(metamorworks/Shutterstock)
There’s been loads of concern, uncertainty, and doubt (FUD) in regards to the potential for generative AI to take folks’s jobs. The potential of enormous language fashions (LLMs) to reply questions and deal with digital duties when prompted has caught folks’s consideration, for higher and for worse. However what are the chances that LLMs truly will change human staff? A brand new examine from Certainly sheds some gentle on that query.
The digital job board Certainly just lately carried out a check to find out the efficacy of LLMs at dealing with fundamental work abilities. The Certainly Hiring Lab signed up for GPT-4o, the newest LLM from OpenAI, and requested it to carry out greater than 2,800 job abilities tracked within the Certainly database, from workplace jobs like account administration and insurance coverage claims to extra bodily demanding jobs, like bus driver and prepare dinner.
For every job talent, the Certainly Hiring Lab arrange a solution to measure how profitable the LLM accomplished the duty. They created refined, 1,000-word prompts for every job, which took loads of trial and error. After lastly deciding on the most effective immediate, the Hiring Lab staff ran the immediate by GPT-4o 15 instances, after which aggregated the outcome. GPT-4o was requested to evaluate its personal functionality at every immediate, and the outcomes had been validated by human researchers.
The Hiring Lab centered on three essential areas with the experiment, together with the potential of GenAI to offer theoretical data associated to the talent; the potential of GenAI to resolve issues utilizing the talent; and GenAI’s dedication of the significance of bodily presence in using that talent. GPT-4o analyzed its personal functionality to make the most of these attributes with a given job on a five-point scale. The researchers tabulated the outcomes and printed them final week in a paper titled “AI at Work: Why GenAI is Extra Prone to Assist Staff Than Substitute Them,” which you’ll be able to obtain right here.
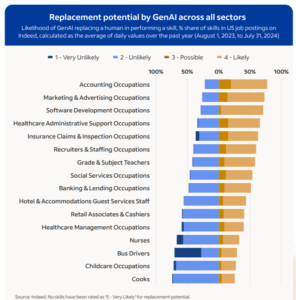
The title is a giant trace at Certainly’s findings with the GenAI experiment. The report’s authors, Annina Hering and Arcenis Rojas, write that not one of the 2,800 work abilities are “very probably” to get replaced by GPT-4o or some other LLM. In reality, Certainly discovered practically 69% of the talents are both “very probably” or “unlikely” to get replaced by GenAI.
Clearly, no jobs that require hands-on execution or the appliance of bodily pressure, akin to bus driver or emergency room nurse, are going to get replaced by GenAI, which is simply software program on the finish of the day (self-driving buses and robot-assisted surgical procedure are actual, however in addition they require much more tech than simply GenAI). Contemplating that greater than half of jobs concerned on this report required some kind of bodily execution, the prospects of full GenAI substitute look fairly bleak.
However that’s to not say there might be no profit. Certainly says that, even for jobs like bus driver or nurse, GenAI might assist with repetitive duties, akin to documentation, which can “permit staff to refocus on the core abilities obligatory in these roles,” Hering and Rojas write.
The researchers concluded that about 29% of jobs might “probably” get replaced by GenAI “because it continues to enhance and if sure adjustments to workplaces and/or working norms happen going ahead,” the researchers write. The roles that GenAI can have the most important affect are “extra stereotypical workplace jobs,” the researchers write.
Throughout the three measures on the coronary heart of the examine–theoretical data; downside fixing; and bodily job abilities–GenAI excels probably the most with theoretical data, adopted intently by downside fixing. In reality, theoretical data was the one attribute that GenAI gave itself a 5, the highest rating, due to the intensive coaching of LLMs on giant quantities of knowledge on the Net, and the potential to make use of serps.
GPT-4o additionally scored decently on problem-solving. It rated itself a 3 for 70% of the talents it assessed, and for 28% of these duties, it mentioned it was “attainable” that it might change a human. It additionally acquired a number of 4s, and rated itself “probably” that would change a human for 3% of the duties.
GenAI is more than likely to switch people at workplace jobs and jobs which might be carried out predominantly on the pc. For example, researchers concluded that it was “attainable” or “probably” that GenAI might change a human at greater than 71% of abilities generally present in job postings for software program improvement. Equally, GenAI was “attainable” or “probably” to switch people for 78% of abilities generally present in a typical accounting occupation, the report says.
GenAI is much less prone to change people at jobs that require extra problem-solving than theoretical data. That is an space the place GenAI builders and information scientists could need to focus their efforts.
“If GenAI fashions enhance their problem-solving talents for extra abilities inside extra jobs,” Hering and Rojas write, “it’s probably that the share of abilities that will ultimately get replaced in these jobs can even rise
There are issues that firms can do to assist them put together for GenAI. Within the accounting discipline, for instance, investments in digital record-keeping and digitization will go a great distance in the direction of making ready a agency to efficiently use GenAI.
Fantastic-tuning (no pun meant) one’s interplay with GenAI can even yield higher outcomes. For example, a free immediate might be interpreted any variety of methods by an LLM, which is probably going to offer completely different solutions each time it’s requested. Extra superior duties would require higher immediate writing and immediate engineering abilities to get probably the most out of GenAI, the authors write.
On the finish of the day, it appears probably that GenAI will change at the least among the duties that human staff are doing now, with a number of variation by business and place. Nonetheless, Certainly’s researchers don’t see a time within the close to future when GenAI will change people en masse, just because GenAI, because it exists in the present day, can’t perform with out people.
“At the same time as GenAI evolves and learns to finish demanding duties,” Hering and Rojas write, “people that oversee, information, and proper GenAI-derived output is not going to simply get replaced.”
Associated Gadgets:
GenAI Shaking Up the Job Market, BCG Says
AI Is Coming for White-Collar Jobs, Too
High 10 In-Demand GenAI Expertise