Flutter has been some of the in style platforms for cross-platform cellular app improvement for a number of years now — with assist from Google, a quickly rising group in addition to a formidable set of instruments.
Nevertheless, 2025 brings new challenges and alternatives: elevated competitors, technological modifications, and shifting enterprise priorities are forcing builders and corporations to query whether or not Flutter continues to be the platform of selection for brand spanking new initiatives.
On this article, we’ll break down the important thing benefits and downsides of Flutter in 2025, assessment the newest updates to the ecosystem, and inform you when Flutter is the only option and when it is best to take a look at options.
Flutter Expertise Overview
Flutter is an open-source cross-platform UI SDK developed by Google. It permits you to create natively compiled functions for cellular, internet, desktop, and even embedded programs utilizing a single codebase. Flutter allows builders to get merchandise to market quicker by offering sturdy visible and logical consistency throughout any platform.
Based on Statista, Flutter stays the preferred cross-platform framework, with about 46% of app builders utilizing it in 2023.
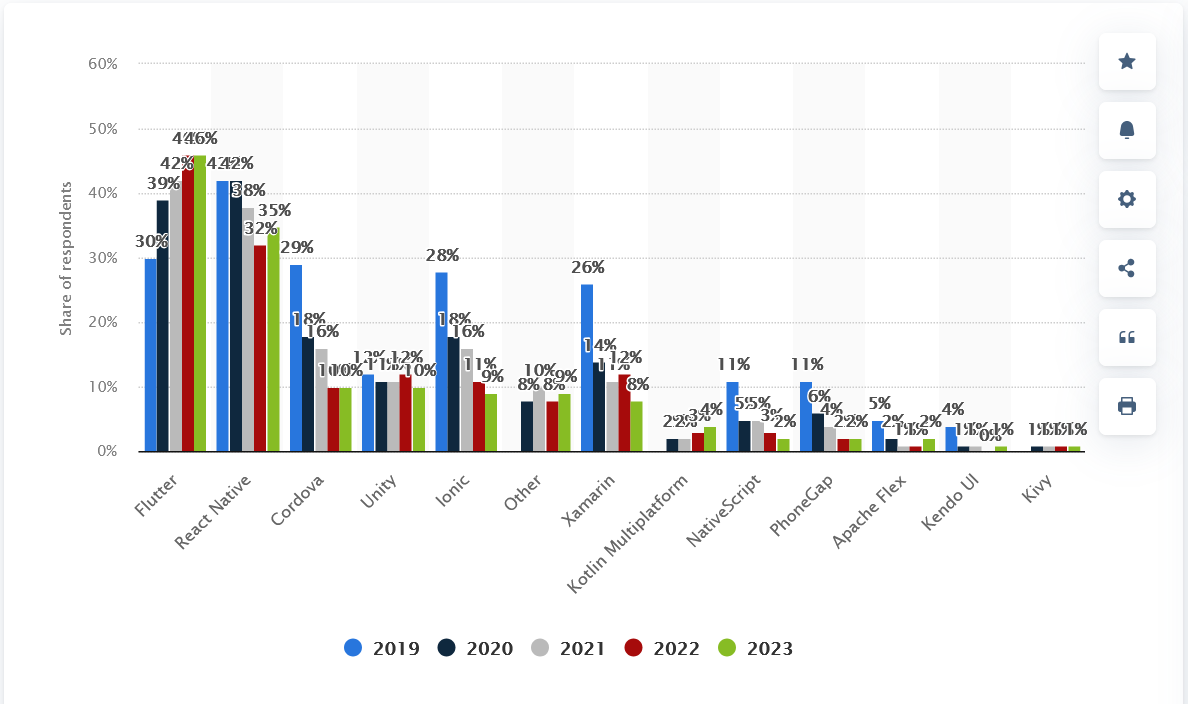
Cross-platform cellular frameworks utilized in software program improvement course of worldwide from 2019 to 2023, Statista
Flutter Expertise: What Makes It Value Contemplating in 2025
Flutter relies on the Dart programming language — additionally developed by Google. Dart helps each JIT compilation for fast prototyping and AOT compilation for prime efficiency in manufacturing.
With the discharge of Dart 3 and subsequent updates, the platform has gained obligatory assist for sound null security, pattern-matching, and the flexibility to compile to WebAssembly, making it much more aggressive.
An essential characteristic of Flutter is its personal engine, written in C++, which makes use of a graphical renderer (previously Skia, now Impeller) and doesn’t depend on normal native UI parts. This enables Flutter to create a totally native UI with out the necessity to “bridge” between platforms — in contrast to, for instance, React Native.
What’s New in 2024-2025
Flutter has matured significantly over the previous 12 months. The primary replace is the change to Impeller, a brand new graphics engine that’s now utilized by default on iOS and Android (beginning with API 29).
It changed Skia and eventually solved one of many main developer ache factors: efficiency sags and lags when rendering advanced animations. With Impeller, the interface grew to become noticeably smoother and extra responsive — particularly on much less highly effective units.
An equally essential change is the total assist for WebAssembly in Flutter Internet. It is a massive step ahead: functions are actually quicker to load and extra steady even within the browser, particularly in poor web circumstances. For customers, it’s simply “every little thing works quicker”, however for builders, there’s much less of a trade-off between usability and pace.
Plus, in 2025, Flutter is noticeably nearer to the platform. Because of Direct Native Interop and FFI enhancements, it’s simpler to make use of native APIs with out writing bridges or wrappers.
That’s, when you immediately want entry to some native Android or iOS characteristic, it’s now simpler and quicker to implement it. On prime of that — up to date DevTools, improved accessibility assist, and steady sizzling reload proper within the browser, which makes improvement much more handy.
Flutter feels an increasing number of assured as a full-fledged platform — and it seems to be prefer it’s not going to cease.
Key Execs of Apps Constructed With Flutter in 2025
Flutter stays some of the engaging instruments for cross-platform improvement in 2025. Beneath are the important thing advantages of Flutter that make it a related selection for builders and companies.
Cross-platform effectivity
One of many major benefits of Flutter is its skill to create iOS, Android, Internet, Home windows, macOS, and Linux functions from a single code. This considerably reduces improvement, assist, and testing prices.
In 2025, Google continues to actively develop assist for Internet and Desktop — efficiency, stability, and compatibility have visibly improved. Flutter Internet now hundreds quicker (particularly with WebAssembly), and desktop apps look and behave as natively as potential.
Excessive efficiency
With the introduction of Impeller, the brand new rendering engine that changed Skia, the efficiency of Flutter functions has improved dramatically. Impeller supplies extra predictable rendering, eliminates delays when shaders are first rendered, and makes animations smoother.
It really works immediately with Steel on iOS and Vulkan on Android, delivering excessive body charges even on weak units.
Quicker improvement with Scorching Reload
Scorching Reload stays some of the handy instruments for fast improvement and testing of the interface. Code modifications may be seen immediately, with out fully rebuilding the appliance, which enormously accelerates the prototyping and debugging course of. Even in 2025, regardless of the provision of options, Flutter stays the chief by way of pace and ease of improvement.
Massive and rising ecosystem
Flutter’s effectiveness is enhanced by a well-developed and continuously increasing ecosystem. Tens of 1000’s of packages can be found on the pub.dev platform, prepared to make use of — from UI parts to integrations with Firebase, Stripe, GraphQL, and different in style providers. Google actively helps the event of this ecosystem by frequently updating official packages and bettering the infrastructure.
Constant UI and enterprise logic throughout platforms
One of the notable benefits of Flutter over different frameworks (e.g. React Native) is the whole absence of UI bridges between code and platform.
Flutter manages UI rendering itself, which permits for full consistency of visible presentation and enterprise logic throughout all units. This reduces the probability of bugs and simplifies testing, particularly when working with customized interfaces.

Need to think about an alternative choice to cellular improvement? Be taught extra concerning the capabilities and limitations of Progressive Internet Functions (PWAs). For those who resolve to implement PWAs, contact us, and SCAND consultants will make it easier to implement an answer tailor-made to your wants.
Cons of Flutter App Growth in 2025
Regardless of its many deserves, Flutter is just not a one-size-fits-all resolution, and in 2025 it nonetheless has limitations to contemplate when selecting a know-how.
Massive cross-platform cellular app measurement
One of the mentioned drawbacks of Flutter is the scale of the ultimate software. Even with intensive optimization efforts, the minimal APK or IPA file measurement continues to be bigger than native apps. This is usually a essential issue for rising markets and units with restricted storage, particularly if obtain pace and minimal measurement are essential.
Restricted assist for platform-specific options
Though Flutter permits entry to native APIs via platform channels, this nonetheless requires extra effort and information of the related native applied sciences (Kotlin, Swift, Goal-C). For some particular options — like Bluetooth LE, AR, biometrics, or native notifications — you both have to make use of third-party packages or write a customized implementation, which reduces the effectivity of the “single code”.
Dart is just not mainstream
Whereas Dart continues to evolve and achieve new options, it stays a distinct segment language. This limits the variety of out there builders in the marketplace and makes staff choice troublesome. Not like JavaScript, Python, and even Kotlin, information of Dart is the exception moderately than the rule, particularly amongst junior builders.
Internet and desktop maturity
Flutter is actively growing Internet and Desktop assist, however in 2025 they’re nonetheless inferior to native options by way of stability and efficiency. In follow, bugs, browser incompatibilities, enter and rendering delays can happen. That is particularly essential for advanced interfaces and interactive functions. Flutter is just not at all times appropriate for production-level Internet functions.
Fragmentation threat
Because the ecosystem grows and turns into extra advanced, so does the danger of fragmentation. Some in style packages, particularly these created by the group, turn out to be out of date or unsupported. As well as, updates to the Flutter SDK itself can generally break backward compatibility, requiring code rework or options. This will decelerate improvement and trigger technical debt when scaling a venture.
When to Select Flutter for Your App in 2025
Regardless of its versatility and highly effective capabilities, Flutter is just not appropriate for each venture. To make an knowledgeable choice, it’s essential to grasp wherein eventualities it brings out its strengths and wherein eventualities it could restrict performance or effectivity. Beneath is a fast information that will help you decide whether or not Flutter is price utilizing in your particular case:
| Use Flutter when… |
Keep away from Flutter when… |
| Want cross-platform with unified UI and enterprise logic |
The minimal APK/IPA measurement is essential |
| Must rapidly launch an MVP or take a look at an thought (Proof of Idea) |
The app contains heavy graphics, AR/VR, or superior native results |
| Requires fast UI updates and fast iteration |
Want to maximise native efficiency, particularly on iOS |
| The applying doesn’t require advanced native integration |
Particular platform APIs or chips are actively used |
| The staff already has expertise with the Dart/ Flutter framework |
No assets to be taught Dart or assist unstable packages |
Flutter execs and cons
In Element: When Flutter Is Your Alternative
Flutter performs significantly nicely in initiatives the place quick time-to-market, multi-platform protection with minimal effort, and versatile visuals are essential. It’s appropriate for firms in search of a solution to pace up improvement with out sacrificing high quality, in addition to these working with restricted budgets or assets.
You construct a product the place improvement time is essential
Whether or not it’s essential to rapidly launch an software, take a look at an thought available in the market, or display an interface to buyers, Flutter is the proper resolution. With a brief improvement cycle, ready-made widgets, and sizzling reload assist, you possibly can understand a working prototype in a short while with out shedding high quality.
This strategy is very helpful for startups that have to persuade buyers or rapidly take a look at a speculation on actual customers.
You’re employed on a good funds
With Flutter, you possibly can have one staff for all platforms — as an alternative of getting separate groups for Internet, Android, and iOS. This severely saves assets not solely within the improvement section but additionally in a while for assist and updates. For smaller initiatives, it may be the essential distinction between launching a product or delaying it indefinitely. And with a big group and lots of ready-made options within the ecosystem, you spend much less time on routine — many typical duties have already been solved earlier than you.
Your staff already has expertise with Flutter
In case you have builders who’re accustomed to Dart and Flutter or have already got some expertise, utilizing this know-how turns into a pure selection. It permits you to keep technical continuity and pace up the launch. For those who don’t have expertise but, you’ll need coaching, however the entry threshold for these with OOP expertise is comparatively low.
You don’t have necessities for deep native integration
Flutter works finest in eventualities the place you possibly can depend on a cross-platform layer and never get into the refined options of Android or iOS. Easy UI interfaces, types, information feeds, and catalogs are ultimate use instances. If it’s essential to work together with the system at a low stage (for instance, with sensors or a streaming digicam), it is best to suppose twice.
UI is the important thing a part of a product
When UI look and responsiveness aren’t only a nice-to-have perk however a business-critical a part of the interface, Flutter shines via. Functions which might be tied to participating UX, whether or not in training, media, or e-commerce, profit from versatile UI customization, animations, and fast adaptation to totally different platforms and resolutions.
You intend to scale the product
Flutter integrates seamlessly with CI/CD, DevOps, and analytics instruments. That is particularly essential when you’re not simply MVPs, but additionally at software improvement in the long run. Steady updates from Google and intensive assist for cloud options (e.g. Firebase) make it a stable basis.
Want to attenuate technical debt
The Flutter codebase is usually simpler to take care of than a set of native options. This reduces the dangers of accumulating technical debt because the product grows and reduces dependence on specialised consultants in every particular person platform.
The place Flutter Might Not Match
Nevertheless, Flutter is just not a magic resolution. There are eventualities the place it’s higher to favor native improvement or different frameworks.
Functions with strict measurement limits
Flutter apps, particularly with plugins connected, can have a better preliminary weight in comparison with their native counterparts. If each megabyte counts — for instance, in international locations with restricted cellular web — that is price contemplating.
Complicated native integration
In case your venture requires deep work with Bluetooth, digicam, AR/VR, real-time geolocation, or advanced native graphics, Flutter might not be the only option. Whereas FFI and Interop are actively growing, they’re nonetheless inferior to native capabilities by way of usability and adaptability.
Maximize efficiency and response
GPU-intensive initiatives that require minimal latency and most management over system assets are higher served in a local setting. This is applicable, for instance, to video games, navigation programs, video editors, or functions with heavy UI.
Ecosystem limitations and dependency on third-party packages
Though there are millions of libraries in pub.dev, not all of them are equally dependable and supported. Typically there isn’t any steady bundle for essential duties, and writing your individual resolution from scratch may be too time-consuming. Additionally, Flutter SDK updates can immediately break current dependencies.
Lack of expertise within the improvement firm
In case your staff has no expertise with Dart or Flutter, implementation can take time to be taught and rise up to hurry with new approaches. For initiatives with tight deadlines, this is usually a downside.
Requires most nativeness below one platform
In case your app is designed solely for Android or iOS and must combine deeply into the platform’s ecosystem, it’s simpler and extra logical to decide on native improvement. Flutter provides you extra versatility right here, however not at all times most depth.

Hiring a Flutter Growth Staff: What to Look For
Flutter is usually a nice technical selection, however the high quality of the top consequence at all times relies on the staff. A top quality implementation is just not solely about having the fitting stack but additionally expertise, processes, assist strategy, and understanding of the challenges. Right here’s what to look out for when you’re in search of a contractor or constructing an inside Flutter staff.
Expertise and Portfolio: Not Simply Cell App Growth
The very first thing to contemplate is that not each cellular developer robotically works nicely with Flutter. It is a separate ecosystem that requires an understanding of the specifics of the framework, the Dart language, architectural approaches (e.g., BLoC or Supplier), and the peculiarities of working with graphics and animations. Due to this fact, you will need to specify not normal expertise in cellular app improvement, however particularly expertise with Flutter initiatives.
A very good signal is the presence of profitable instances with actual customers, particularly in the event that they suit your area of interest — be it e-commerce, fintech, media, or SaaS. Take note of initiatives with multi-platform options (e.g. Android + iOS + Internet), customized animations, or integration with native APIs. If the case solved a enterprise downside just like yours, it’s a plus within the staff’s favor.
Who Ought to Be On the Staff: Not Solely Builders
A profitable Flutter venture requires extra than simply builders. You will need to understand that the minimal staff composition contains the next:
- Flutter developer (or a number of if the venture is giant);
- UI/UX designer who understands the specifics of cross-platform format and creates Android and iOS-specific interfaces;
- QA engineer who exams the app on all goal platforms (ideally with actual units);
- The venture supervisor or staff chief who organizes the method, works with deadlines, and most significantly — can translate your corporation aims into technical necessities.
Extra critical options might require a DevOps specialist (e.g. for CI/CD), an analyst, or a product supervisor. However even with a small funds, you shouldn’t skimp on fundamental roles: the absence of a designer or tester typically results in rework and misplaced time for revisions.

Code High quality and Upkeep
Since Flutter continues to be comparatively younger, you might encounter contractors in the marketplace who write that it’s untrustworthy. Due to this fact, you will need to consider not solely the exterior consequence but additionally how clear and structured the code is. Examine whether or not the staff follows architectural patterns, and makes use of unit exams, code protection, CI/CD, and model management.
It’s a good follow to ask for a code assessment or technical description of an already accomplished venture. Even if you’re not a technical skilled, your CTO or exterior advisor will likely be ready that will help you assess the standard of the implementation.
The post-release upkeep of the venture is just not least essential. Discover out if there are SLAs, how typically updates are launched, how the staff reacts to bugs, and ideas for enchancment. A reliable Flutter staff affords not simply “handing over the appliance”, however a long-term partnership: from assist and analytics to scaling performance.
Flutter for App Growth: Why Do You Want Flutter Experience?
Many firms place themselves as generalist cellular groups, however Flutter requires a particular strategy. Shifting from native considering to Flutter improvement entails understanding rendering, state administration, format nuances, and adapting to totally different platforms.
A staff with out correct experience can “drag and drop” approaches from native improvement, leading to inefficient architectures, duplicate code, and bugs in cross-platform logic.
Due to this fact, it will be significant that the chosen developer isn’t just accustomed to Flutter however actively makes use of it of their work. This may be verified by open supply exercise (GitHub, packages in pub.dev), common releases of functions on Flutter, and inside practices on structure and testing.
Having sturdy inside experience and expertise in fixing enterprise issues on Flutter is a assure that the venture is not going to simply be “written” however will likely be reliably applied and scalable sooner or later.
SCAND has been actively growing Flutter improvement for a number of years, implementing initiatives for purchasers from totally different industries. Our staff is ready to launch cross-platform merchandise rapidly and effectively, and assist and scale them in the long run, counting on collected experience and well-established processes.
Apps Constructed Utilizing Flutter: Actual-World Cross-platform App Use Circumstances
Flutter is actively utilized by each startups and enormous multinational companies. These are only a few examples of profitable apps with Flutter that show its scalability and adaptability. Among the many most well-known examples is Google Advertisements, an official cellular app for managing promoting campaigns constructed completely on Flutter.
Alibaba makes use of Flutter in a number of e-commerce options, which has helped speed up time-to-market for brand spanking new options and cut back improvement prices.
BMW makes use of Flutter to create interfaces in its infotainment programs, emphasizing its reliability even in automotive functions.
Curiosity in Flutter is rising in key industries as nicely:
- Within the banking sector, firms equivalent to Nubank and ING use Flutter due to its skill to rapidly launch sturdy multi-platform interfaces with excessive ranges of safety.
- In e-commerce, it’s chosen for its fast improvement and UX consistency throughout cellular platforms.
- In media and streaming, Flutter helps you understand easy UIs and sophisticated animations with minimal effort — for instance, in Google’s Stadia and Reflectly apps.
These instances present how Flutter supplies the pliability to serve very totally different industries with constant efficiency and UI high quality.
Cross-platform App Growth: Get Began With Flutter
In 2025, Flutter continues to be the most effective options for cross-platform app improvement. Flutter affords excessive efficiency, a quick improvement cycle, and a constant consumer interface throughout all Flutter cellular and desktop platforms.
With sturdy assist from Google, the fast improvement of applied sciences equivalent to Impeller and WebAssembly, and a powerful Flutter group it stays sturdy even within the face of rising competitors.
However, the selection of this know-how must be a aware one. For those who’re aiming for quick supply, constant UI throughout platforms, and value effectivity, Flutter is sweet for app improvement in 2025 and past. But when minimal software measurement, entry to deep native performance, or peak efficiency are essential, it is best to think about options.
The choice finally relies on the venture aims, technical necessities, and strategic objectives of your organization.
FAQ
Is Flutter appropriate for enterprise improvement and the way can or not it’s used to enhance productiveness?
Sure, in 2025, Flutter is a mature resolution for cross-platform improvement that’s nicely fitted to the enterprise stage. We at SCAND actively use Flutter to construct scalable options with excessive app efficiency. Fashionable Flutter widgets help you create advanced interfaces, and the Impeller engine makes animations easy even in enterprise functions. If you wish to make Flutter a part of your digital technique — we may help you get it proper.
What can I do with Flutter and why think about it for internet improvement?
Flutter is a contemporary software program improvement package that can be utilized to create not solely cellular but additionally internet apps. With WebAssembly assist and the rising variety of Flutter widgets, it’s now simpler and quicker to run visually wealthy interfaces immediately within the browser. At SCAND, we suggest contemplating Flutter for these in search of a fast solution to create a cross-platform resolution with out sacrificing UX.
Is Flutter nonetheless related in 2025?
Sure, Flutter stays extremely related in 2025. It continues to be some of the in style cross-platform improvement frameworks, with sturdy group assist and energetic improvement by Google. New options just like the Impeller rendering engine and WebAssembly assist preserve it aggressive.
Will Flutter change native improvement?
Not completely. Whereas Flutter covers many use instances successfully, native improvement continues to be most well-liked for initiatives that require most efficiency, tight integration with platform-specific APIs, or very small app sizes. Flutter is finest seen as a complementary possibility moderately than a full substitute.
What are the principle Flutter options in 2025?
The primary options to Flutter in 2025 embrace React Native, Kotlin Multiplatform, and .NET MAUI. Every has its strengths: React Native advantages from a big JavaScript ecosystem, Kotlin Multiplatform affords glorious native integration, and MAUI fits groups already working with Microsoft applied sciences.
Is Dart nonetheless essential to be taught Flutter?
Sure, Dart is the core language used within the Flutter improvement course of. Whereas it’s not as mainstream as JavaScript or Kotlin, Dart is comparatively simple to be taught, particularly for builders accustomed to object-oriented languages. Studying Dart is important to unlock the total potential of Flutter.