Latest analysis has linked a collection of cyberattacks to The Masks group, as one notable assault focused a Latin American group in 2022, the place attackers compromised the group’s MDaemon electronic mail server and exploited the WorldClient webmail element to take care of persistent entry.
Whereas the preliminary compromise vector stays unknown, the profitable exploitation of the MDaemon server highlights the potential dangers related to outdated or misconfigured electronic mail methods.
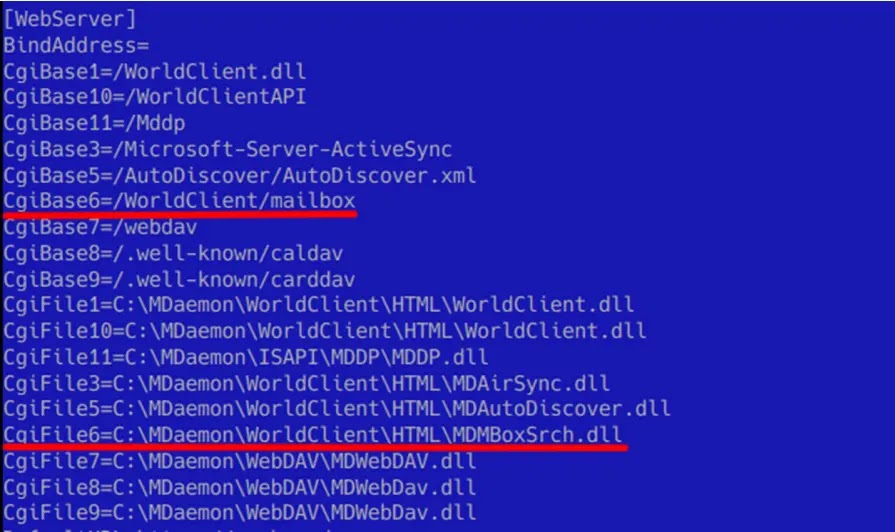
The risk actor exploited a vulnerability in MDaemon WorldClient’s extension loading mechanism. By leveraging the WorldClient.ini configuration file, they had been capable of introduce malicious extensions.

These extensions, designed to intercept and manipulate HTTP requests, supplied a persistent backdoor into the e-mail server, which allowed the attacker to take care of unauthorized entry and probably execute additional malicious actions.
Free Webinar on Finest Practices for API vulnerability & Penetration Testing: Free Registration
The risk actor exploited WorldClient’s extension function by crafting a malicious extension DLL and configuring it with malicious URLs within the CgiBase6 and CgiFile6 parameters.
It allowed the actor to remotely work together with the malicious extension through HTTP requests to the desired URL on the webmail server, bypassing safety measures and probably gaining unauthorized entry to delicate data.


Attackers leveraged a malicious eThe extension to infiltrate a Latin American group in 2022, which executed instructions to assemble system data and laterally transfer inside the community.
By using authentic software program like HitmanPro Alert’s driver and malicious DLLs, .bat information, and XML information for scheduled duties, they propagate the an infection, compromising a number of methods inside the group.
They exploited a vulnerability within the Tpm-HASCertRetr.xml description file to schedule duties that executed instructions from the ~dfae01202c5f0dba42.cmd file, which put in the hmpalert.sys driver, which, resulting from an absence of verification, might load malicious DLLs.
By putting their payload DLLs at C:WindowsSystem32hmpalert.dll, the attackers had been capable of inject these DLLs into privileged processes like winlogon.exe and dwm.exe on system startup, gaining persistent and elevated entry to the compromised methods.
In early 2024, adversaries exploited a vulnerability within the hmpalert.sys driver to contaminate a system. In contrast to earlier assaults, they bypassed scheduled duties, using a novel approach involving Google Updater.
The malicious hmpalert.dll payload, recognized as FakeHMP, enabled attackers to steal information, log keystrokes, seize screenshots, and deploy further malware, the place risk actors additional compromised methods with a microphone recorder and file stealer.
The group was compromised by a complicated assault leveraging two malicious frameworks, Careto2 and Goreto, the place Careto2, put in through a multi-stage course of, used COM hijacking for persistence and a digital filesystem to retailer plugins for numerous malicious actions.
Whereas Goreto, a Golang-based toolset, related to Google Drive for command-and-control, executing instructions, keylogging, and capturing screenshots. Each frameworks employed superior strategies, indicating a classy and protracted risk actor, probably the Masks.
Based on Safe Record, the risk actor often known as Careto stays a formidable pressure within the cyber risk panorama.
Regardless of a decade-long absence, the group continues to innovate, using superior strategies like persistence by MDaemon and implant loading through HitmanPro Alert.
Their skill to craft intricate, multi-component malware underscores their technical prowess. Whereas the timing of their subsequent marketing campaign is unsure, it’s anticipated to be equally refined and disruptive.
Examine Actual-World Malicious Hyperlinks, Malware & Phishing Assaults With ANY.RUN – Strive for Free

