
A menace actor focused low-skilled hackers, referred to as “script kiddies,” with a faux malware builder that secretly contaminated them with a backdoor to steal knowledge and take over computer systems.
Safety researchers at CloudSEK report that the malware contaminated 18,459 gadgets globally, most situated in Russia, america, India, Ukraine, and Turkey.
“A trojanized model of the XWorm RAT builder has been weaponized and propagated,” reads the CloudSEK report.
“It’s focused specifically in direction of script kiddies who’re new to cybersecurity and instantly obtain and use instruments talked about in varied tutorials thus exhibiting that there isn’t a honour amongst thieves.”
CloudSEK has discovered the malware included a kill change that was activated to uninstall the malware from most of the contaminated machines, however because of sensible limitations, some stay compromised.
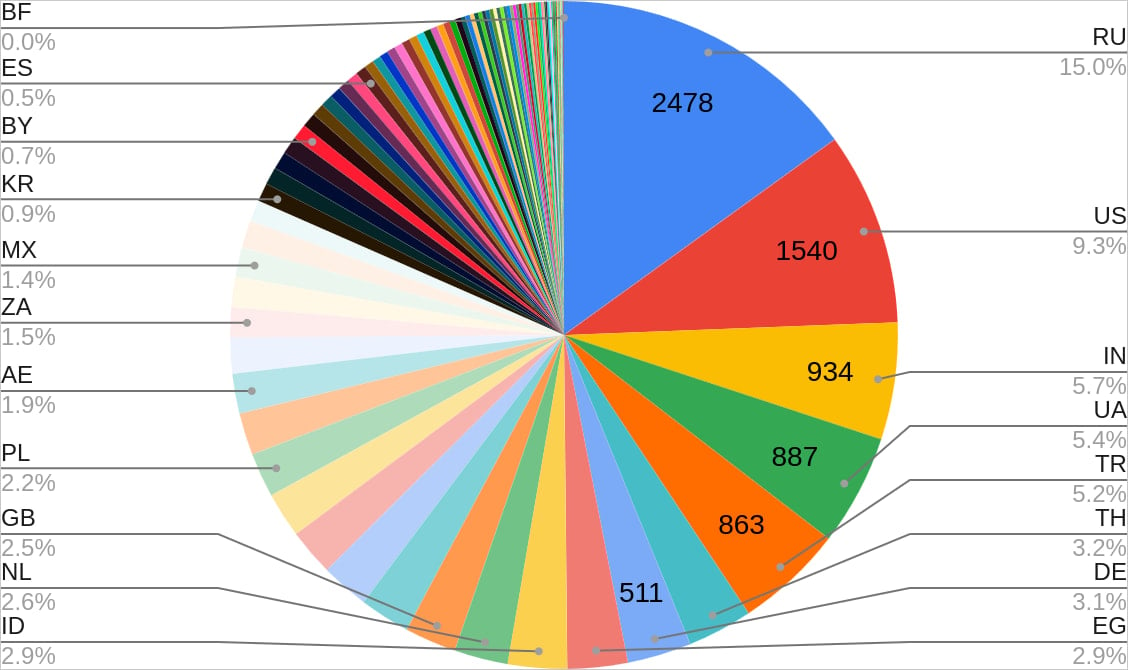
Supply: CloudSEK
Pretend RAT builder installs malware
The researchers say they not too long ago found a Trojanized XWorm RAT builder being distributed by means of varied channels, together with GitHub repositories, file internet hosting platforms, Telegram channels, YouTube movies, and web sites.
These sources promoted the RAT builder, stating it will enable different menace actors to make the most of the malware with out having to pay for it.
Nevertheless, as an alternative of being an precise builder for the XWorm RAT, it contaminated the menace actor’s gadgets with the malware.
As soon as a machine is contaminated, the XWorm malware checks the Home windows Registry for indicators it’s operating on a virtualized surroundings and stops if the outcomes are constructive.
If the host qualifies for an infection, the malware performs the required Registry modifications to make sure persistence between system boots.
Each contaminated system is registered to a Telegram-based command and management (C2) server utilizing a hardcoded Telegram bot ID and token.
The malware additionally robotically steals Discord tokens, system info, and placement knowledge (from IP tackle), and exfiltrates it to the C2 server. Then, it waits for instructions from the operators.
Out of the 56 instructions supported in complete, the next are significantly harmful:
- /machine_id*browsers – Steal saved passwords, cookies, and autofill knowledge from internet browsers
- /machine_id*keylogger – File every part the sufferer sorts on their laptop
- /machine_id*desktop – Seize the sufferer’s energetic display
- /machine_id*encrypt*
– Encrypt all recordsdata on the system utilizing a offered password - /machine_id*processkill*
– Terminate particular operating processes, together with safety software program - /machine_id*add*
– Exfiltrate particular recordsdata from the contaminated system - /machine_id*uninstall – Take away the malware from the gadget
CloudSEK discovered that the malware operators had exfiltrated knowledge from roughly 11% of the contaminated gadgets, principally taking screenshots of contaminated gadgets, as proven under, and stealing browser knowledge.
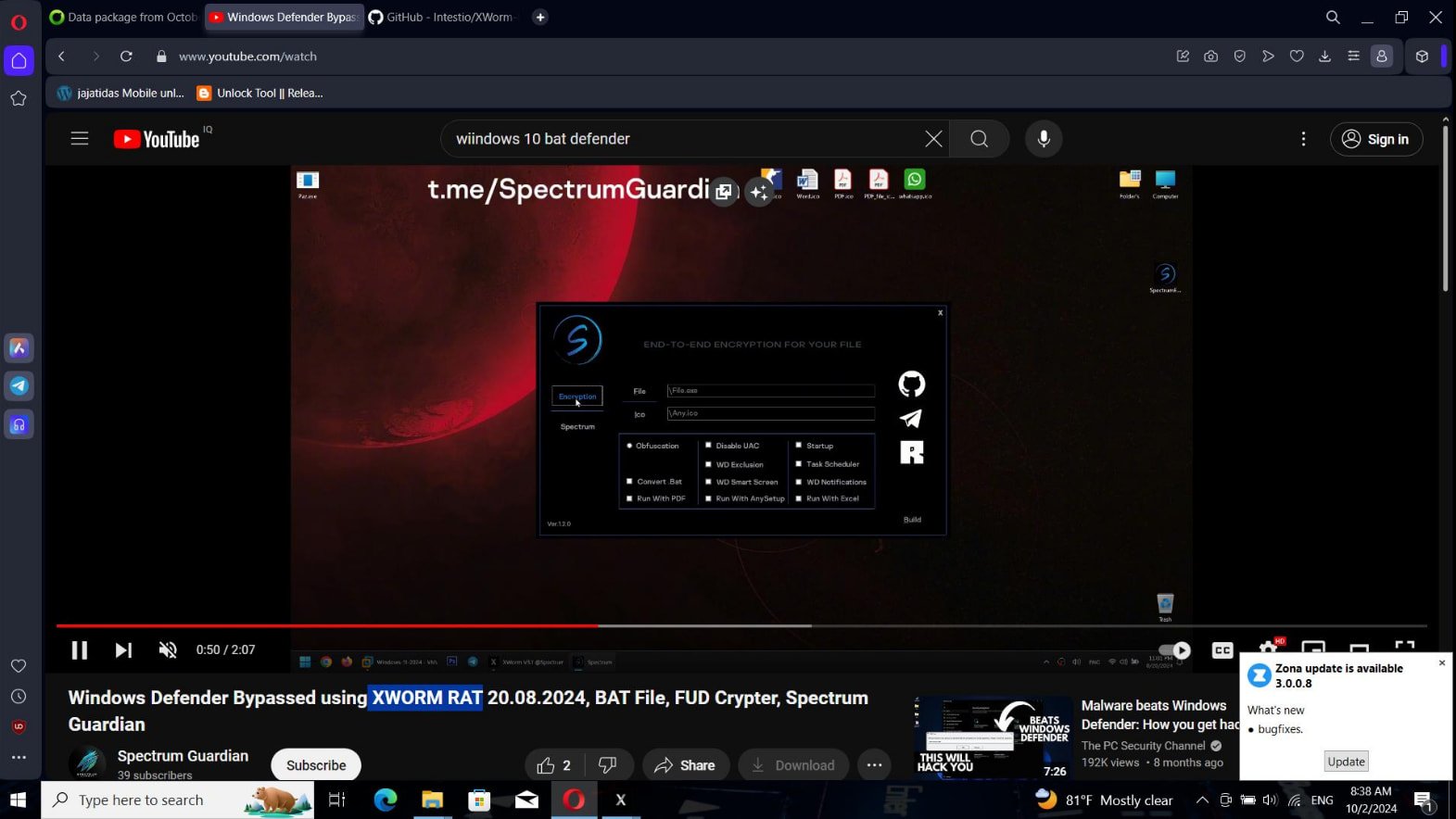
Supply: CloudSEK
Disrupting with the kill change
The CloudSEK researchers disrupted the botnet by using hard-coded API tokens and a built-in kill change to uninstall the malware from contaminated gadgets.
To do that, they despatched a mass uninstall command to all listening purchasers, looping by means of all recognized machine IDs they’d beforehand extracted from Telegram logs. In addition they brute-forced machine IDs from 1 to 9999, assuming a easy numeric sample.
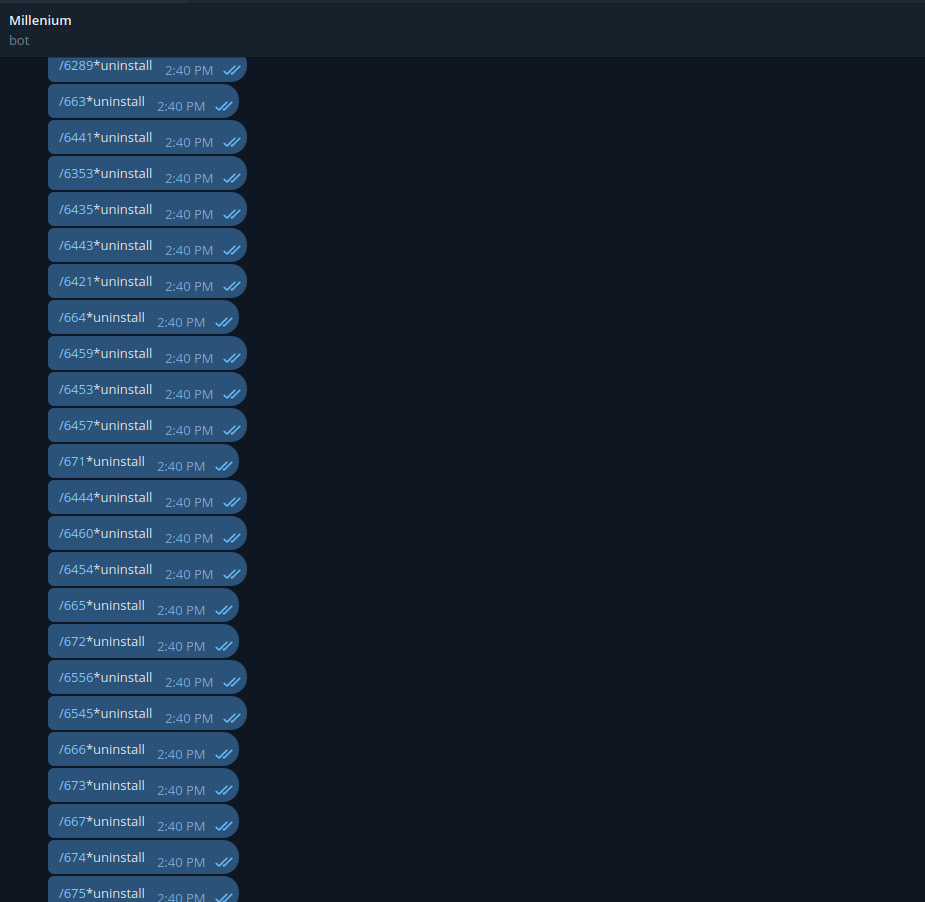
Supply: CloudSEK
Though this brought on the malware to be faraway from most of the contaminated machines, these not on-line when the command was issued stay compromised.
Additionally, Telegram topics messages to price limiting, so a number of the uninstall instructions might have been misplaced in transit.
Hackers hacking hackers is a standard situation we frequently see manifesting within the wild.
The takeaway from CloudSEK’s findings isn’t to belief unsigned software program, particularly these distributed by different cybercriminals, and solely set up malware builders on testing/evaluation environments.
