
The brand new ‘Helldown’ ransomware operation is believed to focus on vulnerabilities in Zyxel firewalls to breach company networks, permitting them to steal information and encrypt gadgets.
French cybersecurity agency Sekoia is reporting this with medium confidence primarily based on current observations of Helldown assaults.
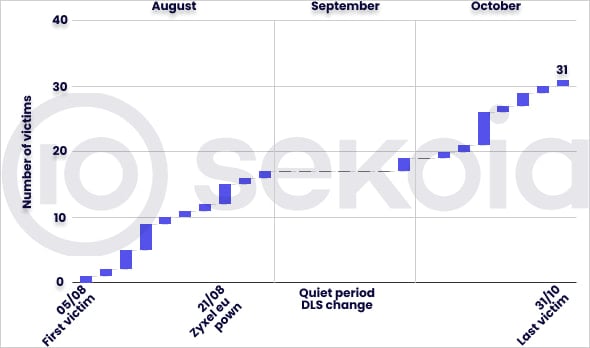
Though not among the many main gamers within the ransomware area, Helldown has shortly grown since its launch over the summer time, itemizing quite a few victims on its information extortion portal.
Supply: Sekoia
Helldown discovery and overview
Helldown was first documented by Cyfirma on August 9, 2024, after which once more by Cyberint on October 13, each briefly describing the brand new ransomware operation.
The primary report of a Linux variant of the Helldown ransomware concentrating on VMware recordsdata got here from 360NetLab safety researcher Alex Turing on October 31.
The Linux variant options code to checklist and kill VMs to encrypt photographs, nevertheless, its features are solely partially invoked, indicating that it’d nonetheless be below improvement.
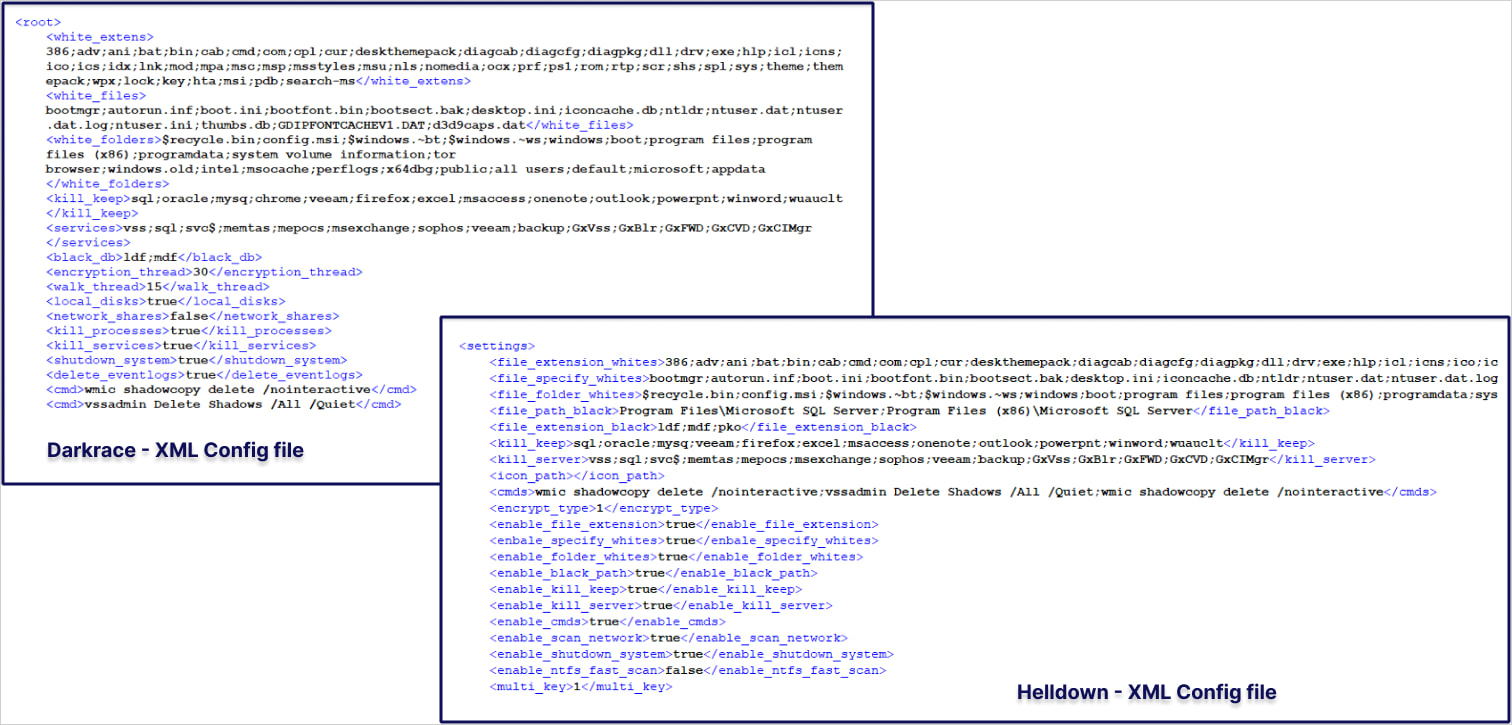
Sekoia experiences that Helldown for Home windows relies on the leaked LockBit 3 builder and options operational similarities to Darkrace and Donex. Nevertheless, no definitive connection might be made primarily based on the accessible proof.
Supply: Sekoia
As of November 7, 2024, the risk group listed 31 victims on its recently-renewed extortion portal, primarily small and medium-sized corporations primarily based in the US and Europe. As of right now, the quantity has decreased to twenty-eight, doubtlessly indicating some had paid a ransom.
Sekoia says Helldown is not as selective within the information it steals as different teams following extra environment friendly techniques and publishes giant information packs on its web site, reaching as much as 431GB in a single occasion.
One of many victims listed is Zyxel Europe, a networking and cybersecurity options supplier.
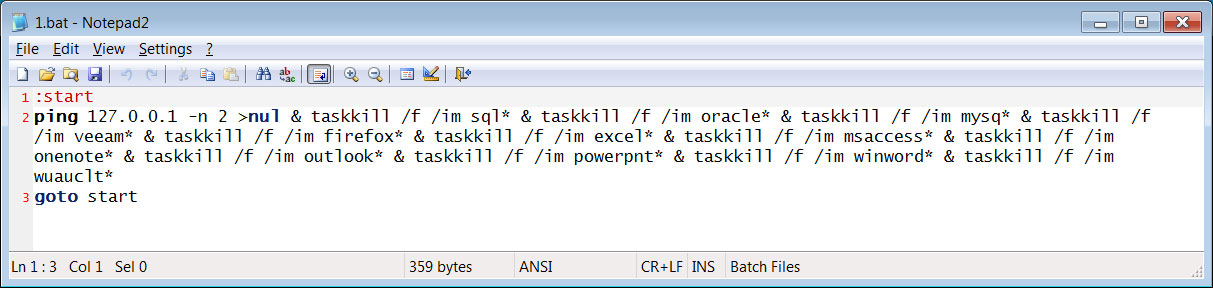
The group’s encryptors don’t seem very superior, with the risk actors using batch recordsdata to finish duties quite than incorporating this performance immediately into the malware.
Supply: BleepingComputer
When encrypting recordsdata, the risk actors will generate a random sufferer string, equivalent to “FGqogsxF,” which will probably be used because the extension for encrypted recordsdata. The ransom notice additionally makes use of this sufferer string in its filename, like “Readme.FGqogsxF.txt”.
Supply: BleepingComputer
Proof pointing to Zyxel exploitation
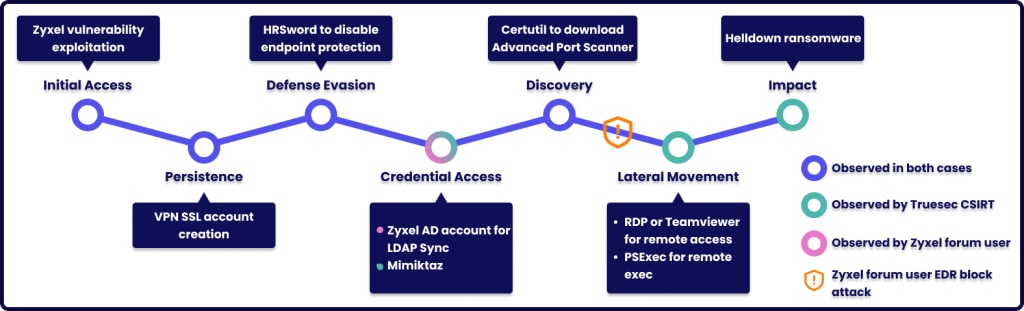
Working its method from a Zyxel Europe lead, Sekoia discovered that at the very least eight victims listed on the Helldown web site used Zyxel firewalls as IPSec VPN entry factors on the time of their breach.
Subsequent, Sekoia observed {that a} Truesec report from November 7 mentions the usage of a malicious account named ‘OKSDW82A’ in Helldown assaults and in addition a configuration file (‘zzz1.conf’) used as a part of an assault concentrating on MIPS-based gadgets, presumably Zyxel firewalls.
The risk actors used this account to determine a safe connection by way of SSL VPN into the sufferer’s networks, entry area controllers, transfer laterally, and switch off endpoint defenses.
By investigating additional, Sekoia discovered experiences of the creation of suspicious person account ‘OKSDW82A’ and configuration file ‘zzz1.conf’ on Zyxel boards, the place the system’s admins reported they have been utilizing firmware model 5.38.
Supply: Sekoia
Primarily based on the model, Sekoia’s researchers hypothesize that Helldown is likely to be utilizing CVE-2024-42057, a command injection in IPSec VPN that permits an unauthenticated attacker to execute OS instructions with a crafted lengthy username in Consumer-Primarily based-PSK mode.
The difficulty was fastened on September 3 with the discharge of firmware model 5.39, and exploitation particulars haven’t been made public as of but, so Helldown is suspected of getting access to personal n-day exploits.
Moreover, Sekoia found payloads uploaded to VirusTotal from Russia between October 17 and 22, however the payload was incomplete.
“It accommodates a base64-encoded string which, when decoded, reveals an ELF binary for the MIPS structure,” explains Sekoia researcher Jeremy Scion.
“The payload, nevertheless, seems to be incomplete. Sekoia assess with medium confidence this file is probably going related to the beforehand talked about Zyxel compromise.”
BleepingComputer contacted Zyxel with questions on these assaults however has not acquired a response at the moment.

.png)