ESET researchers have found a vulnerability that enables bypassing UEFI Safe Boot, affecting the vast majority of UEFI-based techniques. This vulnerability, assigned CVE-2024-7344, was present in a UEFI software signed by Microsoft’s Microsoft Company UEFI CA 2011 third-party UEFI certificates. Exploitation of this vulnerability results in the execution of untrusted code throughout system boot, enabling potential attackers to simply deploy malicious UEFI bootkits (resembling Bootkitty or BlackLotus) even on techniques with UEFI Safe Boot enabled, whatever the put in working system.
The affected UEFI software is a part of a number of real-time system restoration software program suites developed by Howyar Applied sciences Inc., Greenware Applied sciences, Radix Applied sciences Ltd., SANFONG Inc., Wasay Software program Know-how Inc., Pc Training System Inc., and Sign Pc GmbH. Following is the record of susceptible software program merchandise:
- Howyar SysReturn earlier than model 10.2.023_20240919
- Greenware GreenGuard earlier than model 10.2.023-20240927
- Radix SmartRecovery earlier than model 11.2.023-20240927
- Sanfong EZ-back System earlier than model 10.3.024-20241127
- WASAY eRecoveryRX earlier than model 8.4.022-20241127
- CES NeoImpact earlier than model 10.1.024-20241127
- SignalComputer HDD King earlier than model 10.3.021-20241127
The vulnerability is precipitated by way of a customized PE loader as an alternative of utilizing the usual and safe UEFI features LoadImage and StartImage. Because of this, the applying permits the loading of any UEFI binary – even an unsigned one – from a specifically crafted file named cloak.dat, throughout system begin, whatever the UEFI Safe Boot state.
We reported our findings to the CERT Coordination Middle (CERT/CC) in June 2024, which efficiently contacted the affected distributors. The difficulty has now been fastened of their merchandise and the previous, susceptible binaries had been revoked by Microsoft within the January 14th, 2025 Patch Tuesday replace.
Key factors of this blogpost:
- ESET researchers found a brand new vulnerability, CVE-2024-7344, that enables bypassing UEFI Safe Boot on the vast majority of UEFI-based techniques.
- Exploitation of this vulnerability permits execution of untrusted code throughout system boot, enabling deployment of malicious UEFI bootkits.
- All UEFI techniques with Microsoft third-party UEFI signing enabled are affected (Home windows 11 Secured-core PCs ought to have this feature disabled by default).
- The difficulty was fastened by affected distributors and previous, susceptible binaries had been revoked by Microsoft within the January 14th, 2025 Patch Tuesday replace.
Following is the coordinated disclosure timeline. We’d wish to thank CERT/CC for its assist in coordinating the vulnerability disclosure course of, and the affected distributors for clean and clear communication and cooperation throughout the vulnerability disclosure and remediation course of.
Coordinated disclosure timeline:
- 2024-07-08: ESET discovered the vulnerability.
- 2024-07-09: ESET reported the vulnerability to CERT/CC.
- 2024-07-23: CERT/CC agreed to assist us coordinate the vulnerability disclosure course of – public disclosure date was set to 2024-10-21.
- 2024-08-05: CERT/CC efficiently reached out to the affected distributors.
- 2024-08-20: Distributors offered preliminary patch for evaluation.
- 2024-08-20: ESET confirmed the reported difficulty was addressed accurately, however found one other newly launched difficulty with the identical root trigger.
- 2024-08-28: Distributors offered second patch for evaluation.
- 2024-09-23: We agreed with Microsoft on the brand new public disclosure date of 2025-01-14.
- 2025-01-14: Revocation of affected susceptible UEFI purposes by Microsoft.
- 2025-01-16: ESET blogpost printed.
UEFI Safe Boot in the actual world
Earlier than leaping in to describing the vulnerability, let’s take a look at how UEFI Safe Boot verification works on actual gadgets, and who’s accountable for managing the UEFI Safe Boot databases on them.
The essential logic is kind of easy and is depicted in Determine 1. When UEFI Boot Supervisor proceeds to load a boot software, resembling Home windows Boot Supervisor, shim, GRUB2, or related, amongst different checks, it verifies the boot software binary towards two Safe Boot databases:
- db – record of allowed certificates or PE Authenticode hashes, trusted by the platform firmware.
- dbx – record of forbidden certificates or PE Authenticode hashes.
The circumstances are that the verified picture must be trusted by the db and, on the similar time, the file’s hash or its certificates should not be listed within the dbx database. Based mostly on the verification outcomes, the UEFI boot supervisor both causes a safety violation or executes the verified picture.
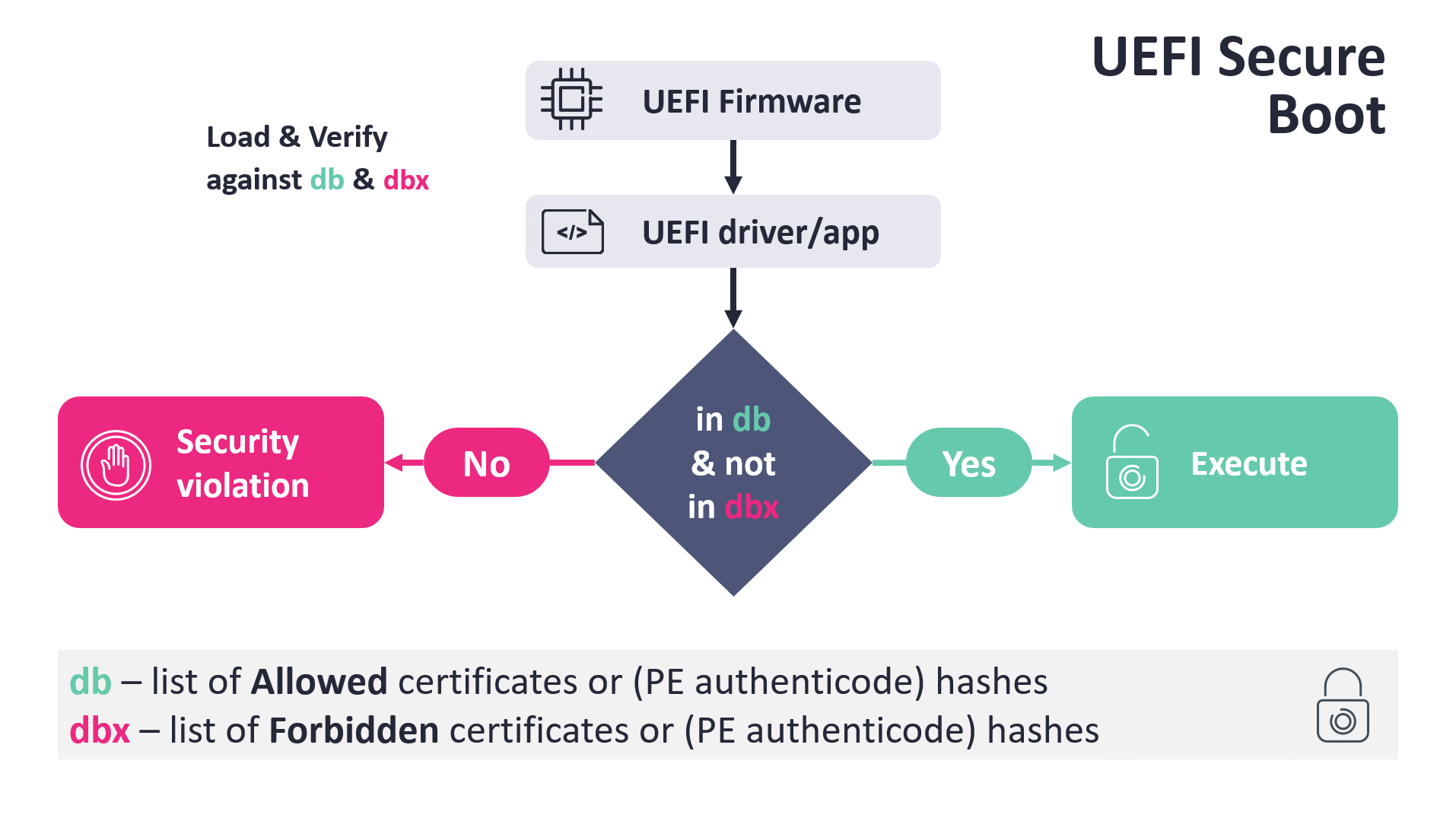
To make sure that UEFI Safe Boot can safe the boot strategy of main working techniques on newly bought UEFI gadgets (by default and with out person interplay), most gadgets include a set of particular UEFI certificates enrolled of their db database. Whereas these certificates can differ primarily based on the OEM and the particular gadget’s necessities and objective, on most common gadgets (resembling laptops, desktops, servers…), Microsoft asks OEMs to incorporate Microsoft’s personal certificates. That’s why Microsoft performs an vital function in securing most of such UEFI-based gadgets, as with Microsoft’s keys enrolled in db, Microsoft can handle what’s allowed, and what’s not allowed, to be executed throughout boot.
Microsoft UEFI certificates
As defined above, many UEFI gadgets include Microsoft’s UEFI certificates enrolled. The next are two particular certificates which might be often current among the many trusted ones on such gadgets:
- Microsoft Home windows Manufacturing PCA 2011
- Microsoft Company UEFI CA 2011
Observe that the Microsoft Home windows Manufacturing PCA 2011 certificates must be revoked and changed with the Home windows UEFI CA 2023 certificates by Microsoft quickly (extra information), as a response to the susceptible Home windows bootloaders associated to the notorious BlackLotus bootkit. New or up to date Home windows gadgets will already belief this new certificates. Within the case of the Microsoft Company UEFI CA 2011 certificates, it nonetheless appears to be used for signing new UEFI purposes; nevertheless, it must also get replaced sooner or later with a brand new certificates referred to as Microsoft UEFI CA 2023. For anybody concerned with Microsoft’s UEFI certificates rolling plan, take a look on the Evolving the Safe Boot Ecosystem slides offered on the UEFI Fall 2023 Builders Convention & Plugfest.
Whereas the previous certificates (the PCA one) is utilized by Microsoft to signal its personal UEFI boot purposes, the latter is utilized by Microsoft to signal UEFI boot software program developed by third events, which incorporates Linux shims, numerous specialised restoration, backup, disk encryption, or upkeep software program, and so forth…
Which means that anybody concerned with having their boot-time software program UEFI Safe Boot-compatible by default can ask Microsoft to signal their binaries (by means of the Home windows {Hardware} Dev Middle dashboard), and if the binaries go Microsoft’s inside evaluation, Microsoft indicators them with its third-party UEFI certificates and thus the information turn out to be suitable with the vast majority of UEFI techniques, which belief Microsoft’s third-party certificates (on Home windows 11 Secured-core PCs, Microsoft’s third-party UEFI certificates shouldn’t be thought of as trusted by default).
From the Microsoft UEFI signing necessities obtainable on-line, it’s unclear what the inner evaluation course of consists of, regardless that it actually evokes some deeper evaluation as an alternative of simply strolling by means of the listed necessities. Whereas we imagine that the handbook evaluation course of is being improved over time with each new vulnerability found, larger transparency in what is definitely being signed and in what checks this handbook evaluation course of consists of might improve the probabilities that such clearly susceptible binaries because the one described on this report are found and glued sooner.
CVE-2024-7344
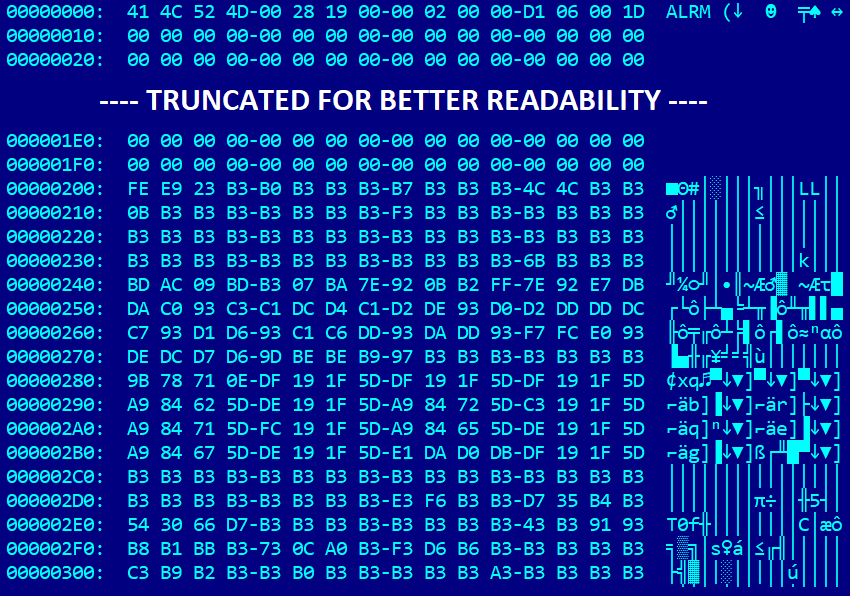
After we encountered Howyar’s SysReturn software program bundle final yr, the very first thing that instantly caught our consideration was the presence of a file named cloak.dat deployed together with a Microsoft-signed UEFI software named reloader.efi. Following are the PE Authenticode hashes of the susceptible reloader.efi software:
- cdb7c90d3ab8833d5324f5d8516d41fa990b9ca721fe643fffaef9057d9f9e48 (64-bit model)
- e9e4b5a51f6a5575b9f5bfab1852b0cb2795c66ff4b28135097cba671a5491b9 (32-bit model)
On this evaluation, we use the 64-bit model of reloader.efi. As proven in Determine 2, the cloak.dat file accommodates a header-like information construction beginning with the magic string ALRM. This header is adopted by unknown information visually resembling the construction of a PE/COFF file header, encrypted utilizing a easy XOR cipher. It’s straightforward to guess the important thing primarily based on the frequency of 0xB3 bytes, comparable to the plethora of 0x00 bytes current in common PE/COFF headers. Decrypting cloak.dat through the use of an XOR operation with the important thing 0xB3 reveals that it certainly accommodates a UEFI software – furthermore, an unsigned one.
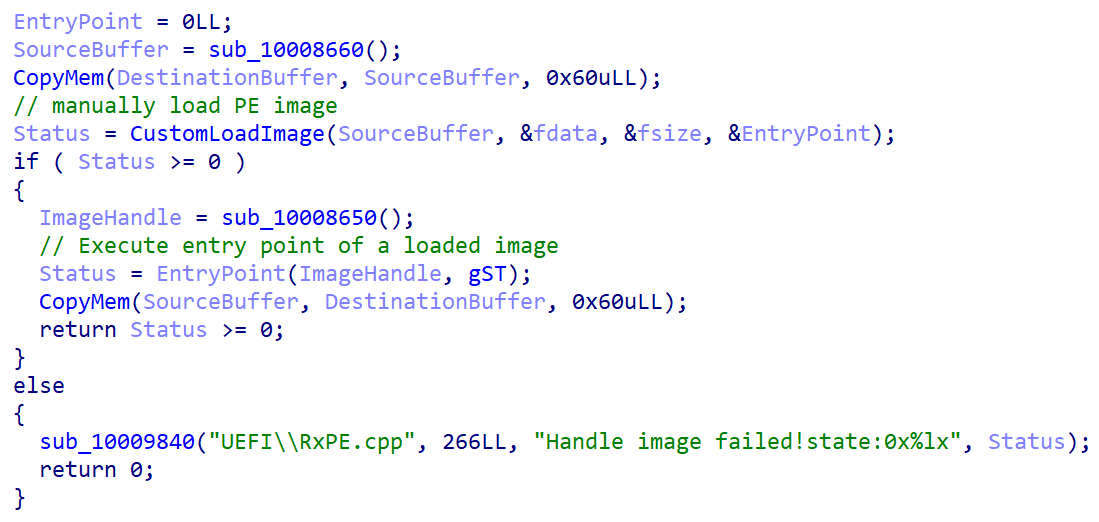
We rapidly came upon that the extracted binary isn’t malicious, however we questioned: is that this binary in some way utilized by SysReturn’s bootloader throughout system begin? If that’s the case, does it take UEFI Safe Boot into consideration and refuse to load this unsigned binary if enabled? After wanting deeper into reloader.efi, we discovered code accountable for loading cloak.dat file into reminiscence and decrypting the embedded picture. As proven in Determine 3, the perform tries to load the file from one of many following areas on the EFI system partition:
- EFIMicrosoftbootcloak64.dat
- EFIbootcloak64.dat
- EFIMicrosoftbootcloak.dat
- EFIbootcloak.dat

Up to now, there wouldn’t be something flawed with that – the bootloader might nonetheless go the buffer containing the decrypted PE picture to the UEFI’s LoadImage perform as an argument, which might be sure that the picture meets the machine’s UEFI Safe Boot coverage by the verification course of described in Determine 1. Sadly, this isn’t the case. After decryption of a PE picture from the cloak.dat file, the susceptible bootloader calls its personal perform depicted in Determine 4, accountable for manually loading and executing the picture with none Safe Boot-related integrity checks.
A proof of idea demonstrating exploitation of the vulnerability on a system with UEFI Safe Boot enabled is proven within the video beneath.
Exploitation of this vulnerability isn’t restricted to techniques with the affected restoration software program put in, as attackers can carry their very own copy of the susceptible reloader.efi binary to any UEFI system with the Microsoft third-party UEFI certificates enrolled. Additionally, elevated privileges are required to deploy the susceptible and malicious information to the EFI system partition (native administrator on Home windows; root on Linux). To take advantage of the vulnerability, an attacker would want to:
- Exchange a default OS bootloader binary on the EFI system partition (ESP) with the susceptible reloader.efi.
- Copy a specifically crafted cloak.dat file, containing a malicious UEFI software, to one of many paths on the ESP supported by the susceptible bootloader.
- Reboot the system.
After we confirmed the vulnerability by making a working proof of idea, we observed that the susceptible reloader.efi software was used not solely by Howyar’s SysReturn software program, but additionally by a number of further restoration software program merchandise. An exhaustive record of affected software program packages will be discovered originally of this blogpost. As a couple of product developed by totally different distributors appeared to be affected, we contacted CERT/CC, who helped us attain out to the affected events and coordinate the vulnerability disclosure course of.
Up to now, now we have not detected any real-world exploitation makes an attempt in our telemetry information.
Safety and detection
The vulnerability will be mitigated by making use of the most recent UEFI revocations from Microsoft. Home windows techniques must be up to date robotically. Microsoft’s advisory for the CVE-2024-7344 vulnerability will be discovered right here. Use the next PowerShell instructions (run with elevated permissions) to examine whether or not you’re affected by the vulnerability and if the mandatory revocations had been put in in your system:
# UEFI techniques; returns True in case your system is affected by the CVE-2024-7344
[System.Text.Encoding]::ASCII.GetString((Get-SecureBootUEFI db).bytes) -match ‘Microsoft Company UEFI CA 2011’
# 64-bit UEFI techniques; returns True should you’re protected (the susceptible driver is revoked in your system)
[BitConverter]::ToString((Get-SecureBootUEFI dbx).bytes) -replace ‘-‘ -match ‘cdb7c90d3ab8833d5324f5d8516d41fa990b9ca721fe643fffaef9057d9f9e48’
# 32-bit UEFI techniques; returns True should you’re protected (the susceptible driver is revoked in your system)
[BitConverter]::ToString((Get-SecureBootUEFI dbx).bytes) -replace ‘-‘ -match ‘e9e4b5a51f6a5575b9f5bfab1852b0cb2795c66ff4b28135097cba671a5491b9’
For Linux techniques, updates must be obtainable by means of the Linux Vendor Firmware Service. Use the next instructions to examine whether or not the mandatory revocations are put in in your system:
dbxtool –list | grep ‘cdb7c90d3ab8833d5324f5d8516d41fa990b9ca721fe643fffaef9057d9f9e48’
dbxtool –list | grep ‘e9e4b5a51f6a5575b9f5bfab1852b0cb2795c66ff4b28135097cba671a5491b9’
Whereas UEFI revocations successfully shield your system towards CVE-2024-7344, there are different kind of efficient methods of defending towards (or a minimum of detecting) exploitation of unknown susceptible signed UEFI bootloaders and deployment of UEFI bootkits, together with:
- Managed entry to information situated on the EFI system partition. In most UEFI bootkit set up situations, an attacker wants to change the contents of the EFI system partition in an effort to set up a UEFI bootkit or to use a vulnerability in a signed UEFI bootloader on the focused system. Most safety merchandise permit creation of customized user-defined file entry guidelines that permit blocking entry to particular information or directories on the system (e.g., right here and right here).
- UEFI Safe Boot customization. As detailed within the NSA’s UEFI Safe Boot Customization report, Safe Boot customization can be utilized to successfully shield towards UEFI bootkits or, a minimum of, to scale back the assault floor or permit quicker revocations of susceptible UEFI purposes to system house owners if official revocation updates take an extended time. Whereas efficient, it typically requires skilled directors (improper Safe Boot configurations could make techniques quickly unbootable) and it may be tough to handle at scale.
- Distant attestation with TPM, the place measurements of UEFI boot parts and configuration will be validated towards their recognized good values by a trusted distant server, and thus used to detect unauthorized boot modifications.
Conclusion
The variety of UEFI vulnerabilities found lately and the failures in patching them or revoking susceptible binaries inside an affordable time window reveals that even such an important function as UEFI Safe Boot shouldn’t be thought of an impenetrable barrier.
Nonetheless, what issues us essentially the most within the case of the vulnerability reported on this blogpost isn’t the time it took to repair and revoke the binary, which was fairly good in comparison with related circumstances, however the truth that this isn’t the primary time that such an clearly unsafe signed UEFI binary has been found. In actuality, a really related Microsoft-signed susceptible UEFI software (CVE-2022-34302), implementing its personal unsafe PE loader, was found about two years in the past by Eclypsium in One Bootloader to Load Them All.
This raises questions of how frequent using such unsafe strategies is amongst third-party UEFI software program distributors, and what number of different such obscure, however signed, bootloaders there may be on the market. We reached out to Microsoft in regards to the scenario, hoping it might carry extra transparency into what third-party UEFI purposes they signal, in order that anybody can rapidly uncover and report such clearly unsafe UEFI purposes in the event that they mistakenly go (or handed a very long time in the past) Microsoft’s UEFI third-party code-signing evaluation. We imagine that Microsoft’s deliberate rollout of latest UEFI certificates gives an amazing alternative to make this occur, pushing UEFI third-party signing transparency and UEFI safety one step ahead.
For any inquiries about our analysis printed on WeLiveSecurity, please contact us at threatintel@eset.com.ESET Analysis gives personal APT intelligence studies and information feeds. For any inquiries about this service, go to the ESET Risk Intelligence web page.
IoCs
Because the susceptible loaders are a part of authentic software program packages which might be doubtlessly current on hundreds of techniques which have by no means been compromised by way of these loaders, we’re not offering indicators of compromise to keep away from large misidentification. As an alternative, defenders ought to observe the recommendation within the Safety and detection part.

