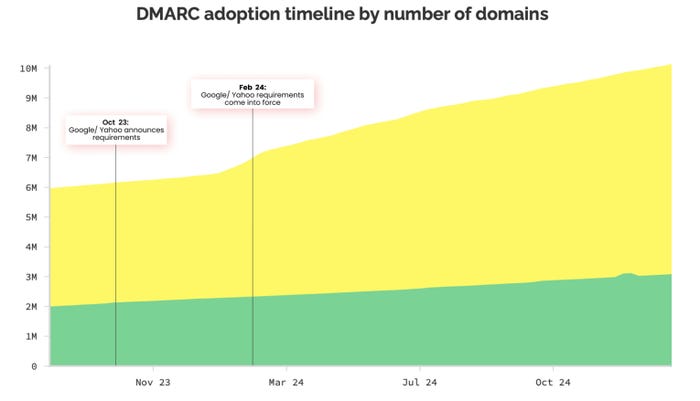
A yr after Google and Yahoo compelled bulk electronic mail senders to implement the Area-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC) normal, the speed of the adoption of DMARC amongst domains has doubled, though most of the identical electronic mail threats proceed to efficiently ship payloads or redirect unwary customers to phishing websites.
The rise in adoption began in February 2024, when Google and Yahoo began requiring bulk electronic mail senders — outlined as any firm sending greater than 5,000 electronic mail messages each day — to make use of DMARC. The e-mail authentication normal makes use of two authentication specs — Sender Coverage Framework (SPF) and DomainsKeys Recognized Mail (DKIM) — to substantiate that an electronic mail comes from a licensed electronic mail server and on behalf of the purported sender. The expertise makes it rather more tough to spoof electronic mail from a professional firm or model.
Prior to now yr, adoption has elevated by about 2.3 million domains, however that also leaves about 87% of domains and not using a DMARC file, in keeping with information printed by cyber-resilience agency Pink Sift on Feb 5. Adoption can be uneven, with organizations in Austria, Japan, and Indonesia seeing a number of the highest development and publicly traded firms making essentially the most vital positive factors.
Whereas doubling the adoption price of DMARC is a major success, the non-public sector must do higher, says Sean Costigan, managing director of resilience technique at Pink Sift.
“DMARC is taken into account an indicator of cyber maturity in lots of sectors, and we’re nonetheless within the early days — healthcare, for instance, is struggling to surpass 40% to 50% adoption,” he says, including that “broadly, correctly managed DMARC adoption will cut back spoofing, phishing and different types of cybercrime.”
Supply: Pink Sift
Google, for instance, has seen a major discount in questionable electronic mail. In 2024, Gmail customers noticed 265 billion fewer unauthenticated emails, or about 65% much less. Through the 2024 holidays, a season that usually sees an enormous spike in phishing assaults, customers encountered 35% fewer scams, says Neil Kumaran, group product supervisor at Google.
“We predict these enhancements characterize an enormous increase within the well being of the e-mail ecosystem general,” he says. “We are literally seeing the business embrace these necessities, seeing how vital they’re to extend the wholesome ecosystem for everyone.”
DMARC Adoption More likely to Speed up
Giant electronic mail senders will not be the one teams quickening the tempo of DMARC adoption. The most recent Fee Card Trade Information Safety Commonplace (PCI DSS) model 4.0 requires DMARC for all organizations that deal with bank card info, whereas the European Union’s Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) makes DMARC a necessity for its capacity to report on and block electronic mail impersonation, Pink Sift’s Costigan says.
“Necessary laws and laws typically function the tipping level for many organizations,” he says. “Failures to do affordable, proactive cybersecurity — of which electronic mail safety and DMARC is clearly a component — are prone to meet with expensive regulatory actions and the prospect of sophistication motion lawsuits.”
General, the authentication specification is working as meant, which explains its arguably speedy adoption, says Roger Grimes, a data-driven-defense evangelist at safety consciousness and coaching agency KnowBe4. Different cybersecurity requirements, resembling DNSSEC and IPSEC, have been round longer, however DMARC adoption has outpaced them, he maintains.
“DMARC stands alone because the singular success as essentially the most broadly carried out cybersecurity normal launched within the final decade,” Grimes says.
Subdomain Assaults Exploit Gaps
But that doesn’t imply that threats have diminished. Attackers have tailored, Grimes says. Sometimes, attackers will simply use lookalike domains — or use inventive punctuation to create confusion — and idiot the top consumer whereas nonetheless sending messages from an authenticated area.
“For the reason that creation and wide-scale adoption of DMARC, the proportion and variety of phishing emails claiming to be from a selected professional area are considerably much less, maybe just some p.c of what they was once,” Grimes says. “Sadly, phishers simply created new illegitimate domains, typically with lookalike names, that they then utilized DMARC on in order that the brand new, illegitimate domains handed DMARC inspection.”
One method used to dodge DMARC is “subdomail,” the place attackers search out SPF data that embrace unregistered domains, after which take management of the orphaned domains as a strategy to conduct huge spamming campaigns. In a single case, an SPF file for msnmarthastewartsweeps.com “included” two domains, permitting any approved mail servers listed in these area data to ship authenticated electronic mail. Within the Sender Coverage Framework, the “embrace” key phrase permits on area to specify that these domains’ lists of authenticated electronic mail servers needs to be trusted. For msnmarthastewartsweeps.com, that resulted in practically 18,000 domains being approved to ship electronic mail on behalf of the area.
As a result of the e-mail messages make it previous DMARC checks, they’re extra prone to efficiently impersonate different firms, says Pink Sift’s Costigan.
“SubdoMailing exploits gaps in DMARC safeguards, permitting attackers to ship emails from subdomains that go each SPF and DMARC checks,” he says. “These messages seem professional and are extremely misleading.”
BIMI on Deck for E-mail Safety
Nonetheless, firms achieve rather more visibility into their electronic mail through the use of DMARC, as the usual features a reporting operate that enables firms — or service suppliers on their behalf — to trace electronic mail failures. Thus, firms ought to quickly transfer from “none” to “quarantine” to “reject” as their coverage, specialists say.
As well as, firms also needs to look to take the following step, shifting to Model Indicators for Message Identification or BIMI, which permits firms to current a brand to electronic mail recipients. BIMI requires strict DMARC, nevertheless, and solely a couple of third of domains at present comply, in keeping with Pink Sift’s information.
Whereas none of those applied sciences remedy the issue of malicious emails, all of them give firms and their electronic mail service suppliers extra dependable alerts to make use of to filter out undesirable messages and potential assaults, says Google’s Kumaran. DMARC adoption doesn’t boil all the way down to “authenticated mail is sweet, and unauthenticated electronic mail is unhealthy,” he says.
“The thought is that authentication offers you confidence of the supply of the message, after which you can begin to do a greater job of classification and really offering protections to customers,” Kumaran says. “So I feel it is a very fascinating habits if 100% of assaults are literally authenticated, as a result of it makes the job of defending individuals — and offers these the oldsters working in defending — stronger alerts on which to function.”
