When constructing data-driven purposes, it’s been a standard apply for years to maneuver analytics away from the supply database into both a slave, information warehouse or one thing comparable. The principle cause for that is that analytical queries, resembling aggregations and joins, are inclined to require much more sources. When working, the detrimental influence on database efficiency might reverberate again to front-end customers and have a adverse influence on their expertise.
Analytical queries are inclined to take longer to run and use extra sources as a result of firstly they’re performing calculations on giant information units and in addition probably becoming a member of a number of information units collectively. Moreover, an information mannequin that works for quick storage and retrieval of single rows most likely gained’t be probably the most performant for giant analytical queries.
To alleviate the stress on the principle database, information groups usually replicate information to an exterior database for working analytical queries. Personally, with MongoDB, transferring information to a SQL-based platform is extraordinarily helpful for analytics. Most information practitioners perceive the right way to write SQL queries, nevertheless MongoDB’s question language isn’t as intuitive so will take time to study. On prime of this, MongoDB additionally isn’t a relational database so becoming a member of information isn’t trivial or that performant. It subsequently can be helpful to carry out any analytical queries that require joins throughout a number of and/or giant datasets elsewhere.
To this finish, Rockset has partnered with MongoDB to launch a MongoDB-Rockset connector. Which means information saved in MongoDB can now be immediately listed in Rockset by way of a built-in connector. On this put up I’m going to discover the use circumstances for utilizing a platform like Rockset on your aggregations and joins on MongoDB information and stroll by way of organising the combination so you may stand up and working your self.
Suggestions API for an On-line Occasion Ticketing System
To discover the advantages of replicating a MongoDB database into an analytics platform like Rockset, I’ll be utilizing a simulated occasion ticketing web site. MongoDB is used to retailer weblogs, ticket gross sales and consumer information. On-line ticketing techniques can usually have a really excessive throughput of knowledge in brief time frames, particularly when wanted tickets are launched and hundreds of individuals are all making an attempt to buy tickets on the identical time.

It’s subsequently anticipated {that a} scaleable, high-throughput database like MongoDB can be used because the backend to such a system. Nevertheless, if we’re additionally making an attempt to floor real-time analytics on this information, this might trigger efficiency points particularly when coping with a spike in exercise. To beat this, I’ll use Rockset to duplicate the info in actual time to permit computational freedom on a separate platform. This fashion, MongoDB is free to take care of the massive quantity of incoming information, while Rockset handles the advanced queries for purposes, resembling making suggestions to customers, dynamic pricing of tickets, or detecting anomalous transactions.
I’ll run by way of connecting MongoDB to Rockset after which present how one can construct dynamic and real-time suggestions for customers that may be accessed by way of the Rockset REST API.
Connecting MongoDB to Rockset
The MongoDB connector is at present accessible to be used with a MongoDB Atlas cluster. On this article I’ll be utilizing a MongoDB Atlas free tier deployment, so ensure you have entry to an Atlas cluster if you’re going to comply with alongside.
To get began, open the Rockset console. The MongoDB connector could be discovered throughout the Catalog, choose it after which click on the Create Assortment button adopted by Create Integration.
As talked about earlier, I’ll be utilizing the absolutely managed MongoDB Atlas integration highlighted in Fig 1.
Fig 1. Including a MongoDB integration
Simply comply with the directions to get your Atlas occasion built-in with Rockset and also you’ll then have the ability to use this integration to create Rockset collections. Chances are you’ll discover you should tweak a number of permissions in Atlas for Rockset to have the ability to see the info, but when every little thing is working, you’ll see a preview of your information while creating the gathering as proven in Fig 2.
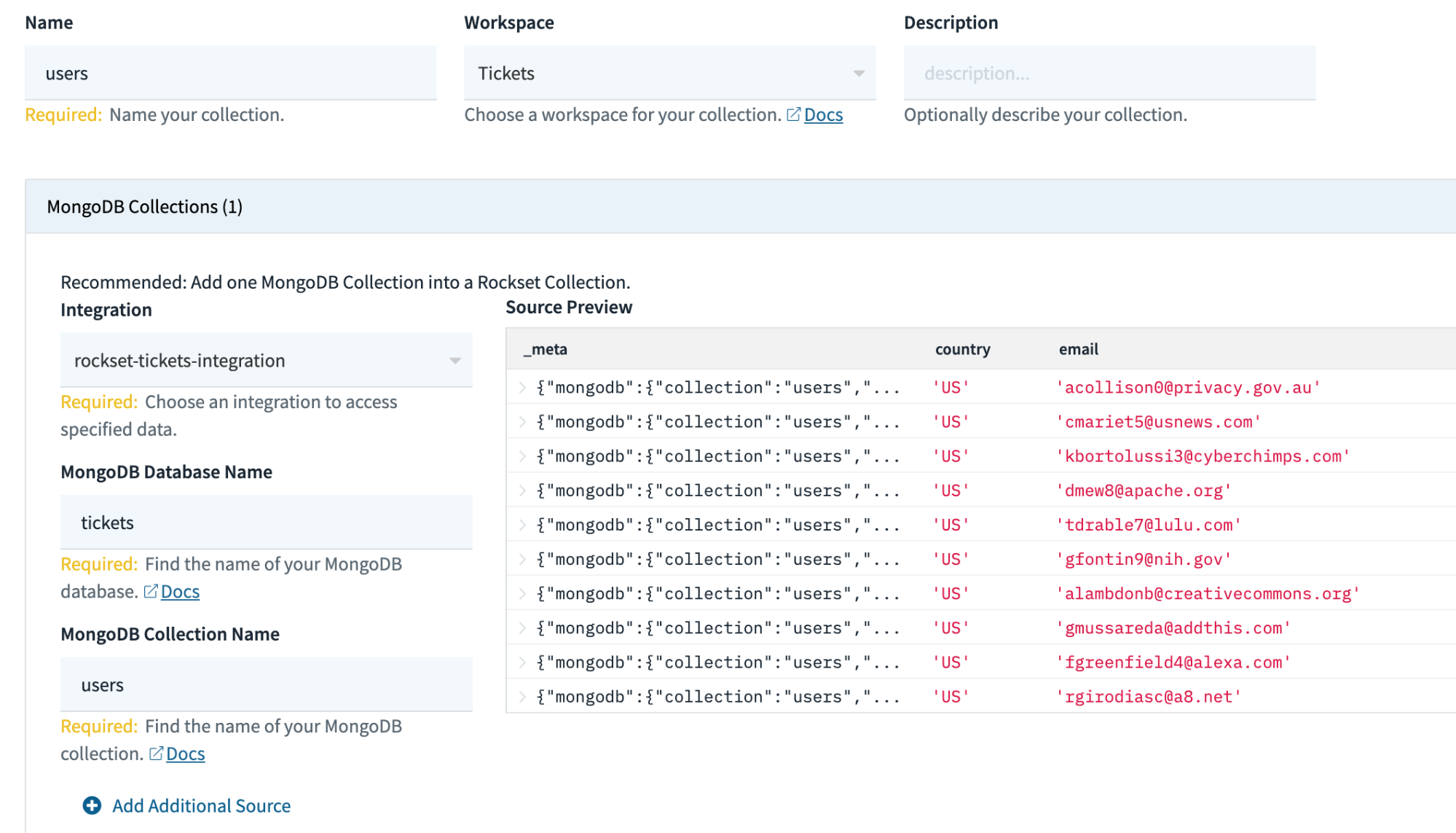
Fig 2. Making a MongoDB assortment
Utilizing this identical integration I’ll be creating 3 collections in complete: customers, tickets and logs. These collections in MongoDB are used to retailer consumer information together with favorite genres, ticket purchases and weblogs respectively.
After creating the gathering, Rockset will then fetch all the info from Mongo for that assortment and offer you a stay replace of what number of information it has processed. Fig.3 exhibits the preliminary scan of my logs desk reporting that it has discovered 4000 information however 0 have been processed.
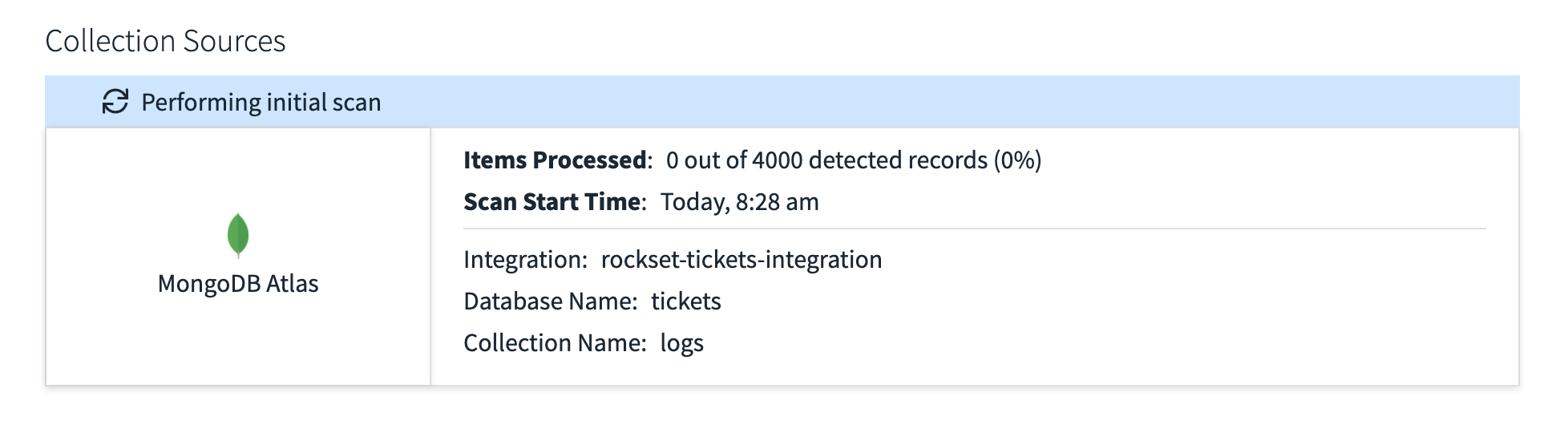
Fig 3. Performing preliminary scan of MongoDB assortment
Inside only a minute all 4000 information have been processed and introduced into Rockset, as new information is added or updates are made, Rockset will mirror them within the assortment too. To check this out I simulated a number of situations.
Testing the Sync
To check the syncing functionality between Mongo and Rockset I simulated some updates and deletes on my information to verify they have been synced appropriately. You may see the preliminary model of the document in Rockset in Fig 4.
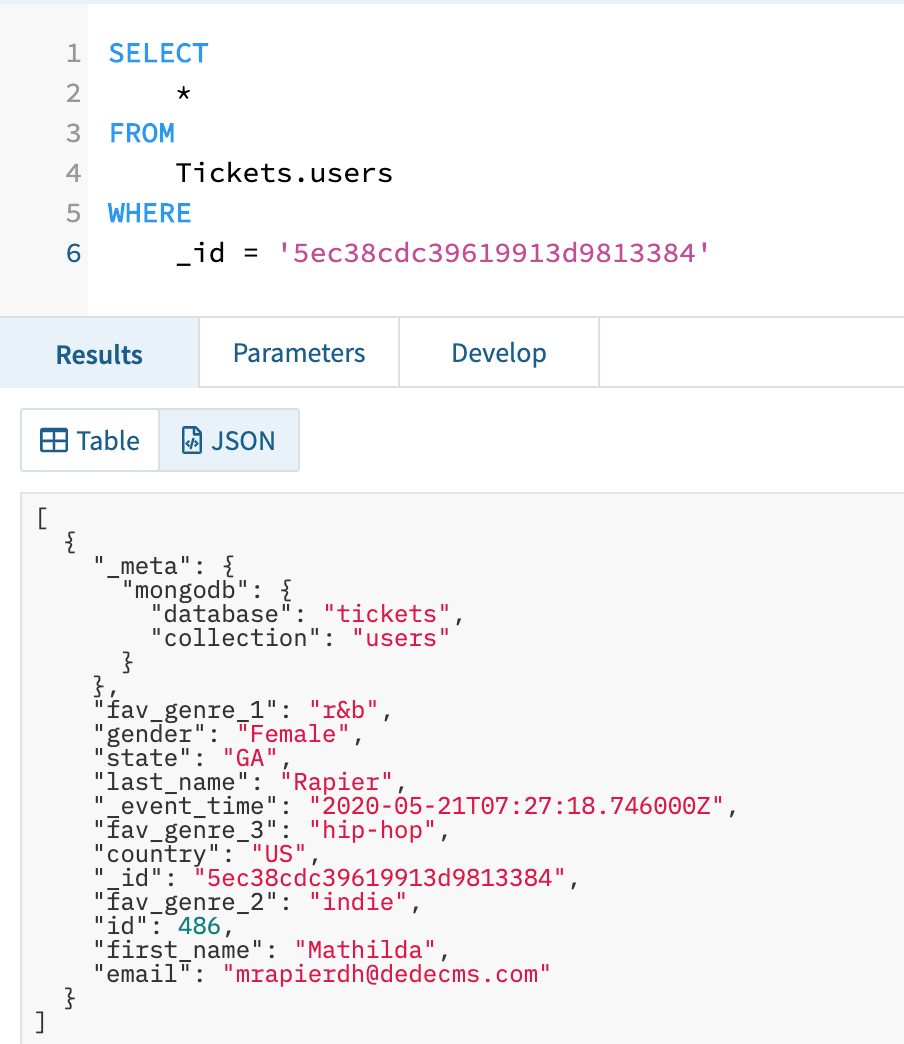
Fig 4. Instance consumer document earlier than an replace
Now let’s say that this consumer adjustments one in every of their favorite genres, let’s say fav_genre_1 is now ‘pop’ as an alternative of ‘r&b’. First I’ll carry out the replace in Mongo like so.
db.customers.replace({"_id": ObjectId("5ec38cdc39619913d9813384")}, { $set: {"fav_genre_1": "pop"} } )
Then run my question in Rockset once more and verify to see if it has mirrored the change. As you may see in Fig 5, the replace was synced appropriately to Rockset.
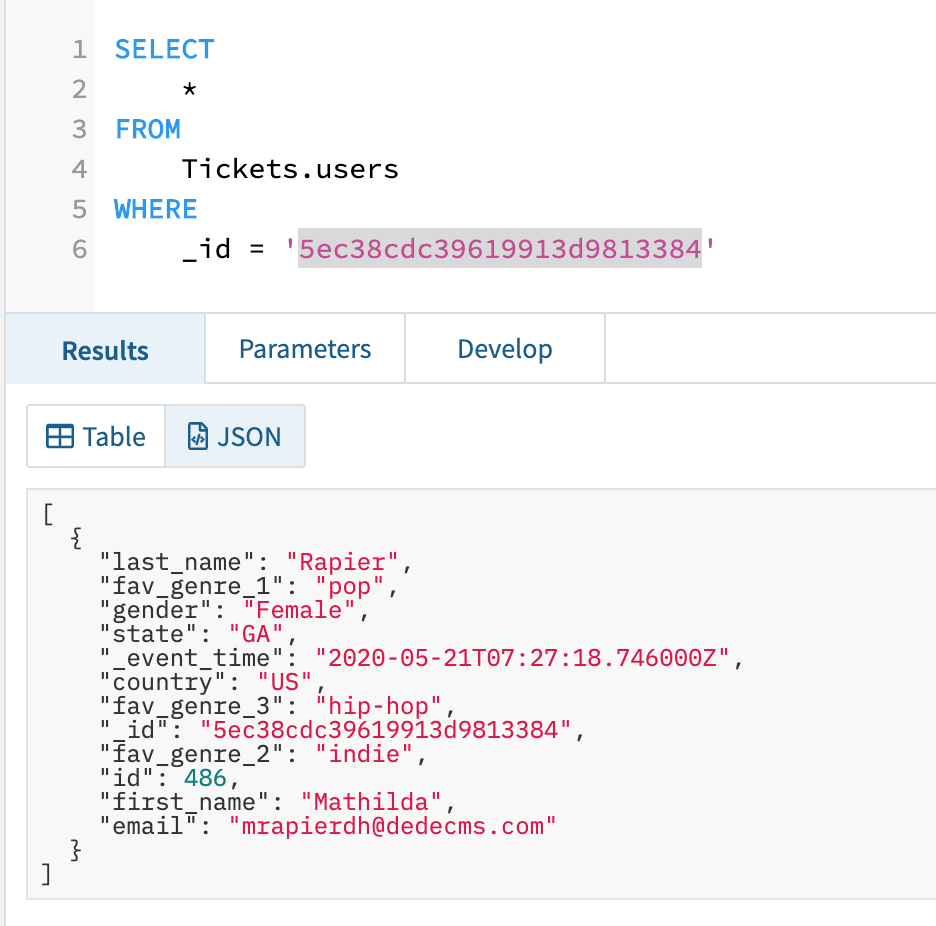
Fig 5. Up to date document in Rockset
I then eliminated the document from Mongo and once more as proven in Fig 6 you may see the document now now not exists in Rockset.
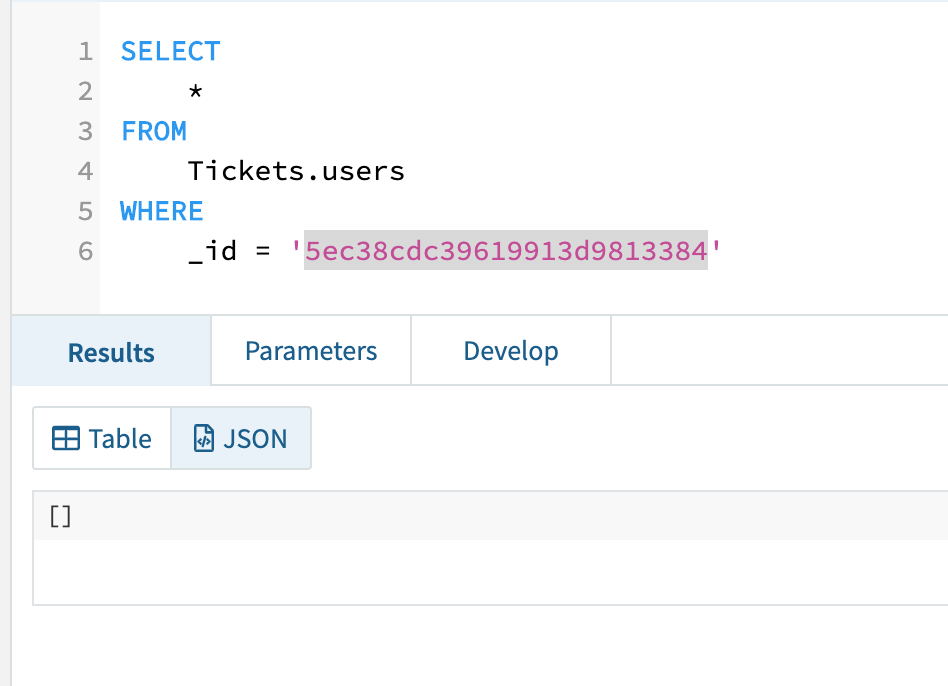
Fig 6. Deleted document in Rockset
Now we’re assured that Rockset is appropriately syncing our information, we will begin to leverage Rockset to carry out analytical queries on the info.
Composing Our Suggestions Question
We are able to now question our information inside Rockset. We’ll begin within the console and take a look at some examples earlier than transferring on to utilizing the API.
We are able to now use customary SQL to question our MongoDB information and this brings one notable profit: the flexibility to simply be part of datasets collectively. If we wished to indicate the variety of tickets bought by customers, exhibiting their first and final title and variety of tickets, in Mongo we’d have to jot down a reasonably prolonged and sophisticated question, particularly for these unfamiliar with Mongo question syntax. In Rockset we will simply write a simple SQL question.
SELECT customers.id, customers.first_name as "First Title", customers.last_name as "Final Title", rely(tickets.ticket_id) as "Variety of Tickets Bought"
FROM Tickets.customers
LEFT JOIN Tickets.tickets ON tickets.user_id = customers.id
GROUP BY customers.id, customers.first_name, customers.last_name
ORDER BY 4 DESC;
With this in thoughts, let’s write some queries to supply suggestions to customers and present how they might be built-in into an internet site or different entrance finish.
First we will develop and check our question within the Rockset console. We’re going to search for the highest 5 tickets which were bought for a consumer’s favorite genres inside their state. We’ll use consumer ID 244 for this instance.
SELECT
u.id,
t.artist,
rely(t.ticket_id)
FROM
Tickets.tickets t
LEFT JOIN Tickets.customers u on (
t.style = u.fav_genre_1
OR t.style = u.fav_genre_2
OR t.style = u.fav_genre_2
)
AND t.state = u.state
AND t.user_id != u.id
WHERE u.id = 244
GROUP BY 1, 2
ORDER BY 3 DESC
LIMIT 5
This could return the highest 5 tickets being advisable for this consumer.
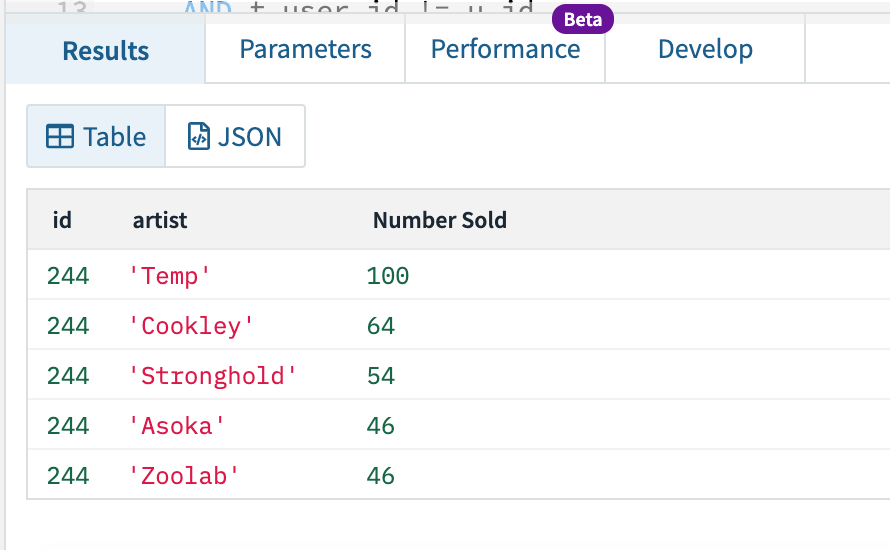
Fig 7. Suggestion question outcomes
Now clearly we would like this question to be dynamic in order that we will run it for any consumer, and return it again to the entrance finish to be exhibited to the consumer. To do that we will create a Question Lambda in Rockset. Consider a Question Lambda like a saved process or a operate. As a substitute of writing the SQL each time, we simply name the Lambda and inform it which consumer to run for, and it submits the question and returns the outcomes.
Very first thing we have to do is prep our assertion in order that it’s parameterised earlier than turning it right into a Question Lambda. To do that choose the Parameters tab above the place the outcomes are proven within the console. You may then add a parameter, on this case I added an int parameter known as userIdParam as proven in Fig 8.
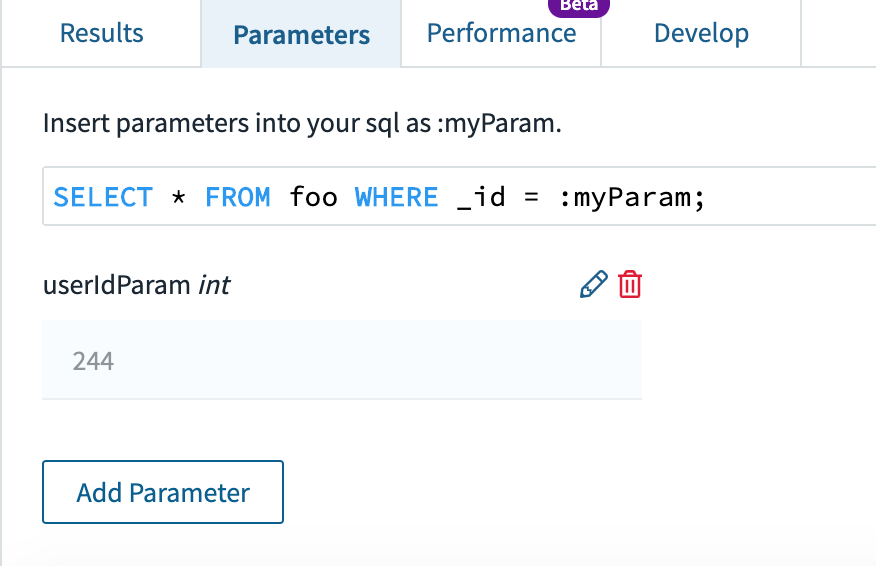
Fig 8. Including a consumer ID parameter
With a slight tweak to our the place clause proven in Fig 9 we will then utilise this parameter to make our question dynamic.
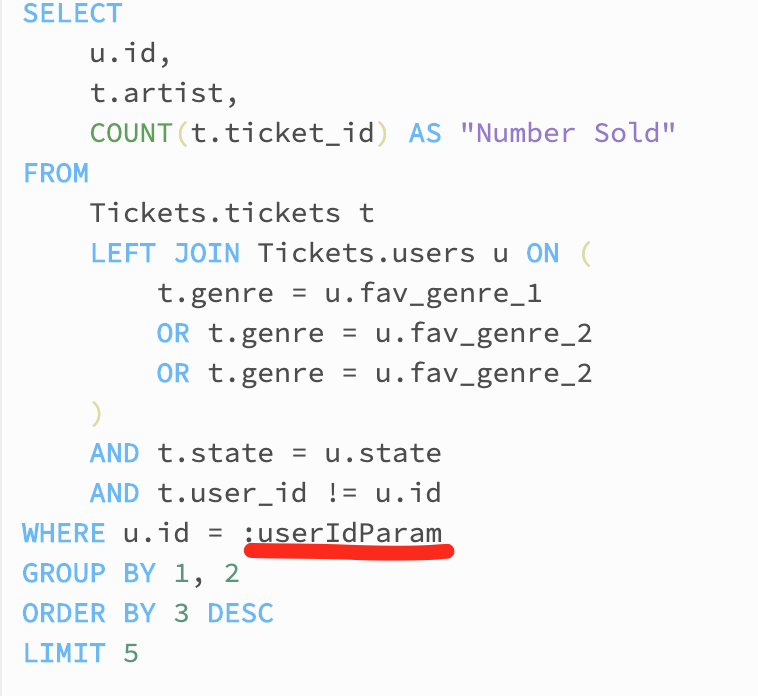
Fig 9. Parameterised the place clause
With our assertion parameterised, we will now click on the Create Question Lambda button above the SQL editor. Give it a reputation and outline and reserve it. That is now a operate we will name to run the SQL for a given consumer. Within the subsequent part I’ll run by way of utilizing this Lambda by way of the REST API which might then permit a entrance finish interface to show the outcomes to customers.
Suggestions by way of REST API
To see the Lambda you’ve simply created, on the left hand navigation choose Question Lambdas and choose the Lambda you’ve simply created. You’ll be introduced with the display screen proven in Fig 10.
Fig 10. Question Lambda overview
This web page exhibits us particulars about how usually the Lambda has been run and its common latency, we will additionally edit the Lambda, take a look at the SQL and in addition see the model historical past.
Scrolling down the web page we’re additionally given examples of code that we might use to execute the Lambda. I’m going to take the Curl instance and replica it into Postman so we will try it out. Notice, you could have to configure the REST API first and get your self a key setup (within the console on the left navigation go to ‘API Keys’).
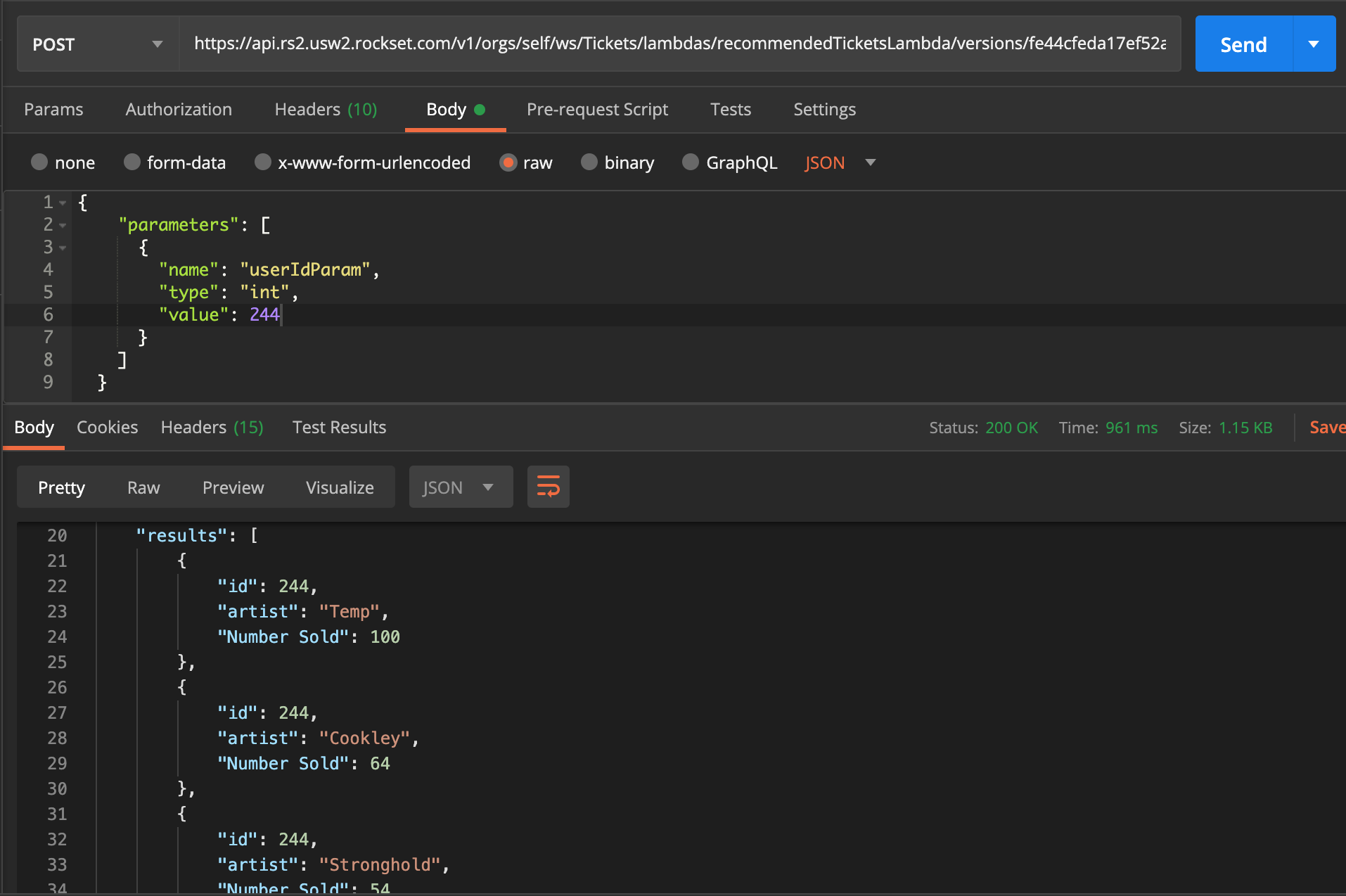
Fig 11. Question Lambda Curl instance in Postman
As you may see in Fig 11, I’ve imported the API name into Postman and might merely change the worth of the userIdParam throughout the physique, on this case to id 244, and get the outcomes again. As you may see from the outcomes, consumer 244’s highest advisable artist is ‘Temp’ with 100 tickets offered just lately of their state. This might then be exhibited to the consumer when searching for tickets, or on a homepage that gives advisable tickets.
Conclusion
The great thing about that is that each one the work is finished by Rockset, liberating up our Mongo occasion to take care of giant spikes in ticket purchases and consumer exercise. As customers proceed to buy tickets, the info is copied over to Rockset in actual time and the suggestions for customers will subsequently be up to date in actual time too. This implies well timed and correct suggestions that can enhance total consumer expertise.
The implementation of the Question Lambda signifies that the suggestions can be found to be used instantly and any adjustments to the underlying performance of constructing suggestions could be rolled out to all customers of the info in a short time, as they’re all utilizing the underlying operate.
These two options present nice enhancements over accessing MongoDB straight and provides builders extra analytical energy with out affecting core enterprise performance.
Different MongoDB sources:
Lewis Gavin has been an information engineer for 5 years and has additionally been running a blog about abilities throughout the Information group for 4 years on a private weblog and Medium. Throughout his laptop science diploma, he labored for the Airbus Helicopter crew in Munich enhancing simulator software program for navy helicopters. He then went on to work for Capgemini the place he helped the UK authorities transfer into the world of Massive Information. He’s at present utilizing this expertise to assist remodel the info panorama at easyfundraising.org.uk, a web based charity cashback website, the place he’s serving to to form their information warehousing and reporting functionality from the bottom up.
Picture by Tuur Tisseghem from Pexels
