What Is Grafana?
Grafana is an open-source software program platform for time sequence analytics and monitoring. You may join Grafana to numerous information sources, from PostgreSQL to Prometheus. As soon as your information supply is linked, you need to use a built-in question management or editor to fetch information, and construct dashboards out of your information supply. Grafana is incessantly deployed for all kinds of use circumstances, together with DevOps and AdTech.
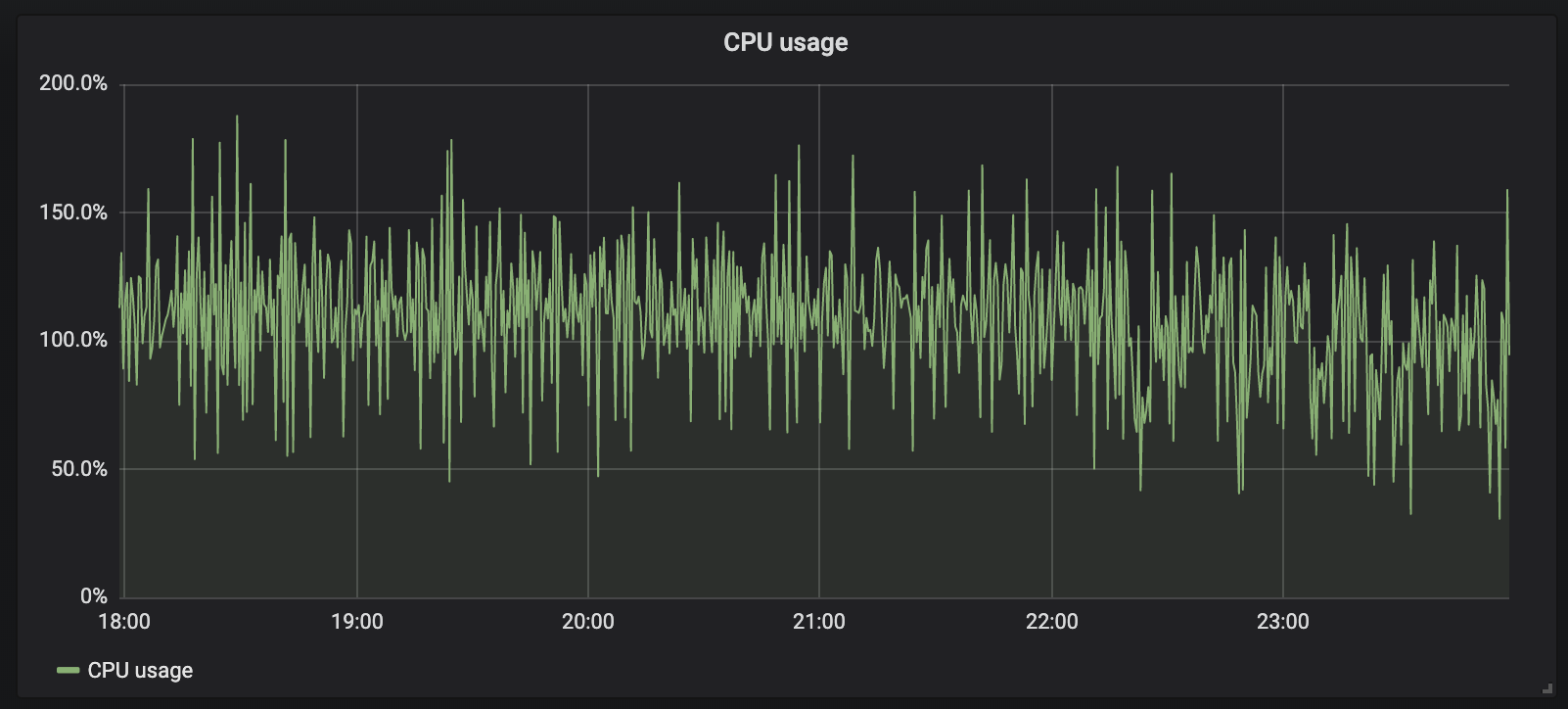
At Rockset, we primarily use Grafana for monitoring our manufacturing techniques, in addition to for DevOps functions. We monitor all kinds of metrics, from the variety of question errors to the CPU utilization of our manufacturing machines. At any time when a graph deviates from a predefined band of anticipated values, we set off an alert which might hook up with one thing like a PagerDuty integration that might ping an on-call engineer.
Why Construct a Plugin?
As energy customers of Grafana ourselves, we had floated the concept of constructing a Rockset connector for Grafana for a very long time. Due to the realtime nature of Rockset as an operational analytics engine, we believed {that a} Grafana plugin may very well be a great match for a variety of issues and queries. We realized that we may start monitoring quite a lot of time sequence metrics that might enable for larger transparency into our engineering practices (by monitoring the heart beat of our GitHub commits into grasp, for instance), in addition to our inside techniques that we’re monitoring via Rockset (comparable to occasions in our Kubernetes cluster). Another excuse a Rockset-Grafana plugin is useful is as a result of an utility developer can use commonplace SQL to fetch any sort of information via Rockset. Lastly, it was one thing that our prospects had beforehand expressed curiosity in. Taking these factors into consideration, constructing a Grafana connector appeared like an apparent and helpful utility of Rockset to boost an already highly effective software.
How To Construct A Grafana Connector
To construct a working Grafana connector, one must implement a set of Typescript strategies, in addition to a customized consumer interface for retrieving information out of your given datasource. After the plugin has been applied and take a look at circumstances written, it’s reviewed by the Grafana maintainer group and built-in into the official checklist of plugins.
The performance that any Grafana connector must implement is:
-
Datasource Specification
When constructing a plugin, it’s good to first truly have the ability to fetch the information you may be setting up dashboards out of. This usually entails having the consumer specify an API key, password, or database connection URL to fetch the information from.
-
Customized Question Interface
As soon as a datasource has been specified, a consumer wants to have the ability to question that datasource. Within the case of Rockset, this concerned implementing a customized question editor in HTML and AngularJS that’s proven to the consumer when they’re making a dashboard with Rockset.
-
Question Execution via the API layer
After the consumer has typed in a question, the information itself wants to truly be fetched and handed to the visualization layer in a really particular format. This entails speaking with the frontend via the consumer’s question enhancing, in addition to question execution via the Rockset API and post-processing of outcomes such that they’re handed to the visualization within the correct timeseries format.
Constructing the Rockset-Grafana Plugin
Going again to the steps outlined above, the very first thing that I wanted to do when constructing out the Rockset Connector was to truly join the Rockset Datasource. I constructed out a type that allowed a consumer to specify the identify of the plugin, in addition to the Rockset API key. This concerned constructing out the shape on the frontend, in addition to writing a testDatasource methodology that validated the right API key with a take a look at question to the Rockset backend via a fast name to the /v1/orgs/self/customers/self/apikeys endpoint within the Rockset API that ensured the API key itself was legitimate.
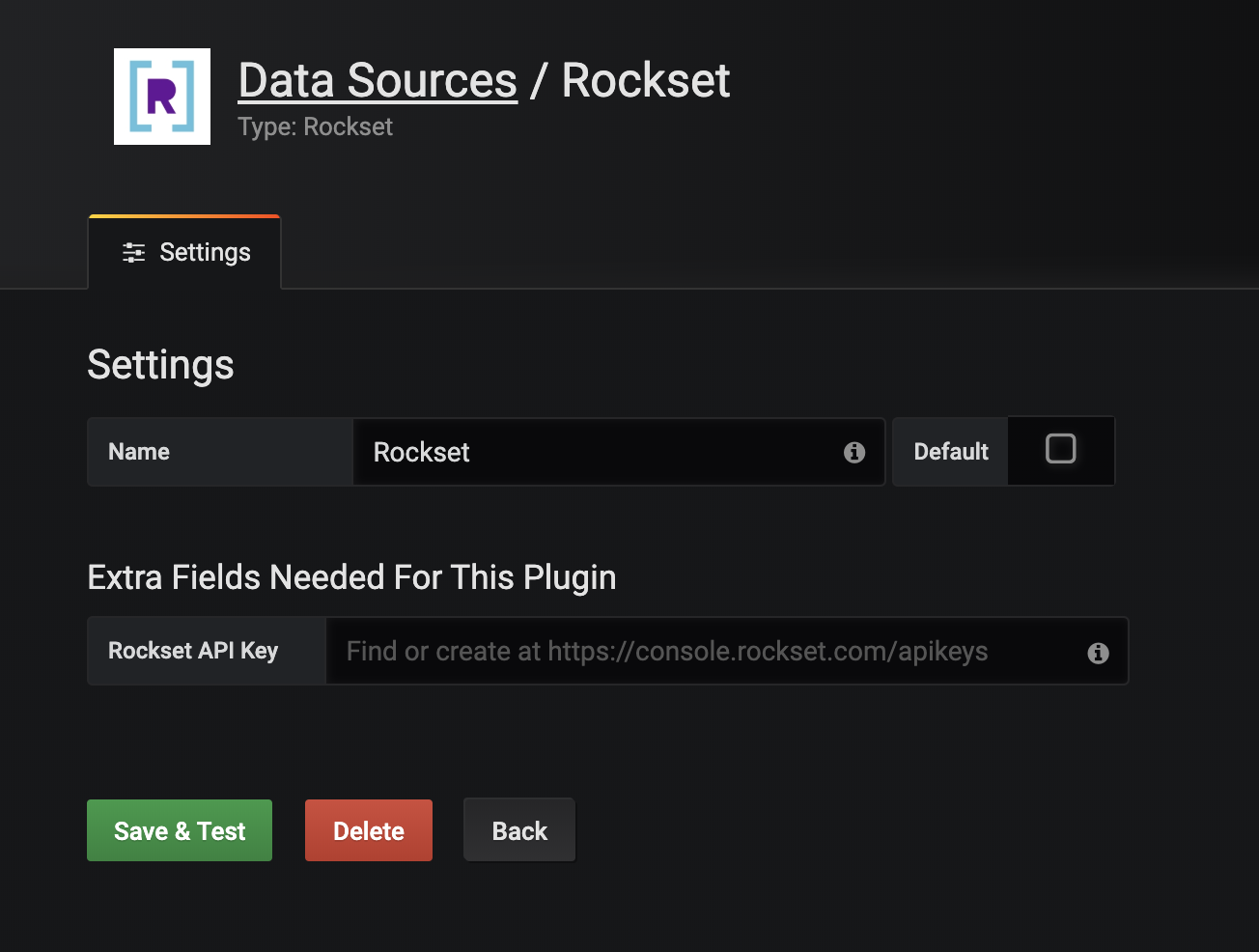
As soon as the important thing was validated, it was time to construct out the question editor. Within the case of Rockset, we have now to permit a consumer to kind in arbitrary SQL to any of their collections. Moreover, you will need to present informative error messages for syntactically invalid queries or if a consumer is querying on a set that doesn’t exist.
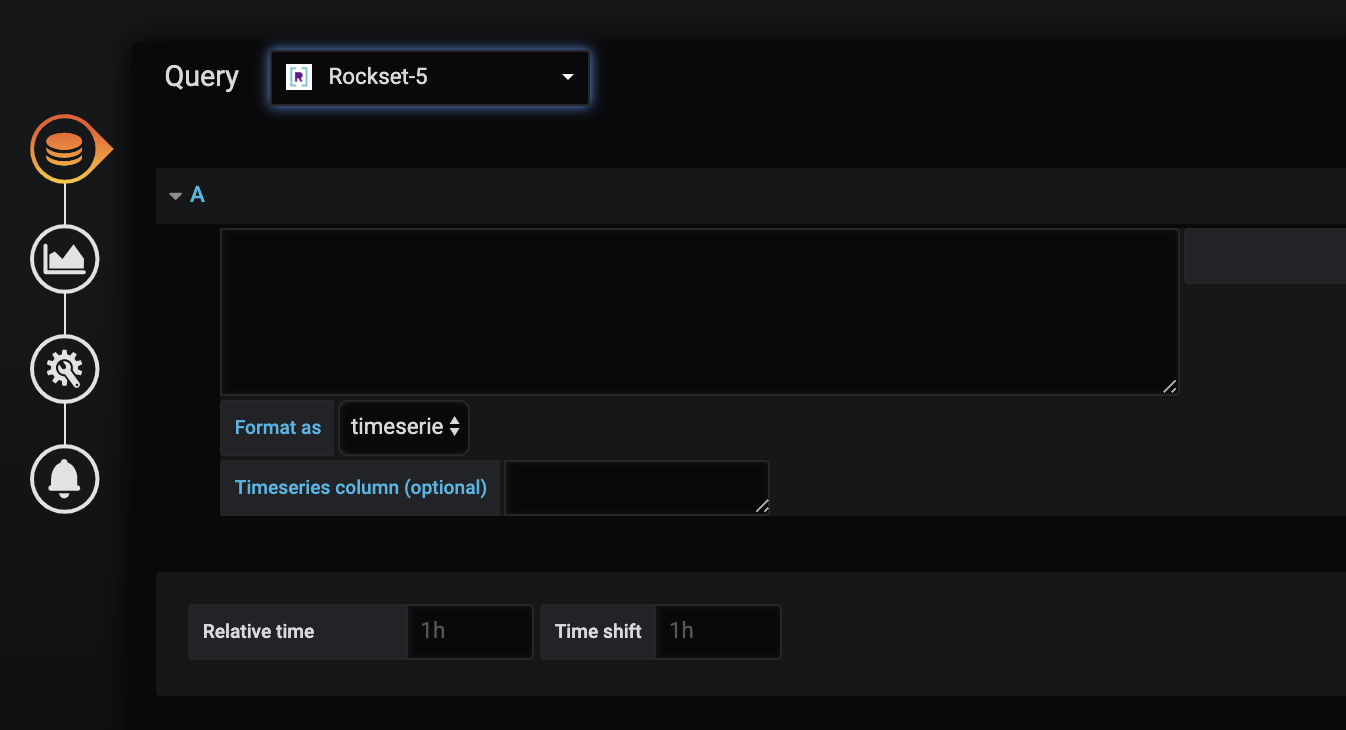
I applied the question editor with a debounce operate that allowed a consumer to kind their question, then pause so it may very well be executed via the Rockset API. The queries are checked for validity on the backend, and the error is handed to the consumer on the frontend to allow them to obtain an informative error message. Moreover, Grafana requires a timeseries column if you wish to categorical the information when it comes to an over-time graph. The Timeseries column field permits a consumer to specify a column of their SQL outcomes that they select to pivot their graph axes on. The Format as field is a straightforward dropdown that permits a consumer to precise a Rockset question as a timeseries or as a desk, and this modifications the formatting of the information handed to the graph layer.
After a question has been typed in, validated, and executed, the information is obtained by the Grafana connector. Sadly, we can not merely go the information to a desk or graph and show it within the Grafana dashboard. We have to extract the user-specified timeseries column, convert it into Unix seconds, and go an array of JSON objects into the visualization layer of Grafana. We will additionally neatly counsel the timeseries column if a consumer specifies just one column that’s of kind datetime.
Lastly, as soon as the entire question and validations steps have been accomplished, it’s now attainable for a consumer of the plugin to visualise their information, and we instantly set about doing that after the plugin had completed being developed.
Use Circumstances and Future Work
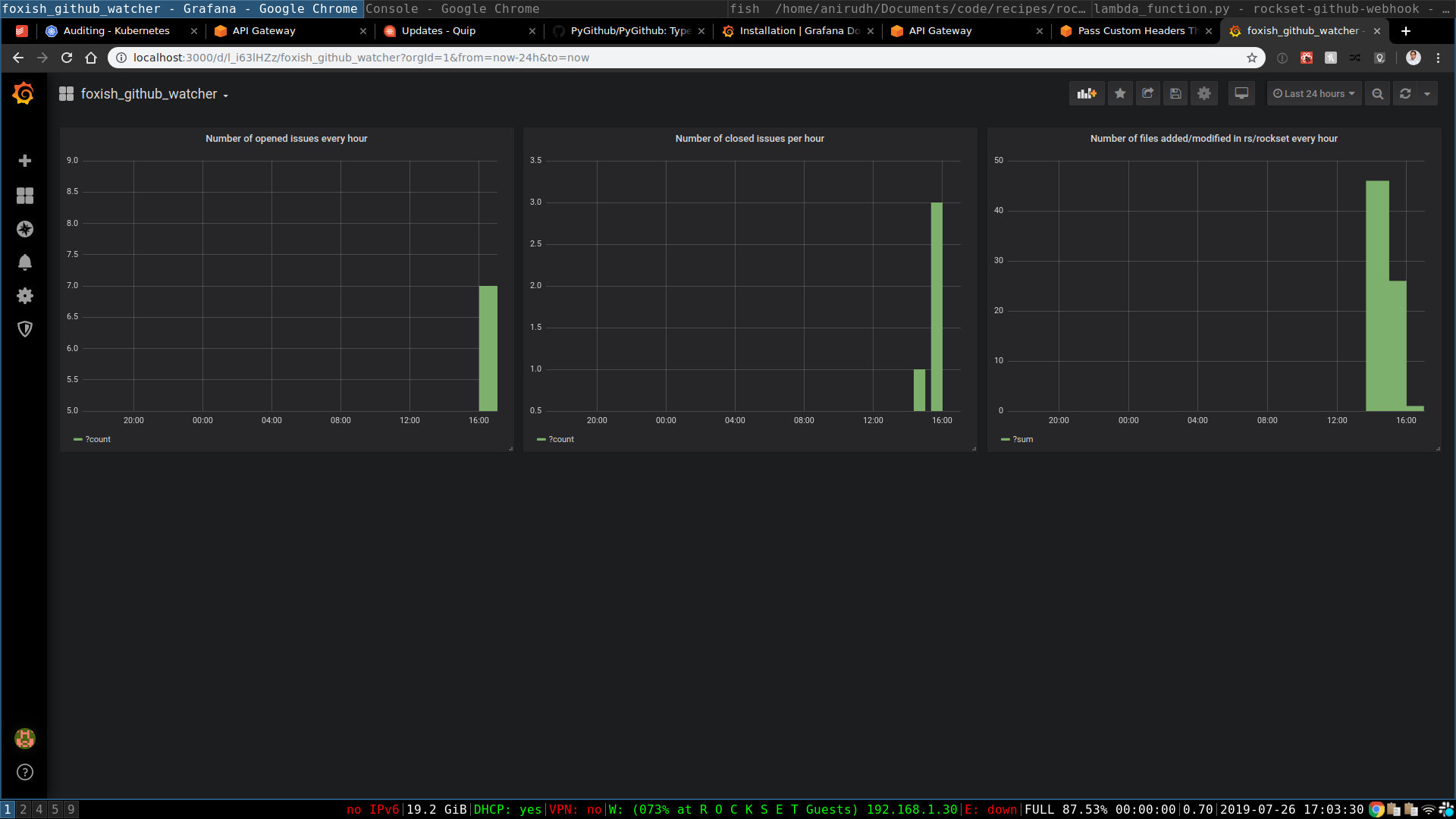
As soon as our plugin was full, we began to make use of it for attention-grabbing queries at Rockset. One factor we began out was our inside GitHub metrics. Particularly, we began wanting on the variety of open points each hour, the variety of closed points and the variety of recordsdata added or modified throughout the course of a day in our firm.
We additionally started monitoring metrics just like the variety of Kubernetes occasions in our dev cluster for higher understanding outages and utilization spikes.
These queries are only a few examples of how Rockset can be utilized with Grafana to supply realtime insights into arbitrary collections of knowledge, and we’re excited to roll this plugin out extra extensively and see how our prospects use it. To see a extra detailed view of the plugin and to get began utilizing it, try the documentation.
