
The Qilin ransomware group has been utilizing a brand new tactic and deploys a customized stealer to steal account credentials saved in Google Chrome browser.
The credential-harvesting methods has been noticed by the Sophos X-Ops group throughout incident response engagements and marks an alarming change on the ransomware scene.
Assault overview
The assault that Sophos researchers analyzed began with Qilin having access to a community utilizing compromised credentials for a VPN portal that lacked multi-factor authentication (MFA).
The breach was adopted by 18 days of dormancy, suggesting the potential of Qilin shopping for their approach into the community from an preliminary entry dealer (IAB).
Probably, Qilin frolicked mapping the community, figuring out crucial belongings, and conducting reconnaissance.
After the primary 18 days, the attackers moved laterally to a site controller and modified Group Coverage Objects (GPOs) to execute a PowerShell script (‘IPScanner.ps1’) on all machines logged into the area community.
The script, executed by a batch script (‘logon.bat’) that was additionally included within the GPO, was designed to gather credentials saved in Google Chrome.
The batch script was configured to run (and set off the PS script) each time a person logged into their machine, whereas stolen credentials had been saved on the ‘SYSVOL’ share underneath the names ‘LD’ or ‘temp.log.’
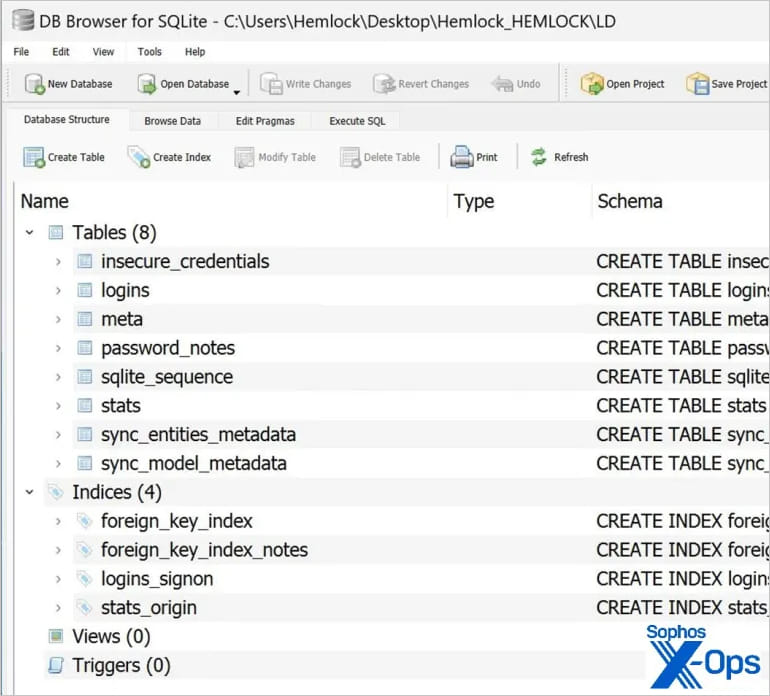
Supply: Sophos
After sending the recordsdata to Qilin’s command and management (C2) server, the native copies and associated occasion logs had been wiped, to hide the malicious exercise. Finally, Qilin deployed their ransomware payload and encrypted information on the compromised machines.
One other GPO and a separate batch file (‘run.bat’) had been used to obtain and execute the ransomware throughout all machines within the area.
Supply: Sophos
Protection complexity
Qilin’s method to focus on Chrome credentials creates a worrying precedent that might make defending towards ransomware assaults much more difficult.
As a result of the GPO utilized to all machines within the area, each system {that a} person logged into was topic to the credential harvesting course of.
Which means that the script doubtlessly stole credentials from all machines throughout the corporate, so long as these machines had been related to the area and had customers logging into them through the interval the script was energetic.
Such intensive credential theft might allow follow-up assaults, result in widespread breaches throughout a number of platforms and providers, make response efforts much more cumbersome, and introduce a lingering, long-lasting menace after the ransomware incident is resolved.
Organizations can mitigate this danger by imposing strict insurance policies to forbid the storage of secrets and techniques on net browsers.
Moreover, implementing multi-factor authentication is essential in defending accounts towards hijacks, even within the case of credential compromises.
Lastly, implementing the rules of least privilege and segmenting the community can considerably hamper a menace actor’s capacity to unfold on the compromised community.
Provided that Qilin is an unconstrained and multi-platform menace with hyperlinks to the Scattered Spider social engineering consultants, any tactical change poses a major danger to organizations.
