Whereas disclosure of software program vulnerabilities and knowledge breaches has change into extra accepted over the previous three a long time, researchers and whistleblowers proceed to danger lawsuits and felony costs relying on the nation by which they dwell.
In April 2022, for instance, police in Istanbul arrested impartial Turkish journalist İbrahim Haskoloğlu after he revealed particulars of a breach of presidency knowledge in Turkey. The nation’s ruling celebration has since proposed a regulation to make the false reporting of a knowledge breach against the law punishable by two to 5 years in jail — a regulation that critics say will forestall disclosure of actual knowledge breaches.
And within the island nation of Malta, three computer-science college students and their lecturer on the College of Malta might be charged in March, two years after they discovered vulnerabilities in scheduling service FreeHour and notified the corporate. FreeHour claimed the disclosure gave the impression to be a ransom demand and reported the scholars to the police — though, since then the agency has criticized the nation’s lack of clear exemptions for researchers.
The scholars proceed to face costs, nonetheless.
“I hope that on the finish of this case, it ends in a greater local weather for cybersecurity, however I am genuinely exhausted from this entire scenario,” Michael Debono, one of many college students, said in a submit on Fb. “It is loopy that I’ve needed to spend nearly two years now coping with the fallout of an incident that ought to have been resolved over a desk in a day with FreeHour and the police.”
Turkey and Malta should not the one international locations to crack down individuals who report knowledge breaches and software program vulnerabilities. In Poland, a practice producer threatened to sue three moral hackers who circumvented a kill code that the cybersecurity professionals declare disabled trains that had been parked in a third-party restore facility. In China, vulnerability researchers who don’t first report software program points to the federal government danger jail time.
Even within the US, the place vulnerability-disclosure points have been debated for many years, corporations and authorities businesses nonetheless often resort to authorized assaults quite than civil engagement. In September 2024, town authorities of Columbus, Ohio, filed a lawsuit towards whistleblower David L. Ross after he disputed the importance of a knowledge breach, claiming that Ross colluded with the ransomware gang behind the breach. Two months later, town settled the lawsuit.
Defensive Driving and Disclosure
Worldwide, vulnerability researchers must take care when disclosing software program safety points. Erring on the aspect of security, like defensive driving, must be the default for cybersecurity researchers and whistleblowers, says Trey Ford, chief data safety officer at San Francisco-based Bugcrowd, who connects its steady of impartial penetration testers with purchasers.
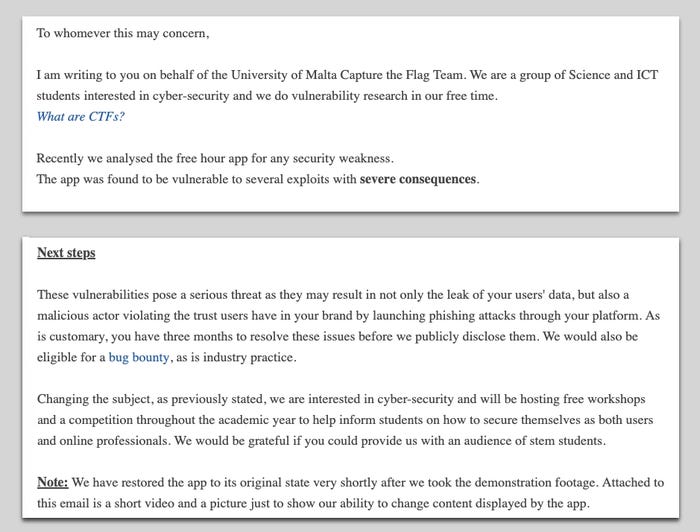
The October 2022 electronic mail that resulted in three college students and their lecturer going through costs. Supply: Lecturer Luke Collins’ website
In the most effective case, researchers ought to get hold of permission from the focused group to conduct analysis and disclose findings, he says.
“The fact now’s: In case you see one thing, and you are not completely positive — and do not have receipts and proof — perhaps do not say something, otherwise you danger going to jail,” Ford says, mentioning that defensive or vindictive organizations may cause bother. Any danger could be “additional amplified by the misaligned incentives of corporations that would favor to not handle a problem. These corporations have the facility to nearly utterly silence the reporter.”
As well as, working with the group quite than instantly adopting an adversarial strategy can assist decrease potential misinformation about what constitutes a breach or vulnerability, says Ilona Cohen, chief authorized and coverage officer at HackerOne, a hacking-services platform.
Researchers also needs to all the time be cognizant of native regulation, she says.
“Whether or not a knowledge breach has occurred or a vulnerability is current should not all the time clear-cut,” Cohen says. “It’s not unusual for international locations to have legal guidelines towards fraudulent misrepresentation, however lawmakers should take care to not goal people that don’t intend to deceive or to trigger hurt.”
Benign Intent or Hostile Actions
To date, the researchers and whistleblowers are paying the worth of the dearth of readability. Turkish journalist Haskoloğlu, for instance, claimed he notified the Turkish authorities two months earlier than his disclosure, after being contacted by the hackers that the information had been stolen. Final month, he introduced he would depart Turkey following escalating dying threats.
In December, Newag — the practice producer in Poland that allegedly bricked trains not repaired in its workshops — filed a lawsuit towards the three hackers who found and publicized their workaround for the kill code. Whereas the European Union adopted a right-to-repair regulation for client items in 2024, it is unclear whether or not industrial tools, reminiscent of trains and equipment, are coated.
The incidents spotlight that organizations are aiming to silence researchers, quite than interact publicly with them, says Dustin Childs, the pinnacle of menace consciousness and the Zero Day Initiative at Pattern Micro, which maintains a third-party bug bounty program.
“It’s a disturbing pattern I hope reverses quickly,” he says. “We have to supply protected harbor to researchers who’re prepared to report vulnerabilities in a coordinated method. Sadly, this pattern is unlikely to vary with out both litigation or laws.”
Globally, nonetheless, laws seems to be shifting in a distinct path. In August 2024, the UN Common Meeting adopted the Conference Towards Cybercrime, which makes it against the law to “entry … an data or communications expertise (ICT) system with out proper” or to intercept knowledge or communications. Digital-rights teams fear that the treaty will result in extra legal guidelines that penalize reliable safety analysis.
Whereas Turkey seems to be the primary nation since August to move a extra strict cybercrime statue, more durable laws appear more and more doubtless, Childs says.
“Total, we’re at present in a local weather the place governments favor companies over particular person researchers,” he says. “It might not shock me to see related measures in different international locations.”
