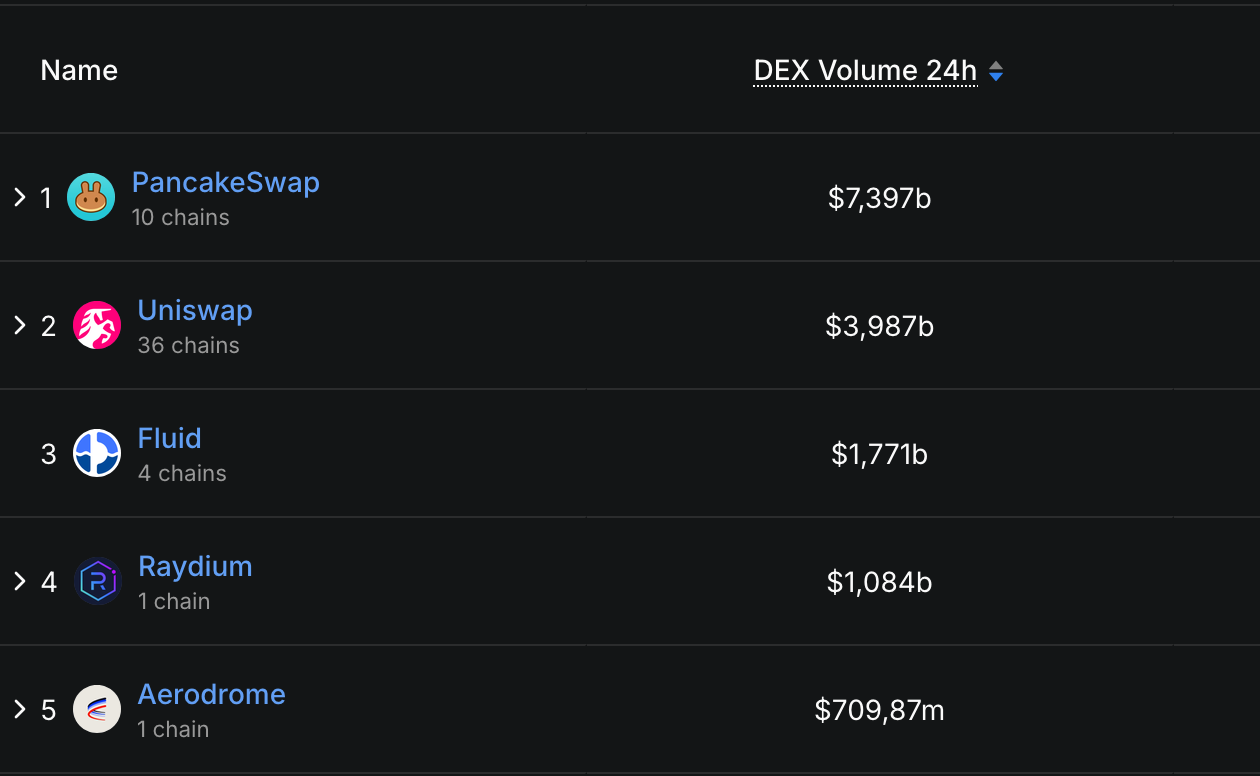
Companies as we speak depend on sturdy, safe, and agile community infrastructures to energy their operations and keep a aggressive edge. For international meals and beverage chief Nestlé, addressing the constraints of legacy methods was important to attaining these objectives. By overhauling its community infrastructure with Cisco SD-WAN, Nestlé unlocked improved resiliency, agility, operational effectivity, and centralized management throughout 1700 places of work, factories, and warehouses in 185 nations.
A latest Cisco webinar that includes particular visitor speaker Giovanni di Marzio, Senior Resolution Architect, WAN – Connectivity, ITP C&V for Nestlé, explored the challenges Nestlé confronted, the Cisco SD-WAN answer it adopted, and the transformative outcomes that enabled the corporate to future-proof its community and improve its total operational efficiency.
Click on right here to look at the on-demand webinar that includes Nestlé.
Navigating legacy community roadblocks
Nestlé’s IT staff is tasked with managing an enormous and complicated international community that spans department places of work, manufacturing services, information facilities, and cloud environments. Nonetheless, a number of key obstacles have hindered their potential to scale, optimize efficiency, and ship a seamless digital expertise, together with:
- Excessive prices of MPLS hyperlinks
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) hyperlinks have been integral to Nestlé’s legacy community infrastructure. Nonetheless, they got here with vital operational prices that made scalability tough and trendy community optimization almost inconceivable. - Fragmented and inefficient instruments
The complexity of managing a fragmented community infrastructure with disparate instruments created many inefficiencies. They not solely lowered operational agility but in addition sophisticated troubleshooting and day-to-day community administration. - Restricted visibility into community efficiency
A scarcity of visibility into a number of cloud and web suppliers made it difficult to troubleshoot points and guarantee optimum efficiency for cloud functions. - Safety and compliance challenges
In sure areas, safety and compliance necessities added one other layer of complexity. Coverage-based routing and centralized compliance controls have been essential to deal with these challenges successfully.
Confronted with these hurdles, Nestlé acknowledged {that a} trendy strategy was important to enhance operational effectivity, cut back prices, and meet the wants of a digitally pushed enterprise.
The answer: An progressive suite of networking applied sciences from Cisco
Nestlé adopted Cisco SD-WAN paired with Cisco ThousandEyes and Cisco 8000 Collection Safe Routers that collectively are designed to reinforce connectivity, digital expertise, safety, and automation. This strategic transfer enabled the corporate to handle its international community with higher effectivity and resilience.
The applied sciences that reworked Nestlé’s community embrace:
- Cisco SD-WAN
Cisco SD-WAN supplies an economical and simplified answer that contains a multi-region cloth (MRF) and a software-defined strategy to managing WAN visitors. With this expertise, Nestlé gained efficiency optimization, resilience, and effectivity throughout its WAN. - Cisco ThousandEyes
Cisco ThousandEyes affords a holistic view of digital experiences throughout Nestlé’s complete service supply chain. This supplies Nestlé with real-time visibility into web paths and the efficiency of cloud and information middle connections, enabling sooner troubleshooting and optimization. - Cisco 8000 Collection Safe Routers
Filled with next-generation safety capabilities, Cisco 8000 Collection Safe Routers characteristic AI-powered automation, post-quantum cryptography, and seamless cloud administration. These routers have helped future-proof Nestlé’s WAN, guaranteeing it will possibly adapt to evolving safety and connectivity wants.
Remodeling and unifying community operations
The adoption of Cisco SD-WAN with Cisco ThousandEyes has yielded outstanding outcomes for Nestlé, driving vital enhancements in each community efficiency and manageability.
Key outcomes for Nestlé embrace:
- Centralized and simplified management
With Cisco SD-WAN, Nestlé IT gained the flexibility to handle department places of work, information facilities, and cloud environments by a single dashboard. This eliminates the necessity for a number of level instruments and has lowered the complexity of community administration. - Enhanced price efficiencies
By changing costly MPLS hyperlinks with a centrally managed SD-WAN and network-as-a-service mannequin, Nestlé considerably lowered leased line and operational prices. This shift to a less expensive infrastructure helps scalability and long-term financial savings. - Finish-to-end community visibility
Cisco ThousandEyes empowers Nestlé with real-time views into web paths and community efficiency. This permits the IT staff to proactively tackle points, optimize cloud app efficiency, and guarantee a seamless digital expertise. - Excessive availability and efficiency enhancements
Automated failover and redundancy mechanisms have improved community reliability, guaranteeing 99.97% availability. Moreover, Nestlé now enjoys a decrease incidence of latency, lowered disruptions, and total enhanced efficiency throughout its international community.
A unified imaginative and prescient for the longer term
Nestlé’s transformation journey highlights how trendy, transformative community applied sciences drive agility, effectivity, and resilience. By adopting Cisco SD-WAN, Cisco ThousandEyes, and safe routers, the corporate has not solely addressed its quick challenges but in addition positioned itself for future success in a related world.
When describing the influence of the corporate’s community transformation, di Marzio stated,
“Cisco SD-WAN supplies web connectivity with none limitations. And as an alternative of each log for 2 thousand routers, we have now a single dashboard to handle the community and a centralized platform for orchestrating configurations throughout all Nestlé websites.”
This centralized strategy has empowered Nestlé to streamline its operations, optimize prices, and ship a seamless digital expertise to its international workforce and prospects.
A blueprint for contemporary enterprises
Nestlé’s community transformation serves as a blueprint for different enterprises grappling with the constraints of legacy methods. The corporate’s resolution to embrace Cisco SD-WAN demonstrates how trendy applied sciences can simplify community administration, cut back prices, and improve efficiency—all whereas guaranteeing safety and compliance.
For organizations seeking to future-proof their community infrastructure, Nestlé’s journey underscores the significance of embracing innovation and partnering with trusted expertise suppliers like Cisco. By doing so, companies can unlock the complete potential of their community and thrive in an more and more digital and interconnected world.
Finally, Nestlé’s story is about extra than simply expertise—it’s about aligning IT technique with enterprise objectives to realize operational excellence. Nestlé’s success is a testomony to the facility of innovation and a forward-looking imaginative and prescient for operational excellence.
Share: