The LangGraph ReAct Perform-Calling Sample presents a strong framework for integrating numerous instruments like serps, calculators, and APIs with an clever language mannequin to create a extra interactive and responsive system. This sample is constructed upon the Reasoning + Appearing (ReAct) method, which permits a language mannequin to not solely purpose via queries but additionally take particular actions, equivalent to calling exterior instruments to retrieve information or carry out computations.
Studying Goal
- Perceive the ReAct Method: Learners will have the ability to clarify the Reasoning + Appearing (ReAct) method and its significance in enhancing the capabilities of language fashions.
- Implement Software Integration: Individuals will acquire the abilities to combine numerous exterior instruments (e.g., APIs, calculators) into language fashions, facilitating dynamic and interactive responses to person queries.
- Develop Graph-Primarily based Workflows: Learners will have the ability to assemble and handle graph-based workflows that successfully route person interactions between reasoning and gear invocation.
- Create Customized Instruments: Individuals will learn to outline and incorporate customized instruments to increase the performance of language fashions, permitting for tailor-made options to particular person wants.
- Consider Consumer Expertise: Learners will assess the influence of the LangGraph ReAct Perform-Calling Sample on person expertise, understanding how real-time information retrieval and clever reasoning improve engagement and satisfaction.
This text was printed as part of the Knowledge Science Blogathon.
What’s ReAct Immediate?
The standard ReAct immediate for the assistant units up the next framework:
- Assistant’s Capabilities: The assistant is launched as a strong, evolving language mannequin that may deal with numerous duties. The important thing half right here is its potential to generate human-like responses, have interaction in significant discussions, and supply insights primarily based on massive volumes of textual content.
- Entry to Instruments: The assistant is given entry to varied instruments equivalent to:
- Wikipedia Search: That is used to fetch information from Wikipedia.
- Net Search: That is for performing common searches on-line.
- Calculator: For performing arithmetic operations.
- Climate API: For retrieving climate information.
- These instruments allow the assistant to increase its capabilities past textual content era to real-time information fetching and mathematical problem-solving.
The ReAct sample makes use of a structured format for interacting with instruments to make sure readability and effectivity. When the assistant determines that it wants to make use of a instrument, it follows this sample:
Thought: Do I want to make use of a instrument? Sure
Motion: [tool name]
Motion Enter: [input to the tool]
Commentary: [result from the tool]
For instance, if the person asks, “What’s the climate in London?”, the assistant’s thought course of may be:
Thought: Do I want to make use of a instrument? Sure
Motion: weather_api
Motion Enter: London
Commentary: 15°C, cloudy
As soon as the instrument gives the consequence, the assistant then responds with a last reply:
Last Reply: The climate in London is 15°C and cloudy.
Implementation of the LangGraph ReAct Perform Calling Sample
Let’s construct on implementing the LangGraph ReAct Perform Calling Sample by integrating the reasoner node and developing a workflow to allow our assistant to work together successfully with the instruments we’ve outlined.
Setting Setup
First, we’ll arrange the setting to make use of the OpenAI mannequin by importing the mandatory libraries and initialising the mannequin with an API key:
import os
from google.colab import userdata
# Setting the OpenAI API key
os.environ['OPENAI_API_KEY'] = userdata.get('OPENAI_API_KEY')from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
#Initializing the language mannequin
llm = ChatOpenAI(mannequin="gpt-4o")Software Definitions
Subsequent, we outline the arithmetic instruments that the assistant can use:
def multiply(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Multiply a and b.
Args:
a: first int
b: second int
"""
return a * b
# This might be a instrument
def add(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Provides a and b.
Args:
a: first int
b: second int
"""
return a + b
def divide(a: int, b: int) -> float:
"""Divide a and b.
Args:
a: first int
b: second int
"""
return a / bAlong with these arithmetic capabilities, we embrace a search instrument that enables the assistant to retrieve info from the online:
# search instruments
from langchain_community.instruments import DuckDuckGoSearchRun
search = DuckDuckGoSearchRun()
# Instance search question to get Brad Pitt's age
search.invoke("How previous is Brad Pitt?")Output:
Brad Pitt. Picture: Amy Sussman/Getty Pictures. Brad Pitt is opening up about
rising older.
The Oscar winner, 60, and George Clooney, 63, spoke with GQ in an interview
printed on
Tuesday, August 13 ... Brad Pitt marked his sixtieth birthday with a celebration
at Mom Wolf
in Los Angeles this week. One onlooker says the actor 'regarded tremendous blissful' at
the celebration,
and 'everybody had a smile on their faces.' Brad Pitt is an American actor
born on December 18,
1963, in Shawnee, Oklahoma. He has starred in numerous movies, gained an Academy
Award, and married
Angelina Jolie. Brad Pitt rang in his six-decade milestone in a giant method —
twice! Pitt celebrated
his sixtieth birthday on Monday, together with associates and his girlfriend, Ines de
Ramon, 33,
with "low key ... Brad Pitt's internet price is estimated to be round $400
million.
His appearing profession alone has contributed considerably to this, with Pitt
commanding as a lot as $20 million
per movie. ... Born on December 18, 1963, Brad Pitt is 61 years previous. His
zodiac signal is Sagittarius
who're identified for being adventurous, unbiased, and passionate—traits ...
Binding Instruments to the LLM
We then bind the outlined instruments to the language mannequin:
instruments = [add, multiply, divide, search]
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(instruments)Defining the Reasoner
The subsequent step is implementing the reasoner operate, which serves because the assistant’s decision-making node. This operate will use the sure instruments to course of person enter:
from langgraph.graph import MessagesState
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, SystemMessage
# System message
sys_msg = SystemMessage(content material="You're a useful assistant tasked with utilizing search and performing arithmetic on a set of inputs.")Node implementation
def reasoner(state: MessagesState):
return {"messages": [llm_with_tools.invoke([sys_msg] + state["messages"])]}Constructing the Graph Workflow
Now that now we have our instruments and the reasoner outlined, we will assemble the graph workflow that routes between reasoning and gear invocation:
from langgraph.graph import START, StateGraph
from langgraph.prebuilt import tools_condition # that is the checker for the in case you bought a instrument again
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode
from IPython.show import Picture, show
# Graph
builder = StateGraph(MessagesState)
# Add nodes
builder.add_node("reasoner", reasoner)
builder.add_node("instruments", ToolNode(instruments)) # for the instruments
# Add edges
builder.add_edge(START, "reasoner")
builder.add_conditional_edges(
"reasoner",
# If the newest message (consequence) from node reasoner is a instrument name -> tools_condition routes to instruments
# If the newest message (consequence) from node reasoner is a not a instrument name -> tools_condition routes to END
tools_condition,
)
builder.add_edge("instruments", "reasoner")
react_graph = builder.compile()
# Show the graph
show(Picture(react_graph.get_graph(xray=True).draw_mermaid_png()))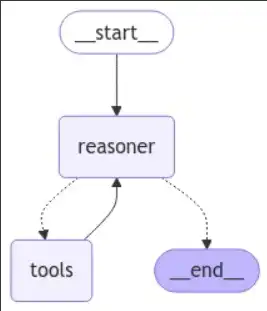
Utilizing the Workflow
We will now deal with queries and use the assistant with the graph constructed. As an example, if a person asks, “What’s 2 occasions Brad Pitt’s age?” The system will first seek for Brad Pitt’s age utilizing the DuckDuckGo search instrument after which multiply that consequence by 2.
Right here’s how you’ll invoke the graph for a person question:
Instance question: What’s 2 occasions Brad Pitt’s age?
messages = [HumanMessage(content="What is 2 times Brad Pitt's age?")]
messages = react_graph.invoke({"messages": messages})
#Displaying the response
for m in messages['messages']:
m.pretty_print()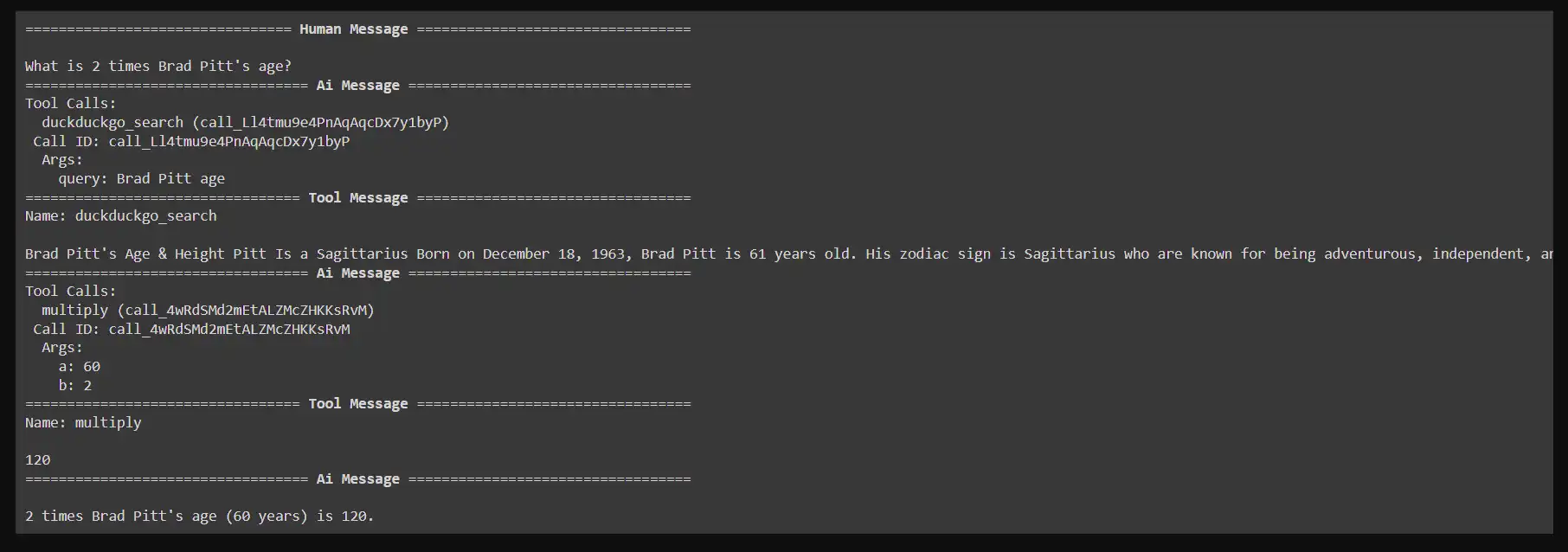
To boost our assistant’s capabilities, we’ll add a customized instrument that retrieves inventory costs utilizing the Yahoo Finance library. This can permit the assistant to reply finance-related queries successfully.
Step 1: Set up the Yahoo Finance Package deal
Earlier than we start, be sure that the yfinance library is put in. This library will allow us to entry inventory market information.
!pip -q set up yahoo-financeStep 2: Import Required Libraries
Subsequent, we import the mandatory library to work together with Yahoo Finance and outline the operate that fetches the inventory worth primarily based on the ticker image:
import yfinance as yf
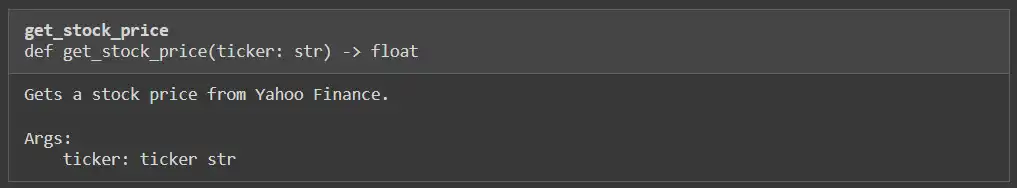
def get_stock_price(ticker: str) -> float:
"""Will get a inventory worth from Yahoo Finance.
Args:
ticker: ticker str
"""
# """This can be a instrument for getting the value of a inventory when handed a ticker image"""
inventory = yf.Ticker(ticker)
return inventory.information['previousClose']
Step 3: Take a look at the Customized Software
To confirm that our instrument is functioning appropriately, we will make a take a look at name to fetch the inventory worth of a particular firm. For instance, let’s get the value for Apple Inc. (AAPL):
get_stock_price("AAPL")Output
222.5
Step 4: Outline the Reasoner Perform
Subsequent, we have to modify the reasoner operate to accommodate stock-related queries. The operate will verify the kind of question and decide whether or not to make use of the inventory worth instrument:
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, SystemMessage
def reasoner(state):
question = state["query"]
messages = state["messages"]
# System message indicating the assistant's capabilities
sys_msg = SystemMessage(content material="You're a useful assistant tasked with utilizing search, the yahoo finance instrument and performing arithmetic on a set of inputs.")
message = HumanMessage(content material=question)
messages.append(message)
# Invoke the LLM with the messages
consequence = [llm_with_tools.invoke([sys_msg] + messages)]
return {"messages":consequence}Step 5: Replace the Instruments Record
Now we have to add the newly created inventory worth operate to our instruments checklist. This can be sure that our assistant can entry this instrument when wanted:
# Replace the instruments checklist to incorporate the inventory worth operate
instruments = [add, multiply, divide, search, get_stock_price]
# Re-initialize the language mannequin with the up to date instruments
llm = ChatOpenAI(mannequin="gpt-4o")
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(instruments)
instruments[4]
We’ll additional improve our assistant’s capabilities by implementing a graph-based workflow for managing queries associated to each arithmetic and inventory costs. This part entails defining the state for our workflow, establishing nodes, and executing numerous queries.
Step 1: Outline the Graph State
We’ll begin by defining the state for our graph utilizing a TypedDict. This enables us to handle and type-check the completely different components of our state, together with the question, finance information, last reply, and message historical past.
from typing import Annotated, TypedDict
import operator
from langchain_core.messages import AnyMessage
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
class GraphState(TypedDict):
"""State of the graph."""
question: str
finance: str
final_answer: str
# intermediate_steps: Annotated[list[tuple[AgentAction, str]], operator.add]
messages: Annotated[list[AnyMessage], operator.add]Step 2: Create the State Graph
Subsequent, we’ll create an occasion of the StateGraph class. This graph will handle the completely different nodes and transitions primarily based on the state of the dialog:
from langgraph.graph import START, StateGraph
from langgraph.prebuilt import tools_condition # that is the checker for the
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode
# Graph
workflow = StateGraph(GraphState)
# Add Nodes
workflow.add_node("reasoner", reasoner)
workflow.add_node("instruments", ToolNode(instruments)) Step 3: Add Edges to the Graph
We’ll outline how the nodes work together with one another by including edges to the graph. Particularly, we need to be sure that after the reasoning node processes the enter, it both calls a instrument or terminates the workflow primarily based on the end result:
# Add Nodes
workflow.add_node("reasoner", reasoner)
workflow.add_node("instruments", ToolNode(instruments)) # for the instruments
# Add Edges
workflow.add_edge(START, "reasoner")
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"reasoner",
# If the newest message (consequence) from node reasoner is a instrument name -> tools_condition routes to instruments
# If the newest message (consequence) from node reasoner is a not a instrument name -> tools_condition routes to END
tools_condition,
)
workflow.add_edge("instruments", "reasoner")
react_graph = workflow.compile()Step 4: Visualise the Graph
We will visualise the constructed graph to know how our workflow is structured. That is helpful for debugging and guaranteeing the logic flows as meant:
# Present
show(Picture(react_graph.get_graph(xray=True).draw_mermaid_png()))
Step 5: Execute Queries
Now that our workflow is about up, we will execute numerous queries to check its performance. We’ll present several types of inquiries to see how nicely the assistant can reply.
Query1: What’s 2 occasions Brad Pitt’s age?
response = react_graph.invoke({"question": "What's 2 occasions Brad Pitt's age?", "messages": []})
response['messages'][-1].pretty_print()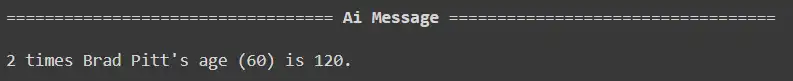
response = react_graph.invoke({"question": "What's the inventory worth of Apple?", "messages": []})
for m in response['messages']:
m.pretty_print()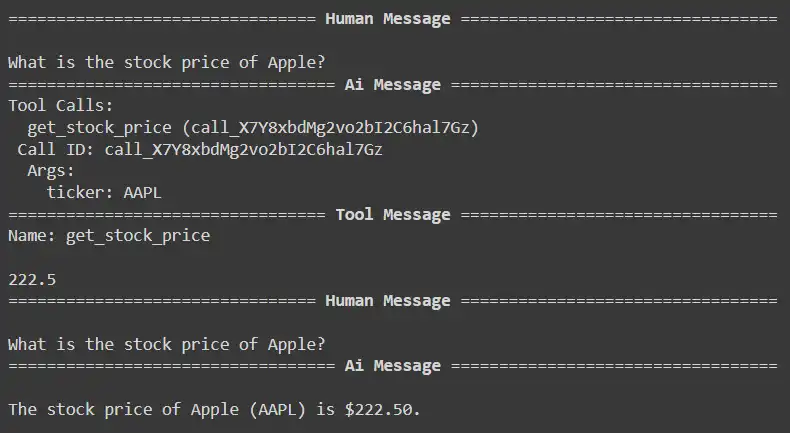
Query2: What’s the inventory worth of Apple?
response = react_graph.invoke({"question": "What's the inventory worth of the corporate that Jensen Huang is CEO of?", "messages": []})
for m in response['messages']:
m.pretty_print()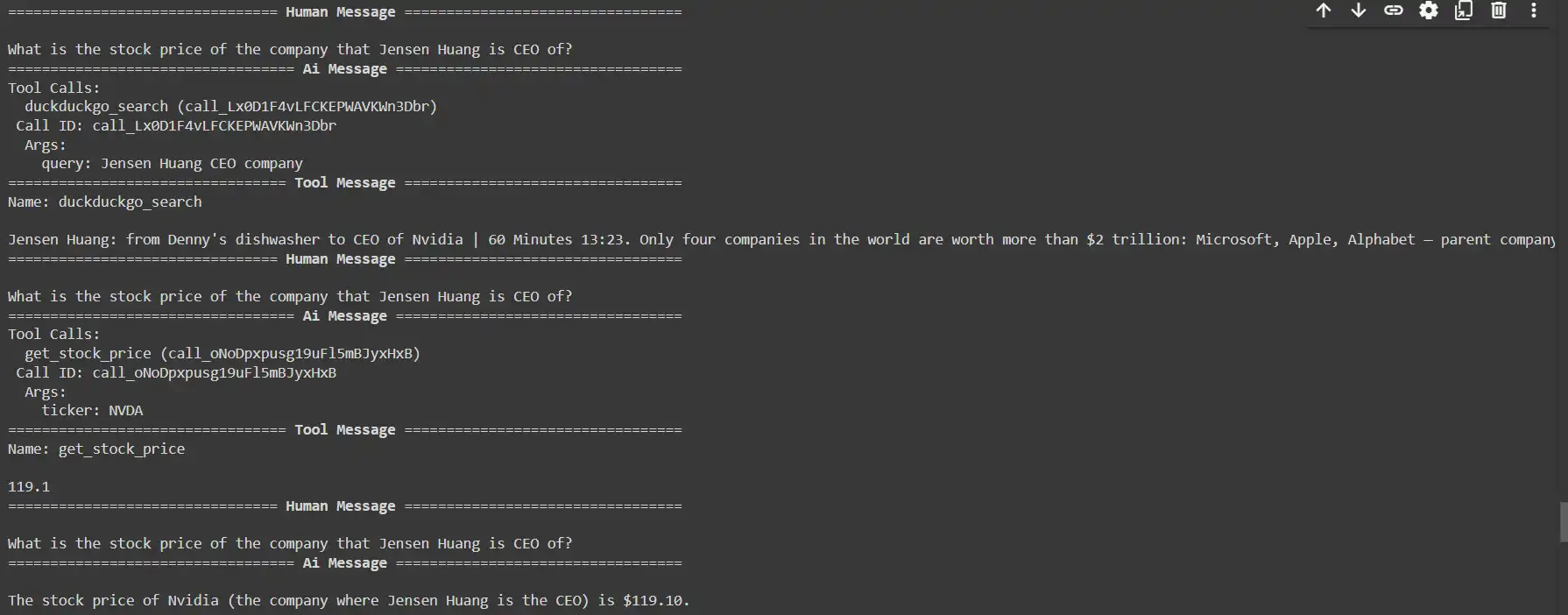
Query3: What would be the worth of Nvidia inventory if it doubles?
response = react_graph.invoke({"question": "What would be the worth of nvidia inventory if it doubles?", "messages": []})
for m in response['messages']:
m.pretty_print()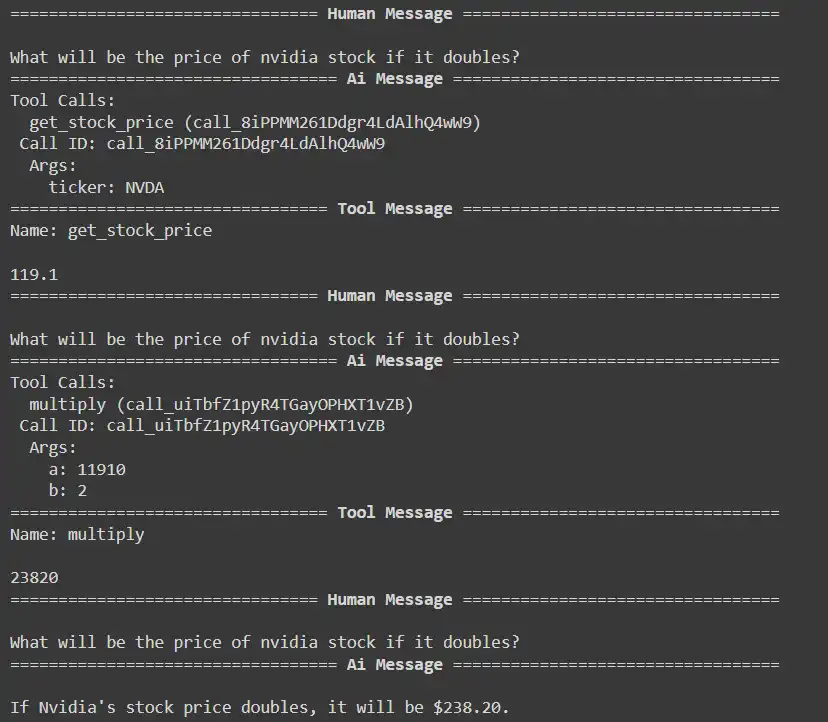
show(Picture(react_graph.get_graph(xray=True).draw_mermaid_png()))
Conclusion
The LangGraph ReAct Perform-Calling Sample gives a strong framework for integrating instruments with language fashions, enhancing their interactivity and responsiveness. Combining reasoning and motion allows the mannequin to course of queries intelligently and execute actions, equivalent to retrieving real-time information or performing calculations. The structured workflow permits for environment friendly instrument utilization, enabling the assistant to deal with numerous inquiries, from arithmetic operations to inventory worth retrieval. Total, this sample considerably enhances the capabilities of clever assistants and paves the best way for extra dynamic person interactions.
Additionally, to know the Agent AI higher, discover: The Agentic AI Pioneer Program
Key Takeaways
- Dynamic Interactivity: The sample integrates exterior instruments with language fashions, enabling extra participating and responsive person interactions.
- ReAct Method: By combining reasoning and motion, the mannequin can intelligently course of queries and invoke instruments for real-time information and computations.
- Versatile Software Integration: The framework helps numerous instruments, permitting the assistant to deal with a variety of inquiries, from fundamental arithmetic to advanced information retrieval.
- Customizability: Customers can create and incorporate customized instruments, tailoring the assistant’s performance to particular purposes and enhancing its capabilities.
The media proven on this article isn’t owned by Analytics Vidhya and is used on the Creator’s discretion.
Often Requested Questions
Ans. The LangGraph ReAct Perform-Calling Sample is a framework that integrates exterior instruments with language fashions to boost their interactivity and responsiveness. It allows fashions to course of queries and execute actions like information retrieval and calculations.
Ans. The ReAct method combines reasoning and appearing, permitting the language mannequin to purpose via person queries and resolve when to name exterior instruments for info or computations, thereby producing extra correct and related responses.
Ans. Varied instruments could be built-in, together with serps (e.g., Wikipedia, internet search), arithmetic operations calculators, real-time information APIs (e.g., climate, inventory costs), and extra.
Ans. The structured format guides the assistant in figuring out whether or not to make use of a instrument primarily based on its reasoning. It entails a collection of steps: figuring out the necessity for a instrument, specifying the motion and enter, and at last observing the consequence to generate a response.
Ans. Sure, the LangGraph ReAct Perform-Calling Sample is designed to deal with advanced queries by permitting the assistant to mix reasoning and gear invocation. As an example, it might fetch real-time information and carry out calculations primarily based on that information.
