Cloud safety researchers have uncovered alarming tendencies in identification compromises inside Amazon Internet Providers (AWS) environments.
Among the many most prolific risk actors is a gaggle dubbed “EC2 Grouper,” identified for exploiting compromised credentials to hold out subtle assaults utilizing AWS instruments.
Over the previous couple of years, EC2 Grouper has been lively in dozens of buyer environments, marking them as a persistent risk to cloud infrastructures.
Ways and Strategies
EC2 Grouper leverages AWS PowerShell instruments to automate their assaults, with their consumer agent offering a key early indicator of their actions.
Initially constant over a number of years, their consumer agent not too long ago advanced to incorporate uncommon hash (#) characters, signaling potential countermeasures towards conventional detection strategies.
Different figuring out markers embody the creation of safety teams with systematic naming conventions resembling “ec2group,” suffixed with sequential numbers (e.g., ec2group12345).
These teams are created utilizing the CreateSecurityGroup API, a tactic enabling lateral motion and potential useful resource hijacking.
The group’s modus operandi includes gathering intelligence about cloud environments by APIs, together with:
- DescribeInstanceTypes: To stock EC2 sorts.
- DescribeRegions: To establish obtainable areas for assets.
- DescribeVpcs, DescribeSecurityGroups, and DescribeInstances: To map the shopper’s setting.
- RunInstances: To launch new EC2 situations.
Curiously, EC2 Grouper usually refrains from configuring inbound entry utilizing the AuthorizeSecurityGroupIngress API.
As a substitute, they often make use of APIs like CreateInternetGateway and CreateVpc to ascertain distant entry pathways.
EC2 Grouper’s assaults are usually fueled by compromised AWS credentials, usually originating from code repositories the place builders unintentionally expose delicate keys.
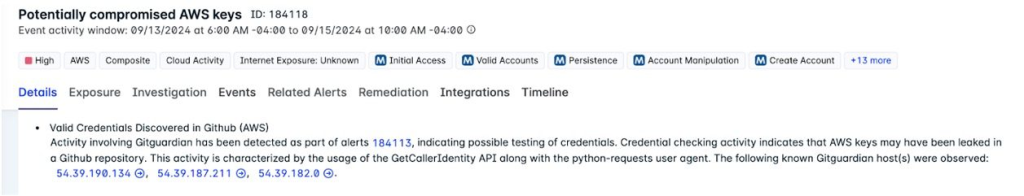

Based on the Fortinet experiences, public repositories have been a hotbed for such incidents, with the group benefiting from credentials leaked by platforms like GitHub.
Detecting EC2 Grouper’s illicit actions hinges on correlating a number of alerts. Whereas atomic indicators like consumer brokers or safety group conventions can help in attribution, they alone are inadequate for dependable detection resulting from their transient nature. Key defensive methods embody:
- Secret Scanning Providers: Using instruments like GitGuardian and GitHub’s secret scanning to detect uncovered credentials.
- Composite Alerts: Correlating varied alerts, resembling uncommon API sequences, privilege escalation makes an attempt, and anomalous setting habits.
- Anomaly Detection: Figuring out deviations in cloud utilization patterns to flag potential reconnaissance or malicious actions.
The rise of attackers like EC2 Grouper underlines the essential want for strong cloud safety practices.
Whereas figuring out malicious use of compromised credentials stays difficult, superior detection mechanisms, supplemented by instruments like Lacework FortiCNAPP, can present complete safety.
As attackers proceed to refine their strategies, organizations should prioritize proactive monitoring, credential hygiene, and anomaly detection to safeguard their cloud environments.
Examine Actual-World Malicious Hyperlinks, Malware & Phishing Assaults With ANY.RUN – Attempt for Free

