Introduction
Within the earlier weblog put up we coated the excessive availability function of Cloudera Operational Database (COD) in Amazon AWS. Cloudera lately launched a brand new model of COD, which provides HA assist to Microsoft Azure-based databases within the Cloud. On this put up, we’ll carry out an analogous check to validate that the function works as anticipated in Azure, too. We won’t repeat ourselves, so it’s assumed that applied sciences and ideas like HA, Multi-AZ, and operational databases are already recognized to the reader by the earlier weblog put up.
Preparation
“Availability zones” in Azure are barely totally different from AWS. In contrast to in AWS, one can’t simply make the most of the subnets to assign assets to the supply zone. Digital networks and subnets are zone redundant in Azure so the supply zone must be specified for digital machines and public IPs to distribute the VMs throughout availability zones. See Azure availability zones. See Azure zone service and regional assist to grasp the areas and providers that assist availability zones.
To make use of the Multi-AZ function for each element within the platform, the next stipulations must be met:
- Azure PostgreSQL Versatile Server: The Azure area that you choose ought to assist Azure PostgreSQL Versatile Server and the occasion sorts for use. See Versatile Server Azure Areas.
- Zone-Redundant Storage (ZRS): The ADLS gen two storage account needs to be created as zone-redundant storage (ZRS). To specify ZRS by way of Azure CLI throughout storage account creation, the –sku choice needs to be set to Standard_ZRS. Under is the Azure CLI command:

Cloudera permits FreeIPA servers, enterprise knowledge lake, and knowledge hub to be configured as Multi-AZ deployment. To arrange a Multi-AZ deployment, availability zones must be configured on the atmosphere stage. We are able to optionally specify an specific checklist of availability zones as a part of CDP atmosphere creation. If not given, all availability zones, i.e. 1, 2, and three, can be used.
Under is the CDP CLI command for a similar:

For present environments, we are able to use CLI to configure an inventory of AZs. Under is the CLI command:

The checklist of configured availability zones may be verified on the abstract web page for the atmosphere on CDP UI:
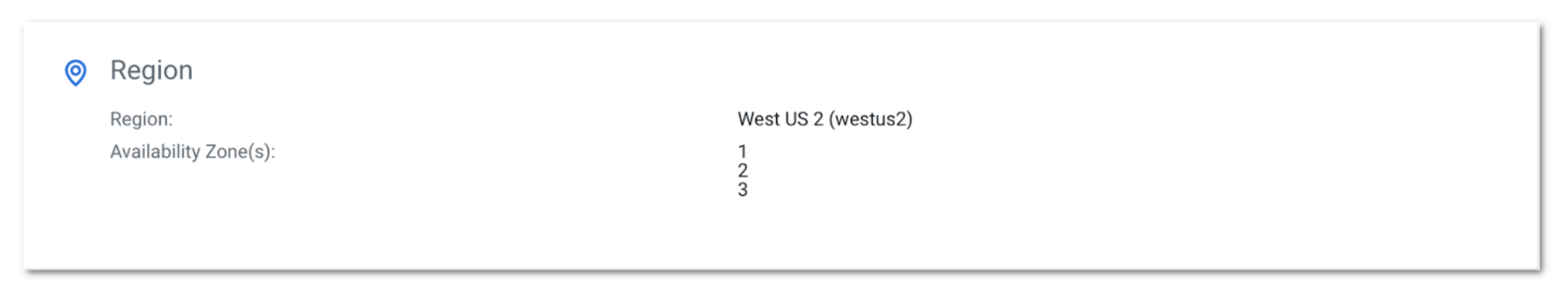
We are able to additionally replace the checklist of availability zones by way of CDP UI. Whereas updating the checklist of availability zones for an atmosphere, it will probably solely be prolonged, which implies we can’t take away the supply zones.
To configure FreeIPA as Multi-AZ, it must be specified as a part of atmosphere creation by way of CLI or GUI. Under is the CLI command:

To configure the information lake as Multi-AZ, it must be specified as a part of knowledge lake creation by way of CLI or GUI. Under is the CLI command:

Notice: Solely enterprise knowledge lake may be configured as Multi-AZ.
For the Multi-AZ knowledge lake, nodes for every occasion group can be distributed throughout configured availability zones. This may be verified by nodes on CDP UI as proven under for the core host group:
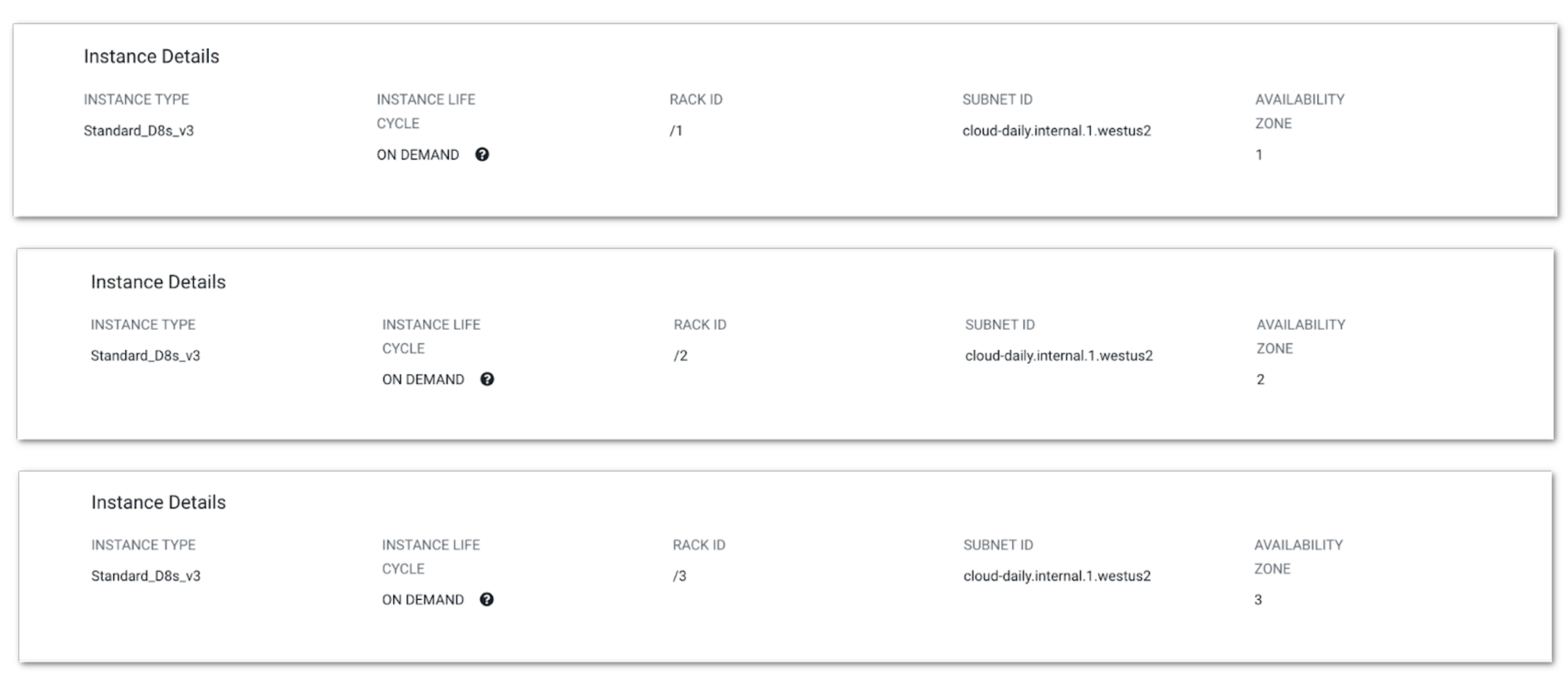
Multi-AZ knowledge lake can even use Postgres Versatile Server because it helps HA.
Along with the Multi-AZ choice, we are able to additionally specify the checklist of AZs for particular occasion teams if wanted. The checklist of availability zones for particular cases must be a subset of AZs configured on the atmosphere stage. If not specified, AZs configured for the atmosphere can be used. For the Multi-AZ knowledge hub, nodes for every occasion group can be distributed throughout configured availability zones for the occasion group. This may be verified by nodes on CDP UI.
To create a Multi-AZ COD cluster, use the next CLI command:

COD automates the information hub creation fully: assuming we have already got the required entitlements in COD, we are able to simply create a brand new database that can be robotically allotted to all out there AZs. Our check cluster has been created with the sunshine responsibility choice, which means it has 9 nodes (two masters, one chief, one gateway, and 5 staff) accommodated in three AZs. Pop the hood and see what it appears to be like like in Azure portal:
Names of digital machines are a bit cryptic. The allocation appears to be like like this:
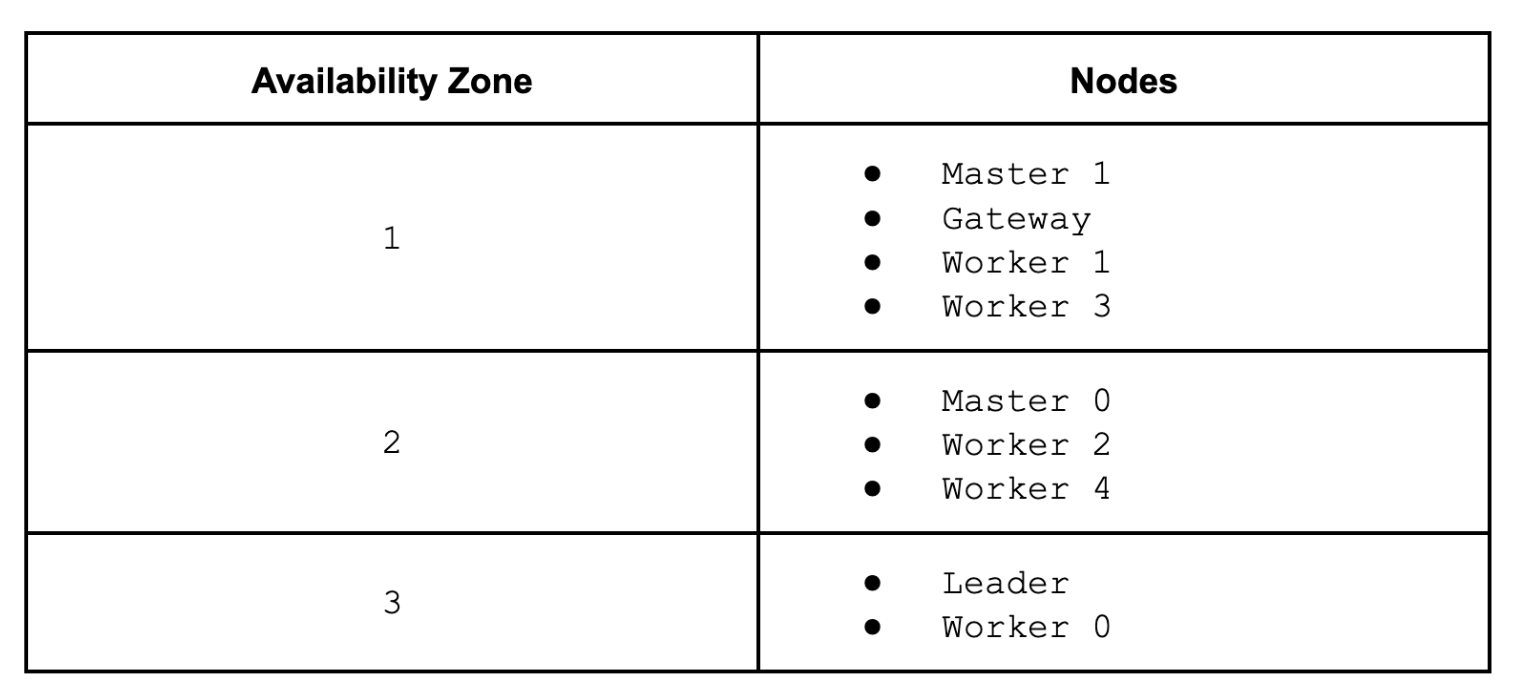
Within the simulation we’re going to cease digital machines in AZ quantity 2, which can even convey down the HBase energetic grasp (grasp 0), so the backup grasp (grasp 1) has to take over the position. The way in which we do the simulation is totally different from the AWS check case as a result of we can’t outline an analogous community rule to dam the visitors. As an alternative, we simply gracefully cease and restart the nodes on Azure portal, however it’s nonetheless appropriate to confirm HBase failover habits.
Take a look at shopper
We use the identical command line to begin the usual HBase load check instrument as a check shopper which can ship write requests to the cluster whereas we’re simulating a failure:
hbase ltt -write 10:1024:10 -num_keys 10000000
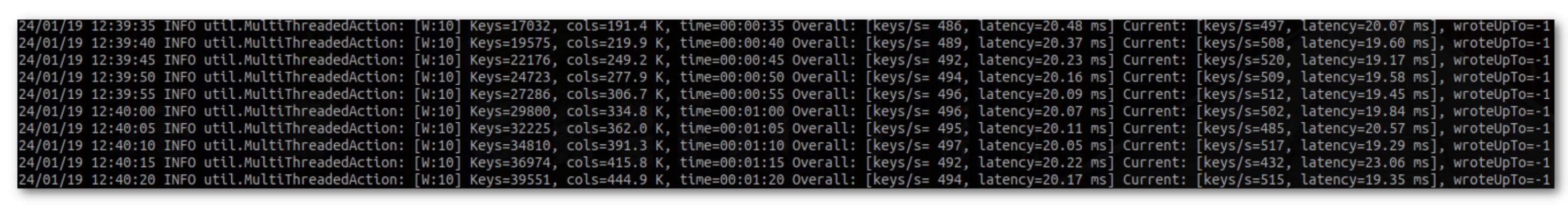
Demo
COD is displaying a inexperienced state, so we are able to begin.
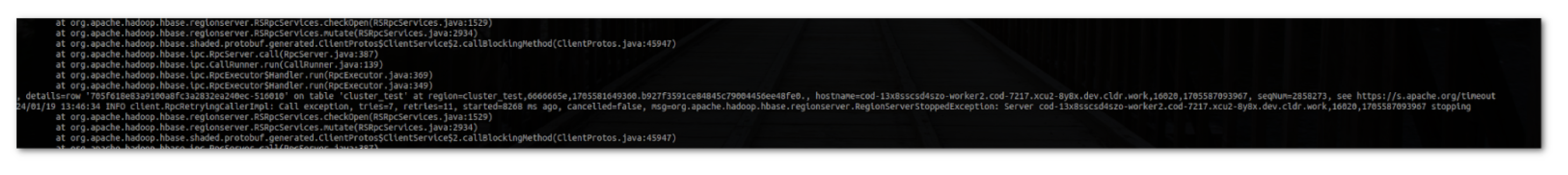
First, we cease the digital machines on the Azure portal display screen and see what occurs. The shopper begins to expertise the failure at 13:46 with exceptions: timeout, unable to entry area, and no path to host errors.
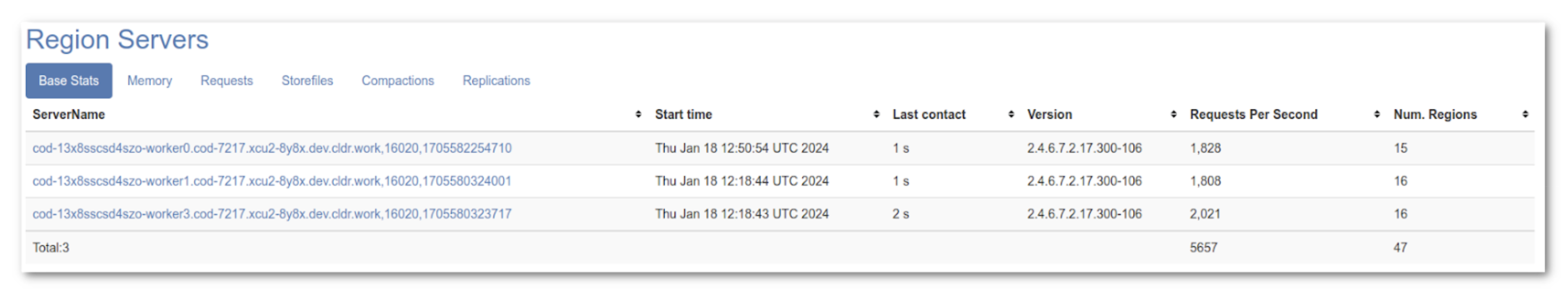
The backup grasp takes over the grasp position and finishes the boot course of at 13:50. It’s displaying we solely have three dwell area servers.
As soon as RITs (area in transition) processes are completed, the shopper recovers and begins making progress at 13:52.

The COD console reveals we’ve got node failure and the cluster is operating on degraded efficiency.
We restart the nodes now. The shopper doesn’t expertise any change and retains progressing. Efficiency is just not impacted on this check state of affairs, as a result of this single shopper doesn’t put sufficient load on the 5 or three staff.
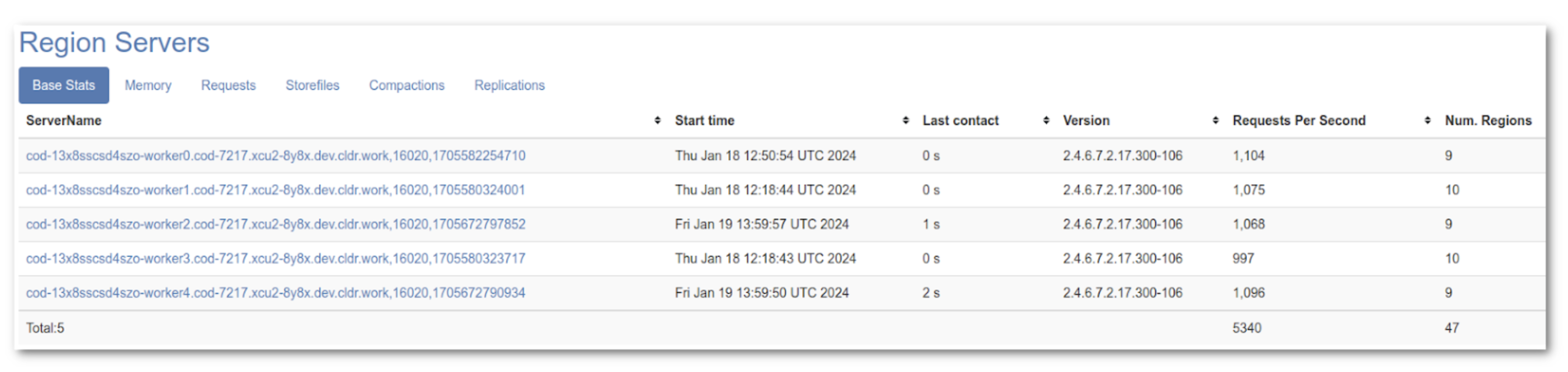
All 5 area servers have joined the cluster and have began receiving write requests.
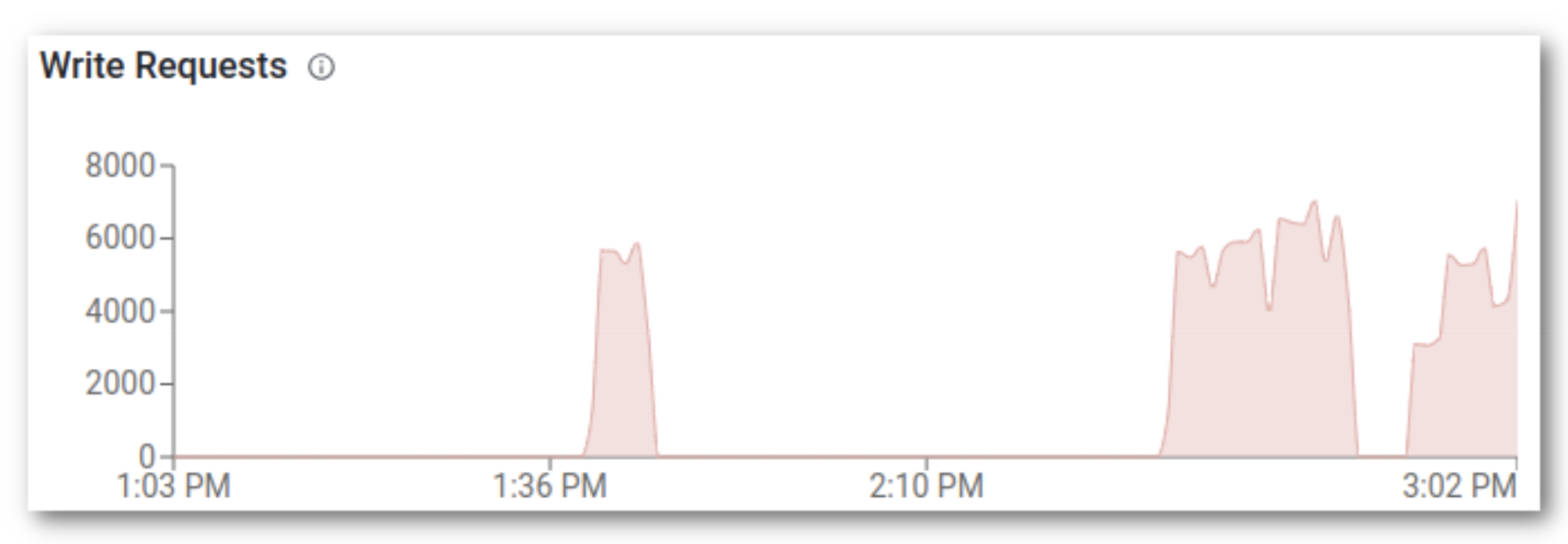
The COD console reveals that we’re again in enterprise and had a six-minute outage in write requests.
Abstract
On this weblog put up we simulate an availability zone failure within the Microsoft Azure cloud atmosphere with Cloudera Operation Database service. We’ve confirmed that HBase can detect the failure and recuperate the service by booting the backup grasp to take over the grasp position in a couple of minutes and transition unavailable areas to dwell area servers. The shopper additionally seen the failure and skilled a seven to eight minute outage, however after HBase recovered it was capable of proceed processing with out handbook intervention.
Nevertheless, there are some things to notice concerning the check. First, it’s unattainable to simulate a real-world AZ outage in any cloud atmosphere. Cloud suppliers merely don’t assist that, sadly, so we are able to solely attempt to method it as intently as doable. An actual-world outage can be totally different in some regard. As an illustration, for our simulation we did a swish cease command on VMs. In a real-world state of affairs, it may take extra time for HBase to detect the failure and recuperate.
Second, efficiency is a important side of an operational database and it’s severely impacted by a complete availability zone failure. This should be intently monitored and manually addressed by lowering the load or mentioning new employee nodes within the out there areas. COD has the auto-scaling function that involves the rescue in a scenario like this.


