Multi-factor authentication (MFA), lengthy thought-about a cornerstone of cybersecurity protection, is going through a formidable new risk: “Cross-the-Cookie” assaults.
Current findings reveal from Lengthy Wall reveals that risk actors exploit browser session cookies to bypass MFA totally, granting full entry to company accounts with out requiring passwords or authentication tokens.
This method poses a big danger to organizations reliant on MFA for Workplace 365, Azure, and different cloud platforms.
The Phantasm of Safety
MFA’s effectiveness hinges on verifying consumer identification by a number of credentials. Nevertheless, attackers now goal session cookies—small knowledge fragments saved by browsers to keep up energetic logins.
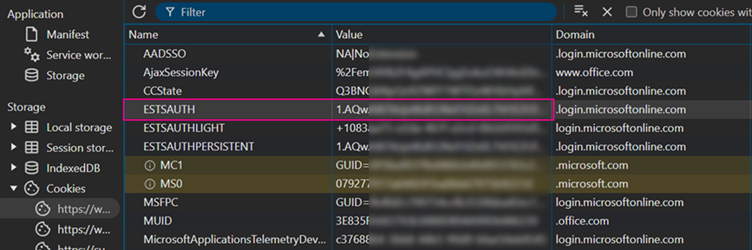
In a typical assault, cybercriminals steal cookies like Microsoft’s ESTSAUTH, which validates classes throughout Workplace 365 providers.

As soon as extracted, these cookies allow adversaries to impersonate customers indefinitely, even from unrecognized gadgets or areas.


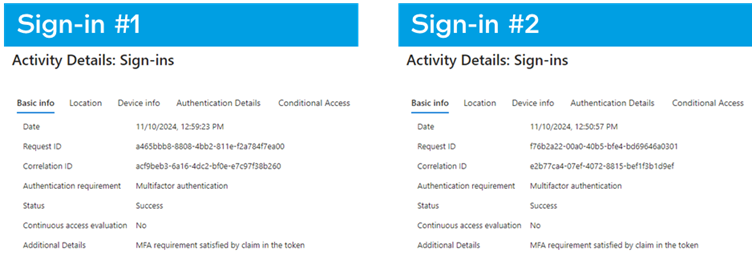
A stark instance entails two Workplace 365 sign-ins logged in Azure:
- Reputable Entry: A consumer logs in by way of Chrome on Home windows 11, finishing MFA by way of the Microsoft Authenticator app.
- Malicious Entry: An attacker makes use of the identical account on Ubuntu/Firefox with no password or MFA immediate—relying solely on a stolen ESTSAUTH cookie.
Azure’s logs present near-identical entries for each occasions, with solely refined variations in browser/OS metadata hinting at foul play.
With out superior detection instruments, these assaults simply evade conventional safety monitoring.
Cookie Hijacking
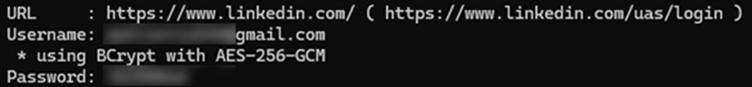
Session hijacking begins when malware like LummaC2, Redline, or Racoon infiltrates a tool. These infostealers—usually disguised as pretend software program updates—scan browsers for cookies and decrypt them utilizing built-in instruments.
For example, LummaC2 exfiltrates ESTSAUTH values, which attackers then implant into their very own browsers by way of developer consoles.
Proof-of-Idea Walkthrough:
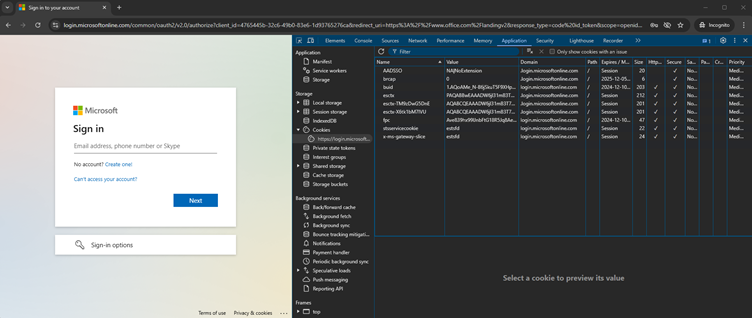
- Cookie Extraction: After compromising a Home windows/Chrome machine, attackers use browser dev instruments to repeat the ESTSAUTH cookie from login.microsoftonline.com.
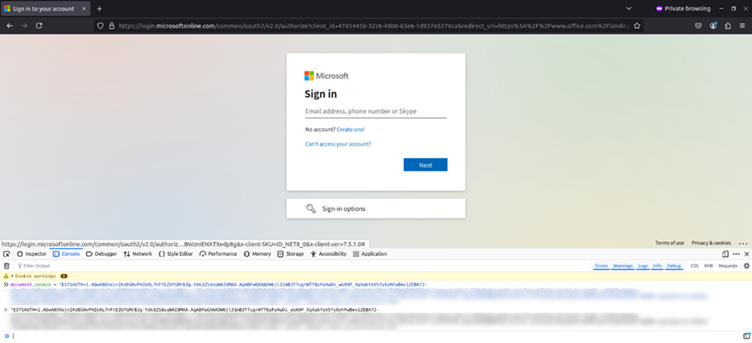
- Session Spoofing: On a clear Ubuntu/Firefox machine, the attacker creates a brand new cookie with the stolen worth. Refreshing the web page grants quick entry to the sufferer’s Workplace 365 account.
This technique bypasses MFA as a result of the cookie validates the session, not the consumer.
Microsoft’s documentation confirms ESTSAUTH cookies persist till express logout or expiration—probably enabling weeks of undetected entry.
The Rise of Cookie-Centric Assaults
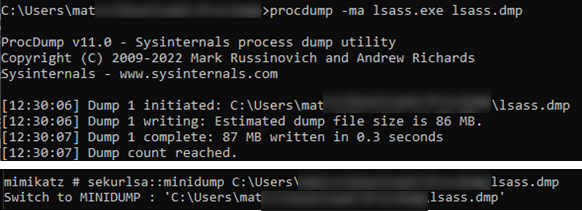
As MFA adoption grows, attackers are shifting from credential theft (e.g., Mimikatz-based LSASS dumping) to cookie harvesting.


Current campaigns noticed by MSSPs present a 300% improve in cookie theft makes an attempt since 2023, focusing on sectors like finance and healthcare.

Why Cookies?
- Persistence: Cookies usually outlive password rotations.
- Stealth: No brute-force makes an attempt or MFA triggers to alert defenders.
- Cross-Platform Usability: Cookies work throughout gadgets and geographies.

Utilizing the definition from Microsoft: (https://be taught.microsoft.com/en-us/entra/identification/authentication/concept-authentication-web-browser-cookies)

Mitigation Methods
To counter this risk, specialists suggest:
- Session Token Monitoring: Deploy UEBA (Person Entity Conduct Analytics) instruments to flag anomalies like sudden OS/browser modifications mid-session.
- Conditional Entry Insurance policies: Prohibit logins to compliant/managed gadgets and implement recurring MFA checks for high-risk actions.
- Cookie Encryption: Use options like Azure AD’s Steady Entry Analysis (CAE) to shorten token lifespans and bind classes to machine fingerprints.
- Infostealer Detection: Block unauthorized credential dumping by way of EDR instruments and limit native admin privileges.
Whereas MFA stays important, the “Cross-the-Cookie” epidemic underscores the necessity for zero-trust architectures.
As Jake Williams, CTO of Rendition Infosec, notes: “Session cookies are the brand new credentials. Defending them requires the identical rigor as passwords—encryption, rotation, and granular entry controls.”.
Organizations should evolve past MFA alone, treating session integrity as a crucial pillar of contemporary cybersecurity.
Gather Risk Intelligence on the Newest Malware and Phishing Assaults with ANY.RUN TI Lookup -> Attempt totally free
