
A Chinese language hacking group is hijacking the SSH daemon on community home equipment by injecting malware into the method for persistent entry and covert operations.
The newly recognized assault suite has been utilized in assaults since mid-November 2024, attributed to the Chinese language Evasive Panda, aka DaggerFly, cyber-espionage group.
As per the findings of Fortinet’s Fortiguard researchers, the assault suite is known as “ELF/Sshdinjector.A!tr” and consists of a set of malware injected into the SSH daemon to carry out a broad vary of actions.
Fortiguard says ELF/Sshdinjector.A!tr was utilized in assaults towards community home equipment, however though it has been documented beforehand, no analytical experiences exist on the way it works.
The Evasive Panda menace actors have been energetic since 2012 and have been just lately uncovered for conducting assaults deploying a novel macOS backdoor, finishing up provide chain assaults by way of ISPs in Asia, and gathering intelligence from U.S. organizations in a four-month-long operation.
Concentrating on SSHD
Whereas Fortiguard has not shared how the community home equipment are initially being breached, as soon as compromised, a dropper part checks if the system is already contaminated and if it is working underneath root privileges.
If situations are met, a number of binaries, together with an SSH library (libssdh.so), can be dropped onto the goal machine.
This file acts as the primary backdoor part, answerable for command and management (C2) communications and knowledge exfiltration.
Different binaries, comparable to ‘mainpasteheader’ and ‘selfrecoverheader,’ assist the attackers safe persistence on the contaminated gadgets.
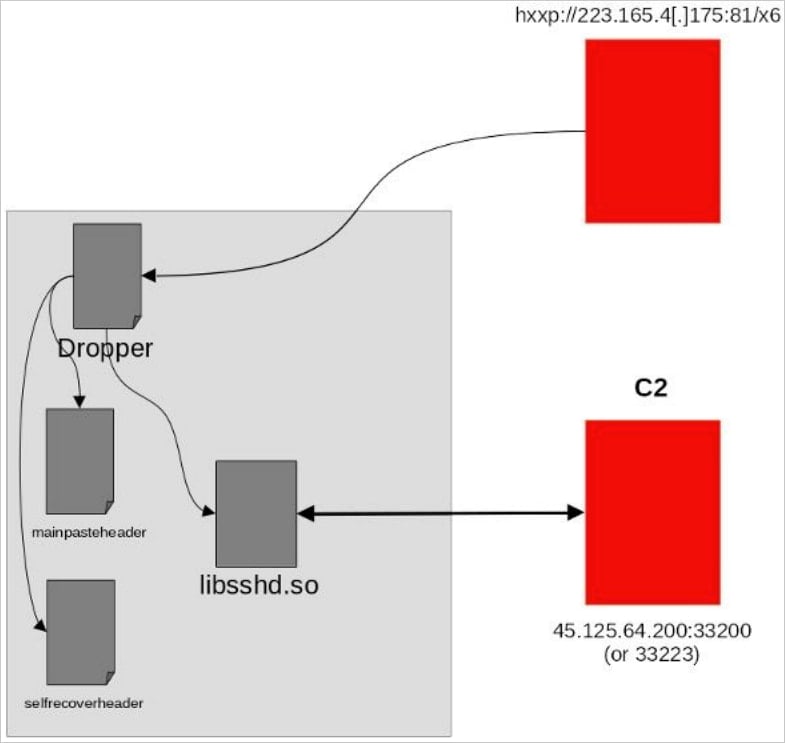
Supply: Fortiguard
The malicious SSH library is injected into the SSH daemon after which waits for incoming instructions from the C2 to carry out system reconnaissance, credential theft, course of monitoring, distant command execution, and file manipulation,
The fifteen supported instructions are:
- Gather system particulars like hostname and MAC handle and exfiltrate them.
- Record put in providers by checking information in /and many others/init.d.
- Learn delicate person knowledge from /and many others/shadow.
- Retrieve an inventory of all energetic processes on the system.
- Try and entry /var/log/dmesg for system logs.
- Attempt to learn /tmp/fcontr.xml for potential delicate knowledge.
- Record the contents of a specified listing.
- Add or obtain information between the system and the attacker.
- Open a distant shell to present the attacker full command-line entry.
- Execute any command remotely on the contaminated system.
- Cease and take away the malicious course of from reminiscence.
- Delete particular information from the system.
- Rename information on the system.
- Notify the attacker that the malware is energetic.
- Ship stolen system data, service lists, and person credentials.
Fortiguard additionally famous that it used AI-assisted instruments to reverse engineer and analyze this malware. Whereas this wasn’t free of great issues comparable to hallucination, extrapolation, and omissions, the device confirmed promising potential.
“Whereas disassemblers and decompilers have improved during the last decade, this can’t be in comparison with the extent of innovation we’re seeing with AI,” commented Fortinet’s researchers.
Fortinet says its clients are already protected towards this malware by way of its FortiGuard AntiVirus service, which detects the threats as ELF/Sshdinjector.A !tr and Linux/Agent.ACQ!tr.
The researchers additionally shared hashes to samples uploaded to VirusTotal [1, 2, 3].

