Have you ever ever been inquisitive about what powers a few of the greatest Search Functions resembling Elasticsearch and Solr throughout use instances such e-commerce and several other different doc retrieval programs which can be extremely performant? Apache Lucene is a strong search library in Java and performs super-fast searches on giant volumes of knowledge. The indexing and search capabilities of Lucene provide the absolute best options for serps.
By the tip of this text, you’ll have mastered the basics of Apache Lucene even in case you are new to the sector of Search Engineering.
Studying Aims
- Be taught the elemental ideas of Apache Lucene.
- See how Lucene powers search functions like Elasticsearch, Solr and many others.
- Perceive how Indexing and Looking out work in Lucene.
- Be taught several types of Queries supported by Apache Lucene.
- Perceive tips on how to construct a easy search software utilizing Lucene and Java.
This text was printed as part of the Knowledge Science Blogathon.
What’s Apache Lucene?
To grasp Lucene in depth, there are a couple of key terminologies and ideas. Allow us to have a look at every one among them intimately together with examples. Contemplate an instance the place we now have the next details about three completely different merchandise in our assortment.
{
"product_id": "1",
"title": "Wi-fi Noise Cancelling Headphones",
"model": "Bose",
"class": ["Electronics", "Audio", "Headphones"],
"worth": 300
}
{
"product_id": "2",
"title": "Bluetooth Mouse",
"model": "Jelly Comb",
"class": ["Electronics", "Computer Accessories", "Mouse"],
"worth": 30
}
{
"product_id": "3",
"title": "Wi-fi Keyboard",
"model": "iClever",
"class": ["Electronics", "Computer Accessories", "Keyboard"],
"worth": 40
}Doc
A doc is a elementary unit of indexing and search in Lucene. A doc ID identifies every doc. Lucene converts uncooked content material into paperwork containing fields and values.
Area
A Lucene doc accommodates a number of fields. Every subject has a reputation and a price. See instance beneath.
- product_id
- title
- model
- class
- worth
Time period
A time period is a unit of search in Lucene. Lucene does a number of pre-processing steps on uncooked content material earlier than creating phrases resembling tokenization and many others.
| Doc ID | Phrases |
| 1 | title: wi-fi, noise, cancelling, headphonesmodel: boseclass: electronics, audio, headphones |
| 2 | title: bluetooth, mousemodel: jelly, combclass: electronics, laptop, equipment |
| 3 | title: wi-fi, keyboard model: icleverclass: electronics, laptop, equipment |
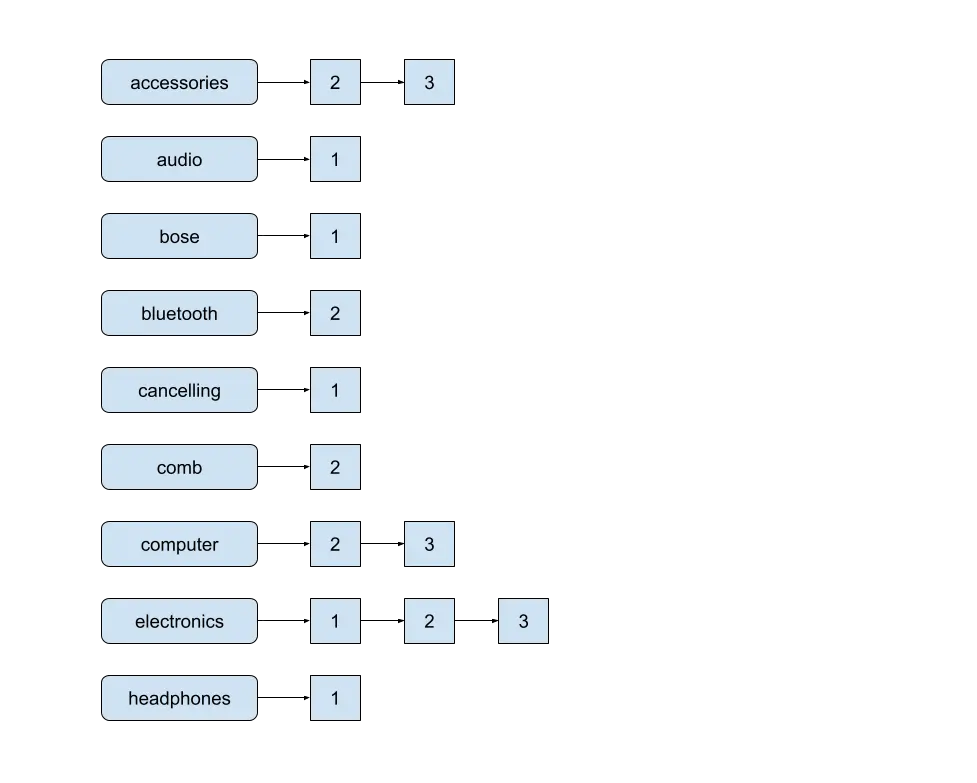
Inverted Index
The underlying information construction in Lucene that allows tremendous quick searches is the Inverted Index. In an inverted index, every time period maps to the paperwork that comprise it, together with the place of the time period in these paperwork. That is known as a Postings Listing.
Section
A index may be sub-divided by Lucene into a number of segments. Every phase is an index in itself. Section searches are often finished serially.
Scoring
Lucene calculates the relevance of a doc by scoring mechanisms resembling Time period Frequency Inverse Doc Frequency (TF-IDF). There are additionally different scoring algorithms resembling BM25 which enhance upon TF-IDF.
Now allow us to perceive how TF-IDF is calculated.
Time period Frequency (TF)
Time period frequency is the variety of occasions a time period t seems in a doc.
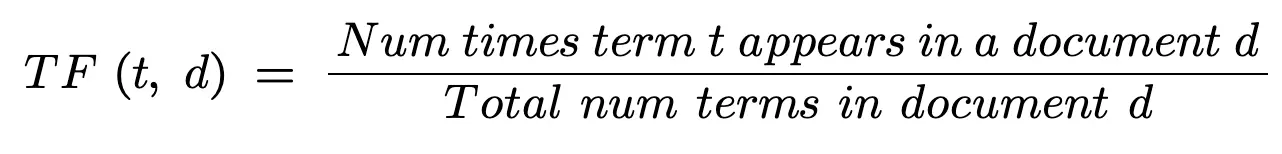
Doc Frequency (DF)
Doc frequency is the variety of paperwork that comprise a time period t. Inverse Doc Frequency divides the variety of paperwork within the assortment by the variety of paperwork containing the time period t. It measures the distinctiveness of a selected time period to stop giving greater significance to repetitive phrases like “a,” “the,” and many others. The “1+” is added to the denominator when the variety of paperwork containing the time period t is 0.
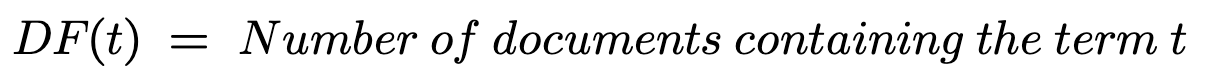

Time period Frequency Inverse Doc Frequency (TF-IDF)
The TF-IDF is the product of Time period Frequency and Inverse Doc Frequency. A better worth of TF-IDF signifies that the time period is extra distinguishing and distinctive in relevance to the entire assortment.
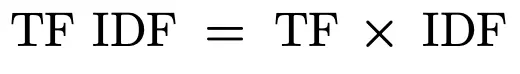
Parts of a Lucene Search Utility
Lucene accommodates two main parts that are:
- Indexer – Lucene makes use of the IndexWriter class for indexing
- Searcher – Lucene makes use of the IndexSearcher class for looking out.
Lucene Indexer
The Lucene Index is accountable for indexing paperwork for the search software. Lucene does a number of textual content processing and evaluation steps resembling tokenization earlier than indexing the phrases into an inverted index. Lucene makes use of the IndexWriter class for indexing.
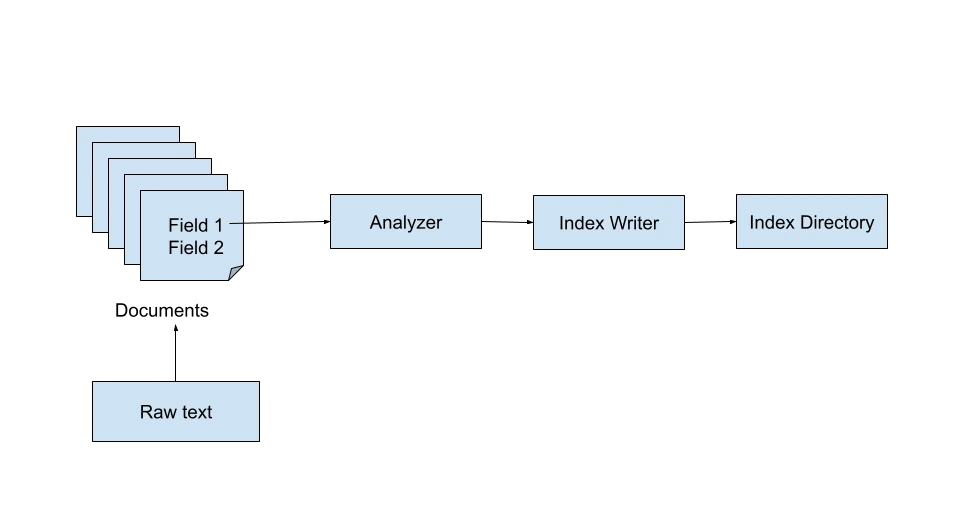
The IndexWriter requires the specification of a listing the place the index shall be saved as nicely an analyzer for the uncooked content material. Though it’s fairly easy to put in writing your individual customized analyzer, Lucene’s StandardAnalyzer does an incredible job at this.
Listing listing = FSDirectory.open(Paths.get(INDEX_DIR));
IndexWriterConfig indexWriterConfig = new IndexWriterConfig(analyzer);
IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(listing, indexWriterConfig);Lucene Searcher
Lucene does search utilizing IndexSearcher class. The IndexSearcher class requires us to specify a legitimate Question object. A consumer question string may be transformed into a legitimate Question object utilizing the QueryParser class.
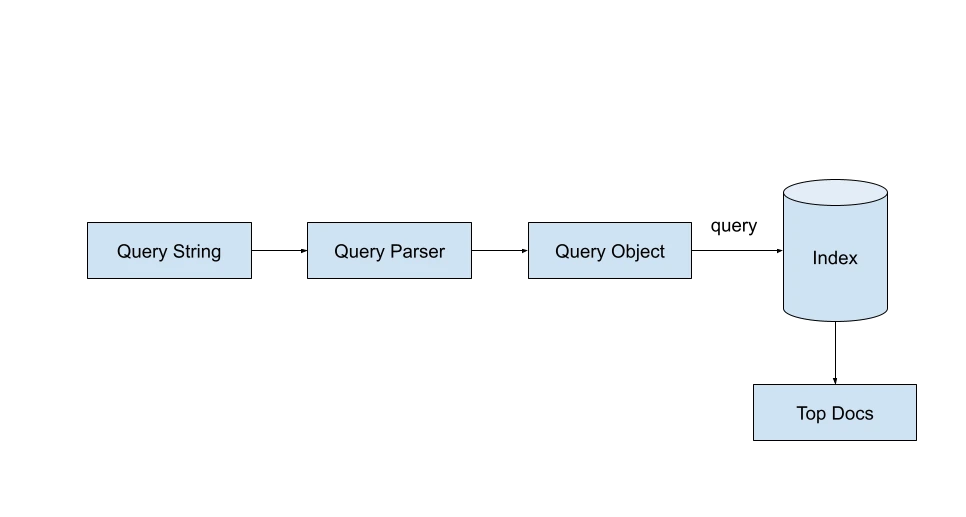
Upon specifying the utmost hits (aka search outcomes) we wish for the question, the Lucene searcher will return a TopDocs object which accommodates the highest hits for the question. Every topDoc accommodates a rating for every of the doc IDs retrieved.
searcher = new IndexSearcher(listing);
parser = new QueryParser("question", new StandardAnalyzer());
Question question = parser.parse(searchString)
searcher.search(question, numHits)Kinds of Search Queries Supported by Lucene
Lucene helps a number of completely different question sorts. Allow us to have a look at 5 mostly used queries together with examples.
Time period Question
A time period question matches paperwork that comprise a selected time period.
Question question = new TermQuery(new Time period("model", "jelly"));Boolean Question
Boolean queries match paperwork that maintain true for a boolean mixture of different queries.
BooleanQuery.Builder builder = new BooleanQuery.Builder();
builder.add(new TermQuery(new Time period("class", "Laptop Equipment")), BooleanClause.Happen.SHOULD);
builder.add(new TermQuery(new Time period("model", "Jelly")), BooleanClause.Happen.SHOULD);
Question question = builder.construct();Vary Question
Vary Queries match paperwork which comprise subject values inside a spread. The instance beneath finds merchandise the place the worth is between 30 and 50.
Question question = NumericRangeQuery.newIntRange("worth", 30, 50, true, true);
Phrase Question
A phrase question matches paperwork containing a selected sequence of phrases.
Question question = new PhraseQuery("title", "Noise", "Cancelling");
Operate Question
Calculates scores for paperwork based mostly on a operate of the worth of a subject. Operate Question can be utilized to spice up the rating of outcomes based mostly on a subject within the doc.
Question question = new FunctionQuery(new FloatFieldSource("worth"));
Constructing a Easy Search Utility with Lucene
To this point, we now have discovered about Lucene fundamentals, indexing, looking out, and the varied question sorts you should use.
Allow us to now tie all these bits collectively right into a sensible instance the place we construct a easy search software utilizing the core components of Lucene: Indexer and Searcher.
Within the instance beneath, we index 3 paperwork the place every doc accommodates the next fields.
Identify is added as a textual content subject and E-mail is added as a string subject. String fields don’t get tokenized by Lucene.
import org.apache.lucene.evaluation.Analyzer;
import org.apache.lucene.doc.Doc;
import org.apache.lucene.doc.Area;
import org.apache.lucene.doc.StringField;
import org.apache.lucene.doc.TextField;
import org.apache.lucene.index.IndexWriter;
import org.apache.lucene.index.IndexWriterConfig;
import org.apache.lucene.retailer.Listing;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MyIndexer {
non-public Listing indexDirectory;
non-public static closing String NAME = "title";
non-public static closing String EMAIL = "e mail";
non-public Analyzer analyzer;
public MyIndexer(Listing listing, Analyzer analyzer) {
this.indexDirectory = listing;
this.analyzer = analyzer;
}
public void indexDocuments() throws IOException {
IndexWriterConfig indexWriterConfig = new IndexWriterConfig(analyzer);
IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(indexDirectory, indexWriterConfig);
indexNewDocument(indexWriter, "john", "[email protected]");
indexNewDocument(indexWriter, "jane", "[email protected]");
indexNewDocument(indexWriter, "ana", "[email protected]");
indexWriter.shut();
}
public void indexNewDocument(IndexWriter indexWriter, String title, String e mail) throws IOException {
Doc doc = new Doc();
doc.add(new TextField(NAME, title, Area.Retailer.YES));
doc.add(new StringField(EMAIL, e mail, Area.Retailer.YES));
indexWriter.addDocument(doc);
}
}As soon as the paperwork are listed, we are able to question them utilizing Lucene queries. Within the instance beneath, we use a easy TermQuery to search out and print the paperwork that match the time period “jane”.
import org.apache.lucene.evaluation.Analyzer;
import org.apache.lucene.evaluation.normal.StandardAnalyzer;
import org.apache.lucene.doc.Doc;
import org.apache.lucene.index.DirectoryReader;
import org.apache.lucene.index.IndexReader;
import org.apache.lucene.index.Time period;
import org.apache.lucene.search.*;
import org.apache.lucene.retailer.Listing;
import org.apache.lucene.retailer.FSDirectory;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class SimpleSearchApplication {
public static void essential(String[] args) throws IOException {
String INDEX_DIRECTORY = "listing";
Listing indexDirectory = FSDirectory.open(Paths.get(INDEX_DIRECTORY));
Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer();
MyIndexer indexer = new MyIndexer(indexDirectory, analyzer);
indexer.indexDocuments();
// Search on the listed paperwork
IndexReader indexReader = DirectoryReader.open(indexDirectory);
IndexSearcher searcher = new IndexSearcher(indexReader);
// Assemble a Time period question to seek for the title "jane"
Question question = new TermQuery(new Time period("title", "jane"));
int maxHits = 10;
TopDocs searchResults = searcher.search(question, maxHits);
System.out.println("Paperwork with title 'jane':");
for (ScoreDoc scoreDoc : searchResults.scoreDocs) {
Doc doc = searcher.doc(scoreDoc.doc);
System.out.println("title: " + doc.get("title") + ", e mail: " + doc.get("e mail"));
}
indexReader.shut();
}
}
The above code returns the next consequence:
Paperwork with title 'jane':
title: jane, e mail: [email protected]Conclusion
Apache Lucene is a strong search library that allows the event of high-performance search functions. With the introduction of Lucene 9.9, vital enhancements in question analysis, vector search, and different options have enhanced its capabilities. All through this information, we’ve lined the elemental parts of Lucene, the workings of indexers and searchers, and tips on how to construct a easy search software in Java. Moreover, we explored the varied kinds of search queries supported by Lucene. Armed with this information, you must now really feel assured in your understanding of Lucene and be able to create extra superior search functions using its highly effective options.
Key Takeaways
- Apache Lucene is a strong Java library that may carry out tremendous quick full-text searches.
- Lucene helps varied question sorts that cater to completely different search use instances.
- Lucene types the spine of a number of excessive efficiency search functions resembling Elasticsearch, Solr, Nrtsearch and many others.
- Lucene IndexWriter and IndexSearcher are essential lessons that allow quick indexing and looking out.
Ceaselessly Requested Questions
A. Sure Apache Lucene has a PyLucene undertaking which helps Python search functions
A. Some open supply serps embrace Solr, Open Search, Meilisearch, Swirl and many others.
A. Sure it does. Nevertheless the utmost dimensions for vector fields is restricted to 1024 which is anticipated to be elevated sooner or later.
A. A few of them embrace Time period Frequency Inverse Doc Frequency (TF-IDF), Greatest Matching 25 (BM25), Latent Semantic Evaluation (LSA), Vector House Fashions (VSM) and many others.
A. Some examples for advanced queries embrace fuzzy queries, span queries, multi phrase question, common expression question and many others.
The media proven on this article isn’t owned by Analytics Vidhya and is used on the Writer’s discretion.
