onto how queries are deliberate in Rockset.
Question Planning
Step one earlier than the planning section is question parsing. The parser checks the SQL question string for syntactic correctness after which converts it to an summary syntax tree (AST). This AST is the enter to the question planner.
Allow us to use the next instance question as we stroll by the completely different steps of question planning.
SELECT foo.a FROM foo, bar
WHERE foo.a = bar.b
The AST for this question is proven in Determine 3.
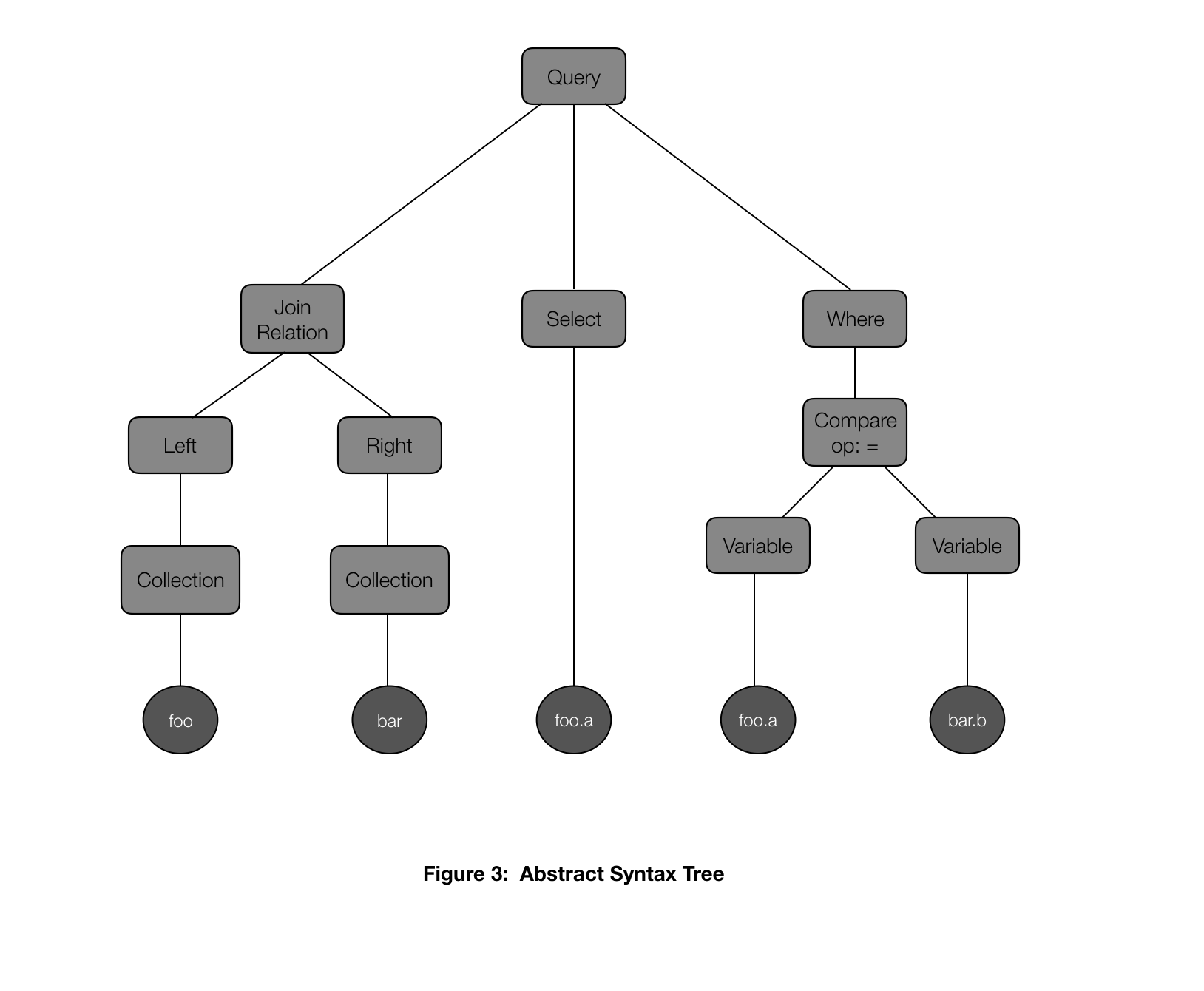
The question planner has the next key parts:
Memo
A Memo is a recursive in-memory knowledge construction used to effectively retailer the forest of question plan alternate options generated throughout question planning.
It consists of the next parts:
Memo Group:
A Memo consists of a set of containers known as teams. Every group comprises logically equal expressions that every obtain the identical group objective in numerous logical methods.
Memo Node:
Every group expression in a memo group is named a memo node. Every memo node is an operator that has different memo teams as youngsters.
The memo nodes are subdivided into 2 sorts:
- Relational (e.g. Assortment, Be a part of Relation)
- Scalar (e.g. Expressions)
We’ve 2 completely different Memo buildings to carry the relational and scalar memo nodes individually. A Relational Memo construction is used to retailer the relational memo nodes whereas a Scalar Memo construction shops the scalar memo nodes. Every memo node has a fingerprint that uniquely identifies it. Each the relational and scalar Memos retailer a singular set of the relational and scalar memo nodes, respectively.
The scalar memo doesn’t have teams for the reason that most simplified model of a scalar memo node is saved within the scalar memo.
Determine 4 exhibits the preliminary contents of the Relational and Scalar Memos for our instance question. The logical question plan interprets to 4 memo teams, 2 for every Assortment, 1 for the InnerJoin with empty predicates, and 1 for the Filter. Group 0 (G0) can also be known as the foundation memo group because it corresponds to the foundation of the logical question plan.
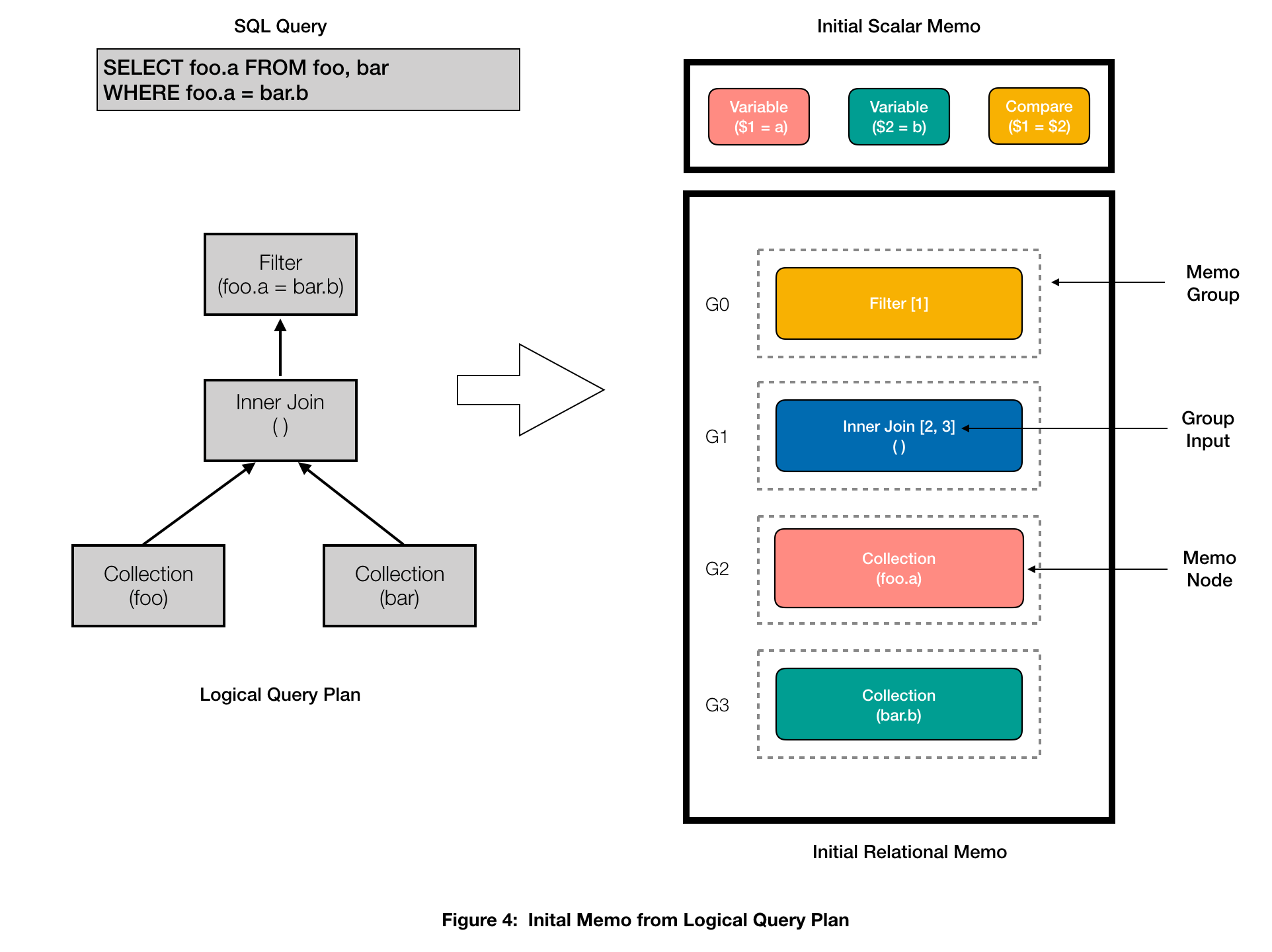
Normalization:
Throughout this step, plan alternate options are generated by making use of a set of normalization guidelines to the plan nodes. Normalization is used primarily to simplify expressions, rework equal expressions to a canonical type, and apply optimizations which can be believed to at all times be useful in an effort to save the CBO some work. These guidelines specify a collection of transformations to be utilized to a plan node when a specific match situation is glad. It’s anticipated that these normalization guidelines don’t result in cyclic dependencies. The ensuing memo nodes are saved within the Memo, which can end in creating new memo teams and/or including new memo nodes to present teams. Memo nodes ensuing from the normalization of scalars (e.g., fixed folding) are thought-about remaining. We ignore the price of computing scalar expressions; we assume that equal scalar expressions (resembling a + 2 and 2 + a) have the identical value (zero). It’s only the relational memo nodes which can be explored.
We’ve applied our personal rule specification language (RSL) to specific these normalization guidelines. We convert these RSL guidelines to C++ code snippets utilizing our personal RSL compiler.
As an example, we will categorical fixed folding in RSL as follows.
[Normalize, Name="evaluateConstantCall"]
FunctionCall(
func: *,
args: * if (allConstant($args))
)
=>
Fixed(worth: evalFunction($func, $args))
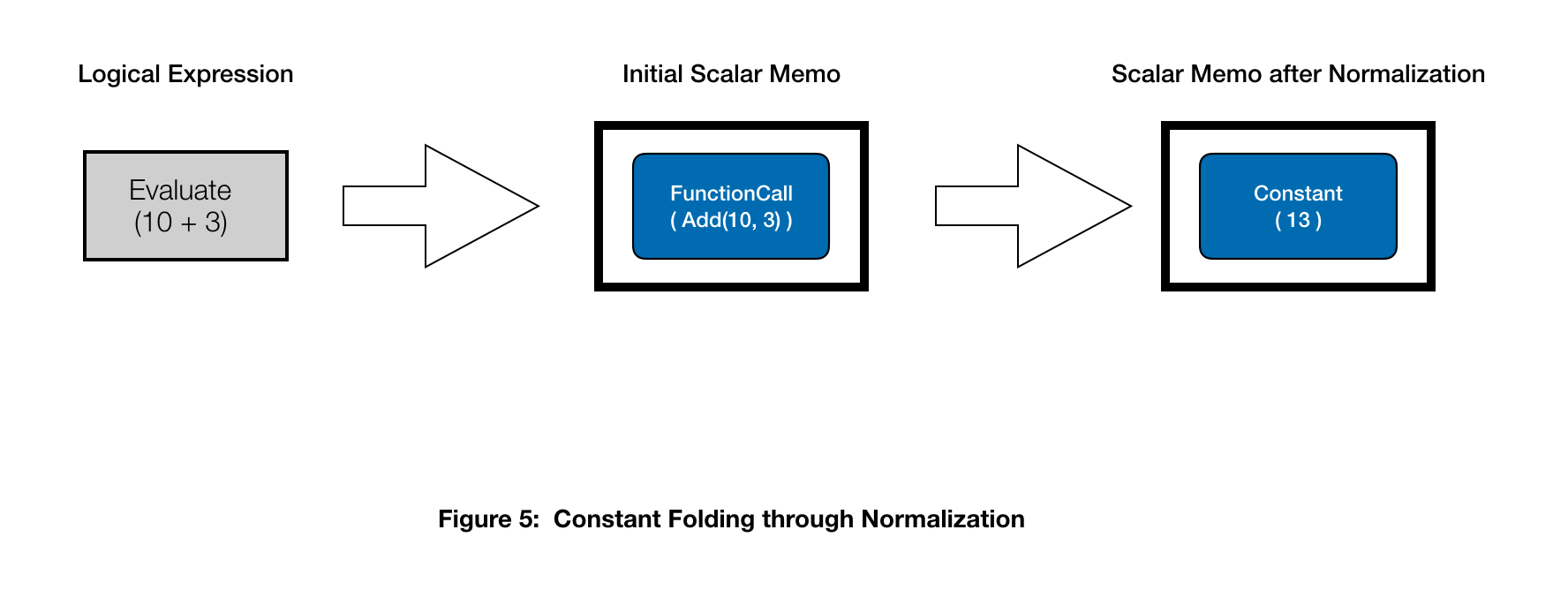
This rule implies that in the event you encounter a FunctionCall scalar memo node that has all constants for its arguments, substitute it with a Fixed scalar memo node with its worth equal to that of the evaluated operate.
That is illustrated in Determine 5.
Going again to our instance question, we will specify a normalization rule that produces an alternate plan by pushing down the predicate foo.a = bar.b into the Interior Be a part of operation, versus making use of it as a put up be part of predicate.
[Normalize, Name="pushAfterJoinPredicatesIntoInnerJoin"]
Filter(
enter: $j=Be a part of(kind: kInner, predicates: $join_pred=*),
predicates: $pred=*)
=>
substitute($j, predicates: intersectPredicates($join_pred, $pred))
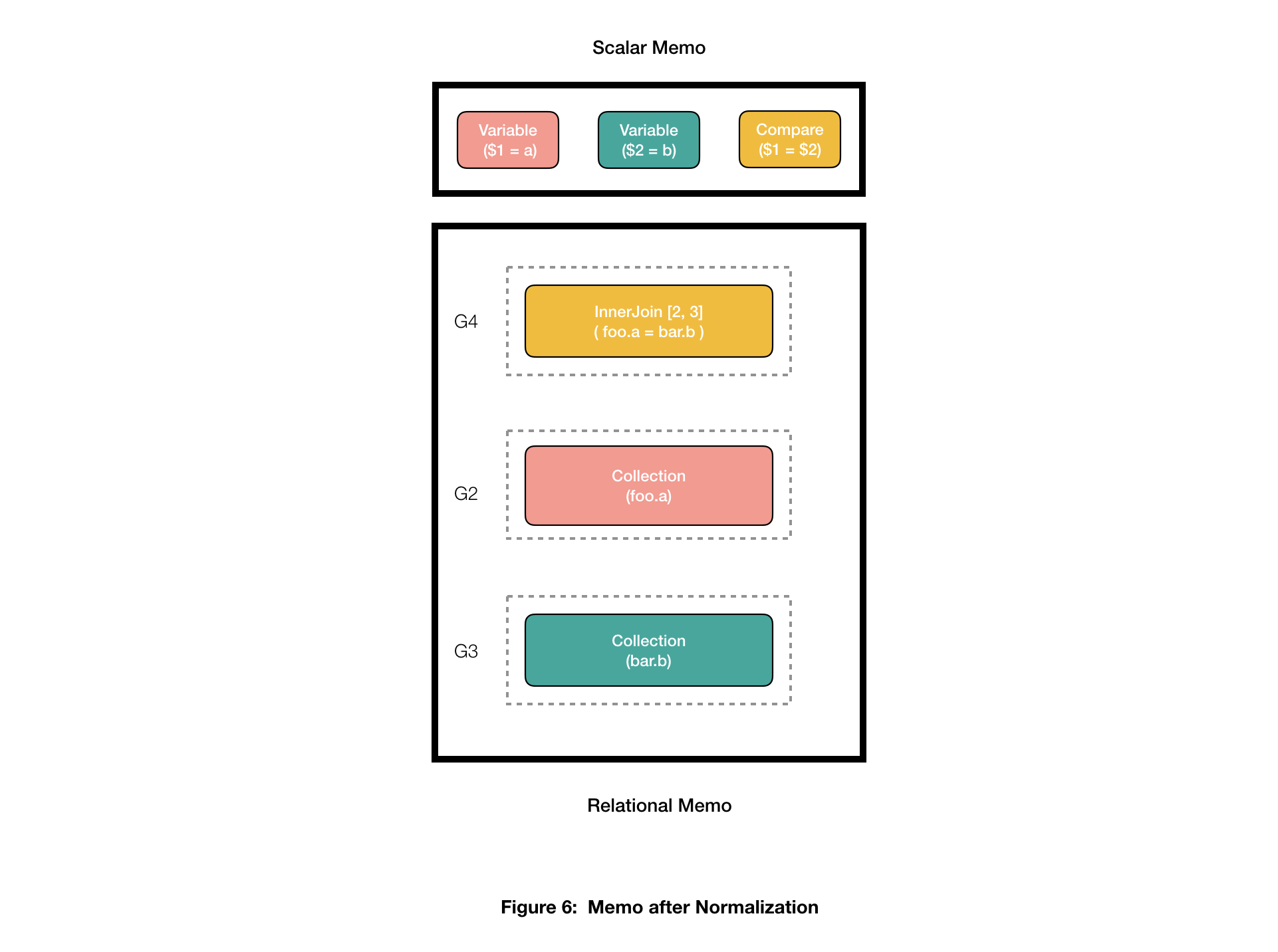
With this normalization,
SELECT foo.a FROM foo, bar
WHERE foo.a = bar.b
successfully converts to
SELECT foo.a FROM foo INNER JOIN bar
ON foo.a = bar.b
Determine 6 exhibits what the brand new Memo would appear like after normalization. It solely exhibits the memo teams that will likely be walked throughout exploration.
Exploration
Exploration occurs as a part of the question optimization stage. Throughout this section, the assorted plan alternate options are costed by scoring dependent memo teams recursively, beginning at a Memo’s root group.
It’s throughout this section that essentially the most environment friendly be part of technique, be part of ordering, and entry path could be picked to execute our instance question.
That is nonetheless work in progress and continues to be an lively space of growth for our group. We are going to speak about it at size in a future weblog put up.
Execution
The execution plan obtained on account of exploration is forwarded to the execution engine, which distributes the duties throughout machines to allow distributed question execution. The ultimate outcomes are then relayed again to the tip person. We are going to cowl the small print about question execution in one in every of our future weblog posts.
Loads of this continues to be actively developed, actually as I write this weblog. If engaged on such thrilling issues is your factor, we’re hiring!
References:
[1] Soliman, Mohamed A., et al. “Orca: a modular question optimizer structure for large knowledge.” Proceedings of the 2014 ACM SIGMOD worldwide convention on Administration of information. ACM, 2014.
[2] CockroachDB: https://github.com/cockroachdb/cockroach/blob/release-19.1/pkg/sql/choose/doc.go
