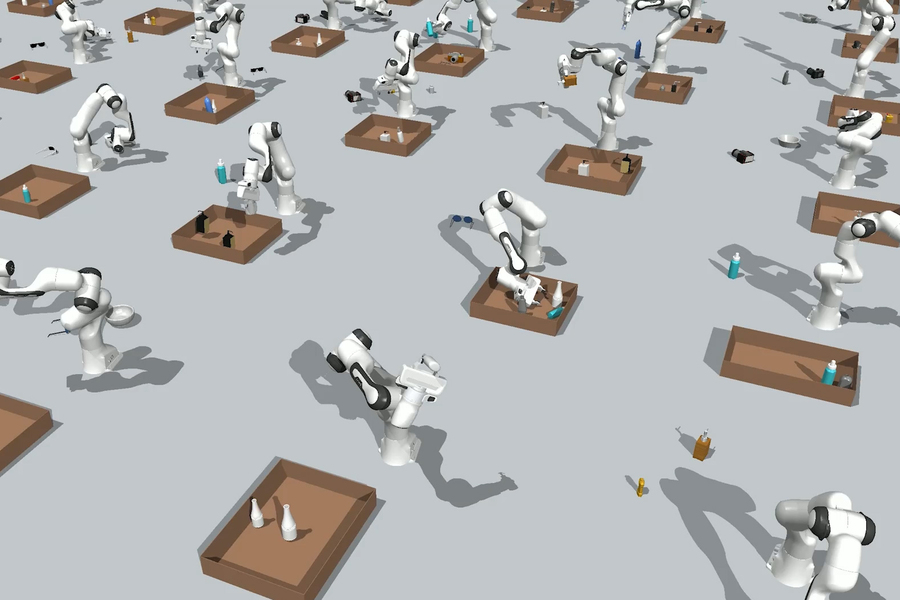

MIT researchers are utilizing generative AI fashions to assist robots extra effectively clear up complicated object manipulation issues, akin to packing a field with totally different objects. Picture: courtesy of the researchers.
By Adam Zewe | MIT Information
Anybody who has ever tried to pack a family-sized quantity of bags right into a sedan-sized trunk is aware of it is a arduous drawback. Robots battle with dense packing duties, too.
For the robotic, fixing the packing drawback includes satisfying many constraints, akin to stacking baggage so suitcases don’t topple out of the trunk, heavy objects aren’t positioned on prime of lighter ones, and collisions between the robotic arm and the automobile’s bumper are averted.
Some conventional strategies deal with this drawback sequentially, guessing a partial resolution that meets one constraint at a time after which checking to see if another constraints had been violated. With an extended sequence of actions to take, and a pile of bags to pack, this course of will be impractically time consuming.
MIT researchers used a type of generative AI, referred to as a diffusion mannequin, to resolve this drawback extra effectively. Their methodology makes use of a group of machine-learning fashions, every of which is educated to symbolize one particular sort of constraint. These fashions are mixed to generate world options to the packing drawback, bearing in mind all constraints directly.
Their methodology was in a position to generate efficient options quicker than different strategies, and it produced a better variety of profitable options in the identical period of time. Importantly, their approach was additionally in a position to clear up issues with novel mixtures of constraints and bigger numbers of objects, that the fashions didn’t see throughout coaching.
As a result of this generalizability, their approach can be utilized to show robots find out how to perceive and meet the general constraints of packing issues, such because the significance of avoiding collisions or a need for one object to be subsequent to a different object. Robots educated on this approach may very well be utilized to a big selection of complicated duties in numerous environments, from order success in a warehouse to organizing a bookshelf in somebody’s dwelling.
“My imaginative and prescient is to push robots to do extra sophisticated duties which have many geometric constraints and extra steady selections that should be made — these are the sorts of issues service robots face in our unstructured and numerous human environments. With the highly effective software of compositional diffusion fashions, we are able to now clear up these extra complicated issues and get nice generalization outcomes,” says Zhutian Yang, {an electrical} engineering and laptop science graduate pupil and lead writer of a paper on this new machine-learning approach.
Her co-authors embody MIT graduate college students Jiayuan Mao and Yilun Du; Jiajun Wu, an assistant professor of laptop science at Stanford College; Joshua B. Tenenbaum, a professor in MIT’s Division of Mind and Cognitive Sciences and a member of the Pc Science and Synthetic Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL); Tomás Lozano-Pérez, an MIT professor of laptop science and engineering and a member of CSAIL; and senior writer Leslie Kaelbling, the Panasonic Professor of Pc Science and Engineering at MIT and a member of CSAIL. The analysis can be offered on the Convention on Robotic Studying.
Constraint problems
Steady constraint satisfaction issues are notably difficult for robots. These issues seem in multistep robotic manipulation duties, like packing gadgets right into a field or setting a dinner desk. They usually contain reaching a lot of constraints, together with geometric constraints, akin to avoiding collisions between the robotic arm and the atmosphere; bodily constraints, akin to stacking objects so they’re steady; and qualitative constraints, akin to putting a spoon to the best of a knife.
There could also be many constraints, they usually differ throughout issues and environments relying on the geometry of objects and human-specified necessities.
To unravel these issues effectively, the MIT researchers developed a machine-learning approach referred to as Diffusion-CCSP. Diffusion fashions study to generate new knowledge samples that resemble samples in a coaching dataset by iteratively refining their output.
To do that, diffusion fashions study a process for making small enhancements to a possible resolution. Then, to resolve an issue, they begin with a random, very unhealthy resolution after which step by step enhance it.
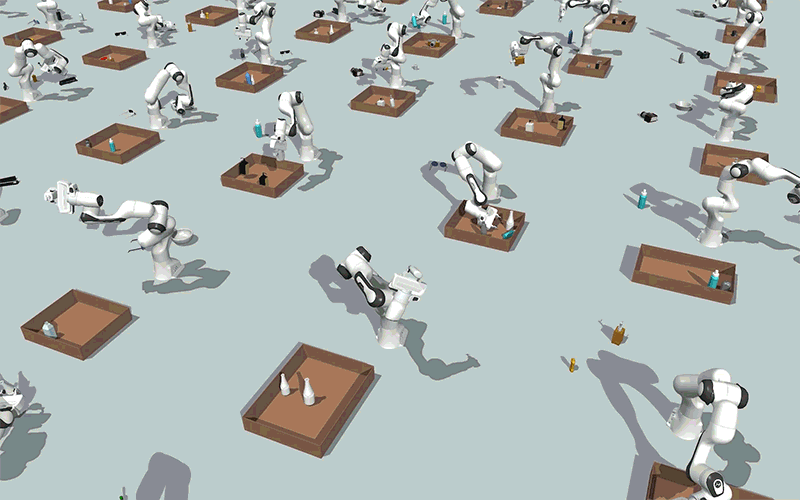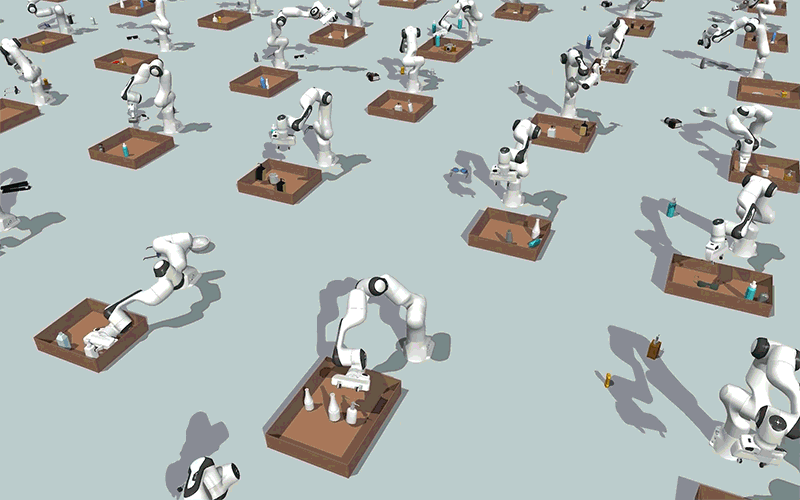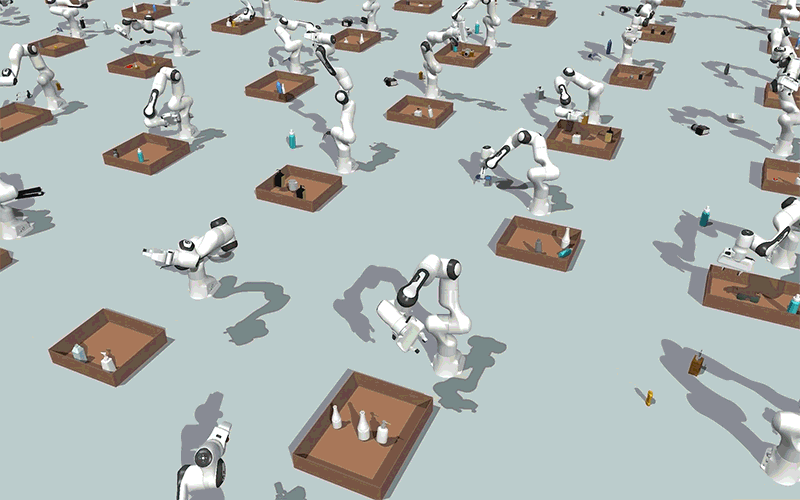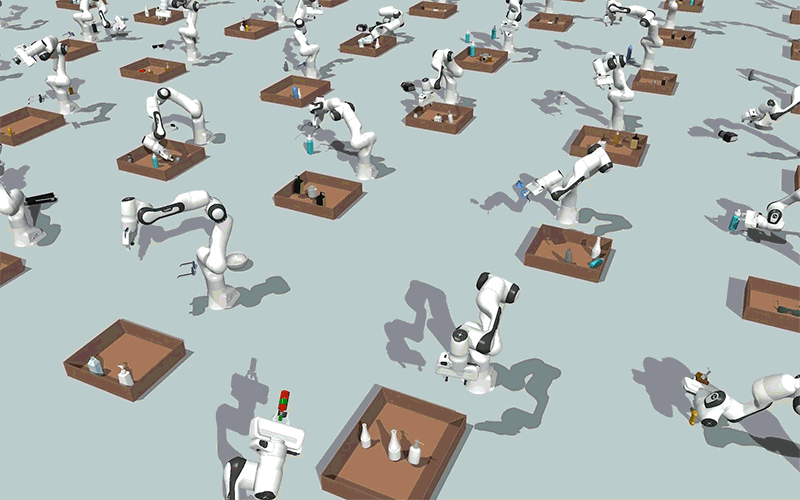
Utilizing generative AI fashions, MIT researchers created a method that might allow robots to effectively clear up steady constraint satisfaction issues, akin to packing objects right into a field whereas avoiding collisions, as proven on this simulation. Picture: Courtesy of the researchers.
For instance, think about randomly putting plates and utensils on a simulated desk, permitting them to bodily overlap. The collision-free constraints between objects will end in them nudging one another away, whereas qualitative constraints will drag the plate to the middle, align the salad fork and dinner fork, and many others.
Diffusion fashions are well-suited for this type of steady constraint-satisfaction drawback as a result of the influences from a number of fashions on the pose of 1 object will be composed to encourage the satisfaction of all constraints, Yang explains. By ranging from a random preliminary guess every time, the fashions can acquire a various set of fine options.
Working collectively
For Diffusion-CCSP, the researchers wished to seize the interconnectedness of the constraints. In packing for example, one constraint would possibly require a sure object to be subsequent to a different object, whereas a second constraint would possibly specify the place a type of objects have to be situated.
Diffusion-CCSP learns a household of diffusion fashions, with one for every sort of constraint. The fashions are educated collectively, in order that they share some information, just like the geometry of the objects to be packed.
The fashions then work collectively to seek out options, on this case areas for the objects to be positioned, that collectively fulfill the constraints.
“We don’t at all times get to an answer on the first guess. However whenever you preserve refining the answer and a few violation occurs, it ought to lead you to a greater resolution. You get steerage from getting one thing flawed,” she says.
Coaching particular person fashions for every constraint sort after which combining them to make predictions significantly reduces the quantity of coaching knowledge required, in comparison with different approaches.
Nevertheless, coaching these fashions nonetheless requires a considerable amount of knowledge that display solved issues. People would wish to resolve every drawback with conventional sluggish strategies, making the associated fee to generate such knowledge prohibitive, Yang says.
As a substitute, the researchers reversed the method by arising with options first. They used quick algorithms to generate segmented bins and match a various set of 3D objects into every phase, guaranteeing tight packing, steady poses, and collision-free options.
“With this course of, knowledge technology is nearly instantaneous in simulation. We will generate tens of 1000’s of environments the place we all know the issues are solvable,” she says.
Educated utilizing these knowledge, the diffusion fashions work collectively to find out areas objects needs to be positioned by the robotic gripper that obtain the packing activity whereas assembly all the constraints.
They carried out feasibility research, after which demonstrated Diffusion-CCSP with an actual robotic fixing a lot of troublesome issues, together with becoming 2D triangles right into a field, packing 2D shapes with spatial relationship constraints, stacking 3D objects with stability constraints, and packing 3D objects with a robotic arm.

This determine reveals examples of 2D triangle packing. These are collision-free configurations. Picture: courtesy of the researchers.
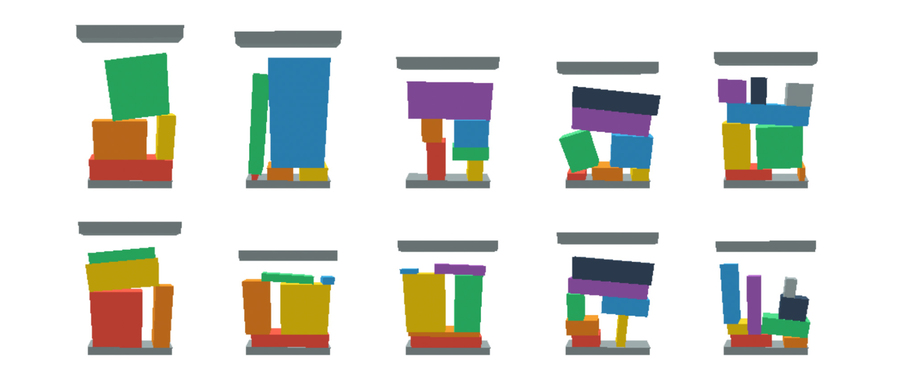
This determine reveals 3D object stacking with stability constraints. Researchers say a minimum of one object is supported by a number of objects. Picture: courtesy of the researchers.
Their methodology outperformed different strategies in lots of experiments, producing a better variety of efficient options that had been each steady and collision-free.
Sooner or later, Yang and her collaborators wish to take a look at Diffusion-CCSP in additional sophisticated conditions, akin to with robots that may transfer round a room. Additionally they wish to allow Diffusion-CCSP to deal with issues in several domains with out the should be retrained on new knowledge.
“Diffusion-CCSP is a machine-learning resolution that builds on current highly effective generative fashions,” says Danfei Xu, an assistant professor within the Faculty of Interactive Computing on the Georgia Institute of Expertise and a Analysis Scientist at NVIDIA AI, who was not concerned with this work. “It could shortly generate options that concurrently fulfill a number of constraints by composing identified particular person constraint fashions. Though it’s nonetheless within the early phases of growth, the continuing developments on this strategy maintain the promise of enabling extra environment friendly, secure, and dependable autonomous techniques in varied purposes.”
This analysis was funded, partially, by the Nationwide Science Basis, the Air Pressure Workplace of Scientific Analysis, the Workplace of Naval Analysis, the MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab, the MIT Quest for Intelligence, the Middle for Brains, Minds, and Machines, Boston Dynamics Synthetic Intelligence Institute, the Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Synthetic Intelligence, Analog Gadgets, JPMorgan Chase and Co., and Salesforce.

MIT Information
