Google’s FLARE workforce has launched GoStringUngarbler, an open-source instrument designed to dismantle string obfuscation in Go binaries protected by the garble compiler.
This innovation addresses rising considerations over malware authors exploiting garble’s superior literal transformations, which render conventional static evaluation ineffective.
The instrument combines emulation-driven string extraction with binary patching to supply deobfuscated executables, basically altering reverse engineering workflows for safety analysts.
Garble’s Obfuscation Structure
The garble compiler enhances Go binary safety by means of AST-level transformations that protect program semantics whereas complicating static evaluation.
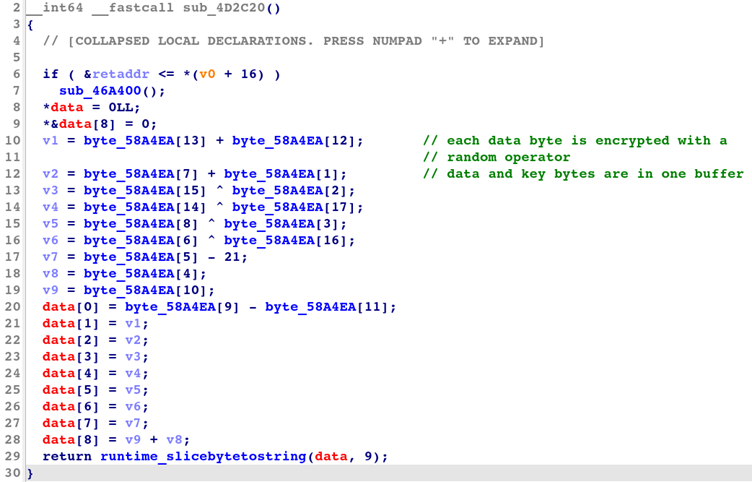

Its -literals flag prompts 4 distinct string encryption methodologies, every requiring specialised decryption approaches.
Stack-Primarily based Transformations
Garble implements three stack manipulation strategies for runtime string decryption:
Easy transformation employs byte-wise arithmetic operations utilizing a randomly generated key and operator (XOR/ADD/SUB). The compiler generates a decryptor operate template as proven under:
key := make([]byte, len(information))
obfRand.Learn(key)
op := randOperator(obfRand)
for i, b := vary key {
information[i] = evalOperator(op, information[i], b)
}This produces meeting patterns the place RBX/RCX registers maintain decrypted string pointers and lengths earlier than calling runtime_slicebytetostring.

Swap transformation introduces position-dependent encryption by means of byte pair swapping and dynamic native keys:
for i := len(positions) - 2; i >= 0; i -= 2 {
localKey := byte(i) + byte(positions[i]^positions[i+1]) + shiftKey
information[positions[i]], information[i+1] = evalOperator(op, information[i+1], localKey),
evalOperator(op, information[i], localKey)
}The ensuing management circulate accommodates nested loops that shuffle byte order whereas making use of cascading XOR operations1.
Shuffle transformation implements multi-layered obfuscation by means of permutation matrices and index scrambling:
shuffledIdxs := obfRand.Perm(len(fullData))
for i, b := vary fullData {
shuffledFullData[shuffledIdxs[i]] = b
}Analysts face encrypted information fragments interleaved with decryption keys throughout randomized reminiscence areas.
Seed Transformation Mechanics
This chain-based method creates cryptographic dependencies between bytes utilizing evolving seed values:
seed := byte(obfRand.Uint32())
for i, b := vary information {
encB := evalOperator(op, b, seed)
seed += encB
}Decompiled code reveals successive CALL directions that sequentially replace the seed by means of arithmetic operations.
Break up Transformation Infrastructure
Garble partitions strings into chunked ciphertexts managed by means of state machines:
switchCases := []ast.Stmt{&ast.CaseClause{
Checklist: []ast.Expr{ah.IntLit(decryptIndex)},
Physique: shuffleStmts(obfRand,
&ast.AssignStmt{
Lhs: []ast.Expr{ast.NewIdent("i")},
Tok: token.ASSIGN,
Rhs: []ast.Expr{ah.IntLit(exitIndex)},
},
decryptLogic)}}Management circulate jumps between randomized SWITCH instances to reassemble encrypted payloads.
GoStringUngarbler’s Deobfuscation Pipeline
The instrument implements a three-stage course of combining sample recognition, emulation, and binary modification:
1. Subroutine Identification
Common expressions goal garble’s meeting fingerprints previous runtime_slicebytetostring calls:
48 8D 5C ?? ?? lea rbx, [rsp+]
B9 ?? ?? ?? ?? mov ecx,
E8 ?? ?? ?? ?? name runtime_slicebytetostring YARA guidelines classify transformation sorts primarily based on register initialization patterns.
2. Emulation Engine
Unicorn-based emulation executes decryptors from recognized prologues:
49 3B ?? ?? cmp rsp, [+]
76 ?? jbe quick Reminiscence snapshots seize decrypted strings post-emulation with out executing malware payloads.
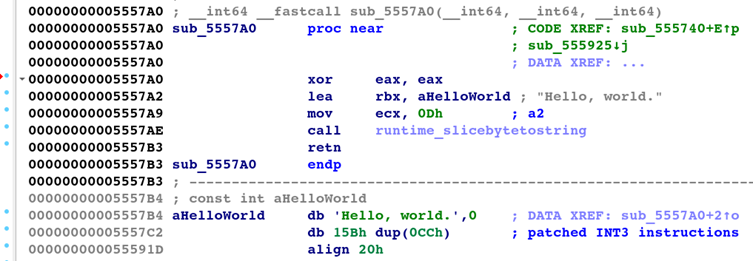
3. Binary Patching
Authentic decryptors endure surgical substitute with static string masses:
xor eax, eax
lea rbx, 0x5FFD00 ; Decrypted string deal with
mov ecx, 0x1A ; String size
name runtime_slicebytetostring
retThe remaining operate house will get padded with INT3 breakpoints to forestall execution artifacts.
Implications for Malware Evaluation
GoStringUngarbler introduces paradigm shifts in three key areas:
- Automated TTP Extraction: Over 92% of garble-obfuscated strings in examined samples had been efficiently recovered, enabling sooner IOC era.
- Cross-Platform Evaluation: Python implementation permits integration with disassemblers like Ghidra and Binary Ninja with out vendor lock-in.
- Proactive Protection: Open-source availability (Mandiant GitHub) lets EDR distributors incorporate deobfuscation into scanning pipelines pre-execution.
Google’s breakthrough demonstrates that garble’s protections—whereas subtle—aren’t insurmountable.
By combining instruction sample evaluation with emulation and surgical binary modifying, GoStringUngarbler delivers sensible countermeasures towards evolving Go malware threats.
Safety groups ought to combine this instrument into reverse engineering workflows to neutralize obfuscation benefits at the moment exploited by adversaries.
Acquire Menace Intelligence on the Newest Malware and Phishing Assaults with ANY.RUN TI Lookup -> Strive free of charge
