The noticeable rise within the reputation of hydroponic kits comes when each appropriate land and climate circumstances are more and more wanted for propagation functions.
As a gardening fanatic, you is perhaps asking your self, “how do I get entangled in hydroponic rising?”
Many novice growers could not have the time and/or endurance to supply the required elements to ascertain an appropriate propagation system.
That’s the place full hydroponic kits come into play.
This text will establish and talk about hydroponic kits as a method for you budding lovers on the market to enter into the world of hydroponic-based rising.
This can help you in buying the suitable develop equipment to your new enterprise into the world of hydroponics.
Climatebiz specialists design, analysis, fact-check & edit all work meticulously.
Affiliate Disclaimer
Climatebiz is reader-supported. We could earn an affiliate fee while you purchase by hyperlinks on our web site.
7 Funds-Pleasant Hydroponic Kits
1. Homend Indoor Hydroponic Develop Equipment

Regardless of being the most cost effective of the lot, this hydroponic equipment means that you can develop as much as 11 crops directly.
It’s versatile in that you should utilize it as a part of each indoor and out of doors develop setups in a wide range of environments, and it takes up little or no area.
The equipment is straightforward to arrange making it very handy for first-time growers, and it comes with an in depth set of directions.
Lastly, it’s made out of food-grade PVC-U supplies, making it excellent for meals cultivation.
2. HighFree Hydroponic System Rising Equipment

This hydroponic equipment by HighFree comes with nearly the whole lot that it’s essential to leap right into a first-time develop. All it’s essential to add are your personal vitamins and seeds/crops, and also you’re good to go.
Suited to indoor vegetable growers, it’s excellent for anybody in search of a setup that requires minimal area — you may even place it in an easy-to-reach spot if wanted whereas doing the cooking.
The equipment gives area for 11 plant websites and is self-watering.
3. Hydrofarm Root Spa Deep Water Tradition Bucket System
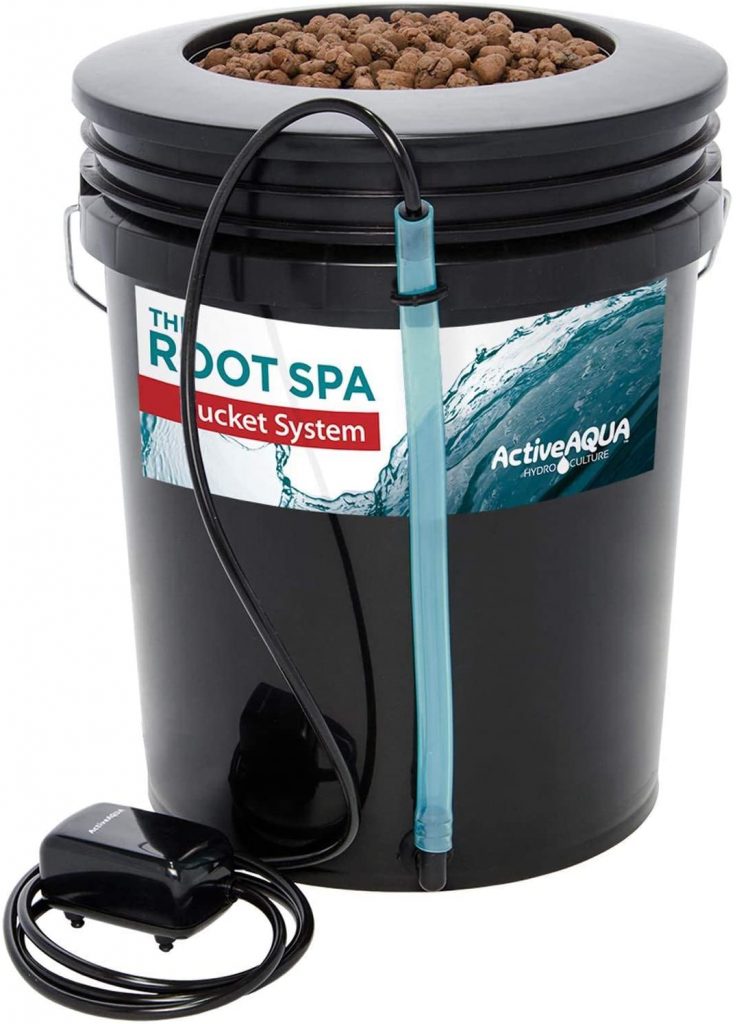

The Root Spa by HydroFarm is a superb instance of a DWC system.
It’s comprised of a 5-gallon bucket system that’s easy, but efficient in its skill to develop bigger crops with ease.
This water-tight bucket system comes with a small single-outlet air pump that enables for oxygenation of the nutrient answer with out the necessity to use air stones.
Its forgiving, cheap and easy-to-use nature makes it an ideal hydroponic equipment for rookies. When you understand how a lot you get pleasure from it you may improve to the 4 or 8-bucket system — each of which include bigger outlet air pumps.
4. iDOO Hydroponic Rising System
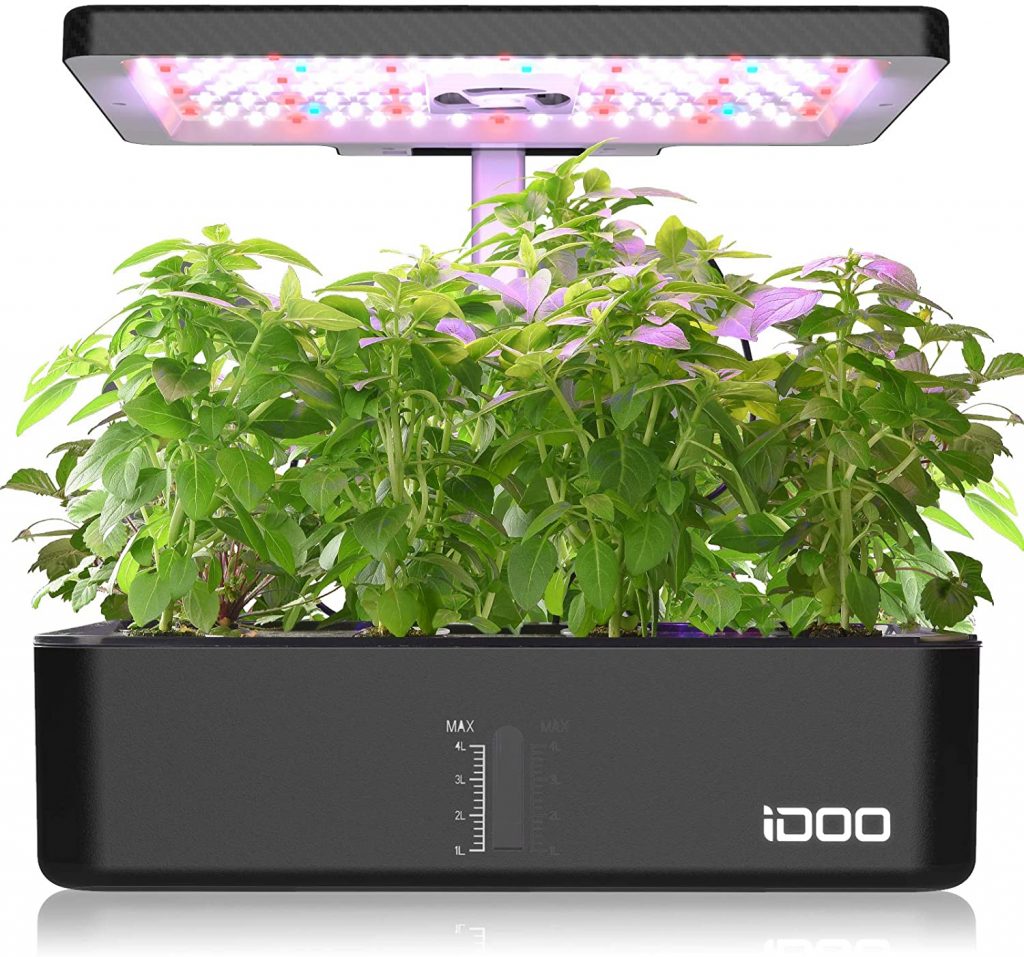

IDOO has actually outdone themselves with this chic, best-selling hydroponic starter equipment.
The high-performance 23-Watt LED lights make this 12-pod indoor system a winner, irrespective of the climate.
The system comes with 2 “sensible develop modes” for vegatables and fruits.
That, mixed with the height-adjustable LED fixture makes for a product that’s extremely versatile.
The perfect a part of all of it — it’s suited to growers of all ability ranges.
5. Vegebox Hydroponics Rising System
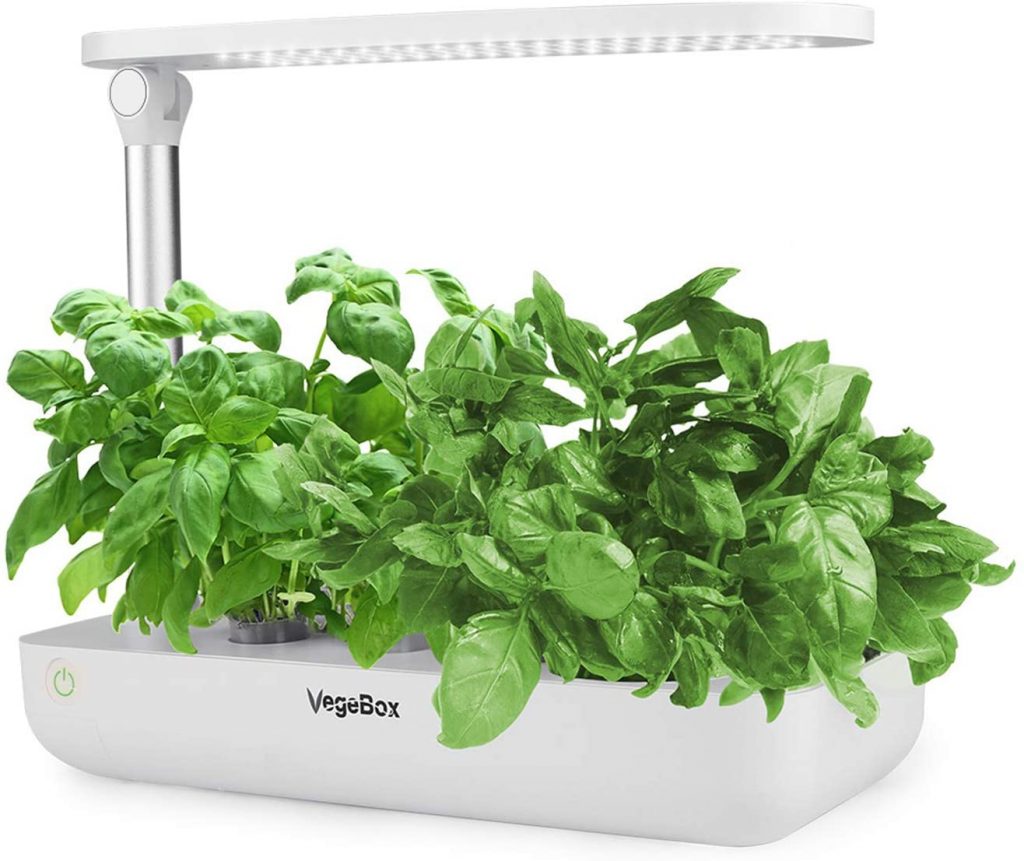

An aesthetically pleasing addition to our record comes within the type of the VegeBox Hydroponics Rising System.
This develop equipment comes with a 1.2 L water tank, 9 planting seed pods, and even comprises 2 bottles of nutrient answer.
Moreover, this hydroponic equipment comes with an adjustable, eco-friendly, full-spectrum set of LED develop lights managed by a Sensible LED Management System.
Greatest suited to something from herbs to tomatoes, strawberries, and lettuce.
6. Sidasu Hydroponic Develop Equipment
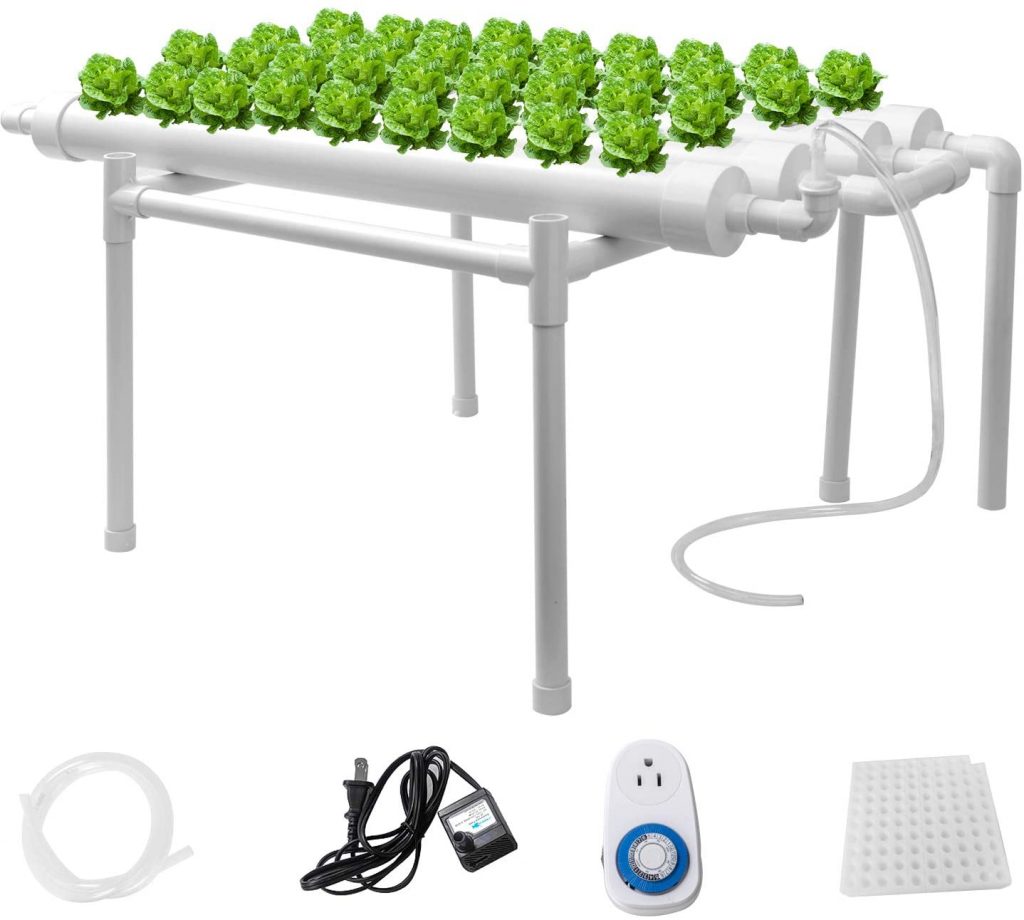

This single-layer system by Sidasu comes with 36 websites spaced out over 4 pipes — essentially the most rising websites on the record to this point.
If that also doesn’t fulfill you, you may go for his or her 3 layer/12 pipe system as a substitute.
This easy to assemble hydroponic equipment makes use of a timed circulation system and is manufactured out of food-grade PVC-U materials.
It is extremely user-friendly and requires no prior rising expertise.
7. Again To The Roots Water Backyard

Deciding between your fish interest and entering into hydroponics? No want.
Our last and most unusual hydroponic equipment possibility comes within the type of a self-cleaning fish tank that may really develop meals.
From microgreens to houseplants, this technique can do all of it, and at an reasonably priced value.
It features by using fish waste as fertilizer for the crops and in flip, the crops assist to maintain the water clear.
Completely the whole lot is included, from natural microgreen seeds to fish meals – simply not the fish.
As an added bonus it comes with a free STEM curriculum on aquaponics and hydroponic methods to encourage youngsters to be taught extra about it.
u003cstrongu003eRelated Studying: u003c/strongu003eu003ca href=u0022https://climatebiz.com/best-vertical-hydroponic-systems/u0022u003e6 Greatest Vertical Hydroponic Techniques On The Market In the present day (Patrons Information)u003c/au003e
What Is Hydroponics?
To grasp what a hydroponic equipment is, we first have to debate hydroponics briefly.
Essentially, hydroponic rising makes use of a nutrient-rich, water-based answer rather than soil as a rising medium for plant propagation.
With this methodology, vitamins are fed instantly from the answer into the roots of the crops.
Moreover, crops can entry ample oxygen, permitting for better high quality produce and noticeably much less time between yields.
There are quite a few different advantages to using hydroponic methods over conventional soil-based cultivation methods. One vital benefit is the power to avoid wasting area.
That is achieved by using customizable nutrient options which are completely calibrated to offer a steady stream of vitamins to the crops.
Because of this, root methods don’t must unfold all through a big space of soil to soak up sufficient vitamins. As such, you’re in a position to place them nearer collectively and save on area.
Associated Studying: DIY Hydroponic Vitamins (How To Make Your Personal System)
What Are Hydroponic Kits?
Now that you’ve a fundamental concept of what hydroponics entails, we are able to transfer on to hydroponic kits.
Listed below are the important thing options of a hydroponic equipment:
Rising Chamber
This element assists in sustaining optimum circumstances for the crops. It does this by serving to to manage elements equivalent to temperature, gentle and defending crops from attainable pest infestations.
Reservoir
An appropriate reservoir is on the coronary heart of each hydroponic equipment. Right here lies the water that holds the nutrient-rich plant answer required for hydroponic grows. Relying on the setup, they will also be used as a further rising chamber.
Rising Media
The substitute for soil, although they don’t present the crops with vitamins independently. As an alternative, they act as a catalyst for nutrient transportation. That is achieved by their porous construction which absorbs and retains each moisture and vitamins. Moreover, they work to assist the crops.
Air Stones/ Air Pumps
Crops which are submerged with out adequate oxygenation can drown in a short time. To keep away from this, hydroponic kits make use of air stones/air pumps. Collectively, these elements present adequate aeration within the answer via tiny oxygen bubbles. This additionally helps to distribute vitamins among the many roots equally.
Internet Pots
These are mesh planters that you should utilize to carry your crops. Their construction facilitates better publicity to each vitamins and oxygen. In addition they permit for a better diploma of drainage.
Lighting
Although not all the time a regular element of hydroponic kits, some dearer kits include develop lights. These lights imitate the solar and assist to hold out photosynthesis. This makes them extraordinarily useful in setups the place pure gentle is tough to come back by.
Associated Studying: 1000 Watt LED Develop Mild (All it’s essential to know)
What Is The Best Hydroponic System To Use?
Chances are you’ll end up misplaced within the a whole bunch of hydroponic kits and methods which are accessible right this moment
These variations fall below 6 foremost varieties of hydroponic methods. We’ll deal with one of the vital appropriate choices for rookies — the Deep Water Tradition (DWC) system.
For those who’re a novice, the title could give the impression that this methodology is complicated. Relaxation assured, it’s a comparatively easy system to grasp.
The DWC system is labeled as such for the next causes:
- Your develop will happen inside a reservoir holding a big quantity of water.
- The quantity of root mass repeatedly submerged in water.
Course of
In a DWC system, roots are suspended over a reservoir stuffed with an oxygenated, nutrient-rich, water-based plant answer. This enables the roots to obtain a gentle uptake of oxygen, vitamins, and water.
Air pumps and air stones provide oxygen. These two elements work in tandem, making certain that the answer is aerated sufficient by dissolving bubbles in order that the crops don’t drown.
Sure, crops can drown. The roots suck up accessible oxygen from the water answer. For those who don’t continuously exchange the oxygen, you may say goodbye to your develop.
FAQs
Can hydroponic methods be used to develop all varieties of crops, or are they extra suited to particular varieties?
Whereas a variety of crops may be grown utilizing hydroponic methods, they’re notably well-suited for leafy greens, herbs, and greens as a result of methods’ skill to effectively ship vitamins on to the crops’ roots.
Nonetheless, with the suitable setup, modifications, and care, many fruiting crops and flowers will also be cultivated hydroponically.
How usually does the nutrient answer in hydroponic methods must be modified?
The frequency of adjusting the nutrient answer in a hydroponic system largely will depend on the system sort, plant sorts, and progress phases.
Sometimes, many growers change the nutrient answer each 1 to 2 weeks to make sure optimum nutrient availability and to keep up acceptable nutrient concentrations and pH ranges.
What’s the preliminary price of establishing a fundamental hydroponic system in comparison with a soil-based backyard?
Preliminary setup prices for a hydroponic system may be greater than a conventional soil-based backyard as a result of want for specialised gear like reservoirs, air pumps, and develop lights.
Nonetheless, hydroponic methods usually provide greater yields, quicker progress, and decrease water and nutrient consumption in the long term, probably offsetting the preliminary funding over time.
How a lot time does it take every day to keep up a hydroponic system?
Upkeep time for hydroponic methods can range relying on the complexity of the system and the varieties of crops being grown.
On common, a small to medium-sized hydroponic system could require round half-hour to an hour per day for duties equivalent to checking and adjusting nutrient ranges, monitoring pH, and observing plant well being and progress.
Are hydroponic greens and fruits as nutritious as these grown in soil?
Sure, vegatables and fruits grown hydroponically may be as nutritious, if no more so, as these grown in soil.
In hydroponic methods, nutrient supply to crops is exactly managed, permitting for optimum nutrient uptake and probably main to provide with greater dietary content material. Nonetheless, the dietary worth additionally will depend on the kind of vitamins offered within the water answer.
Is there a danger of contamination or illness in hydroponic methods, and the way can or not it’s mitigated?
Sure, there may be dangers of contamination or illness in hydroponic methods, primarily as a result of closed surroundings and shared nutrient answer. Illnesses can unfold quickly if not promptly addressed.
To mitigate these dangers, it’s essential to keep up a clear rising surroundings, usually monitor plant well being, promptly take away contaminated crops, and make sure the nutrient answer is well-balanced and freed from pathogens.
Frequently altering the nutrient answer and cleansing the system may assist in stopping the unfold of illnesses.
Remaining Ideas
It’s time so that you can get on the market and seize that first develop equipment of yours.
It might appear a bit overwhelming at first however there’s an abundance of unbelievable hydroponic equipment choices on the market!
So take step one in the direction of being a part of the hydro group, and if you have already got, be happy to element your experiences within the remark part under!