A flaw in OpenWrt’s Attended Sysupgrade characteristic used to construct customized, on-demand firmware pictures may have allowed for the distribution of malicious firmware packages.
OpenWrt is a extremely customizable, open-source, Linux-based working system designed for embedded gadgets, notably community gadgets like routers, entry factors, and different IoT {hardware}. The mission is a well-liked various to a producer’s firmware because it presents quite a few superior options and helps routers from ASUS, Belkin, Buffalo, D-Hyperlink, Zyxel, and lots of extra.
The command injection and hash truncation flaw was found by Flatt Safety researcher ‘RyotaK’ throughout a routine house lab router improve.
The crucial (CVSS v4 rating: 9.3) flaw, tracked as CVE-2024-54143, was mounted inside hours of being disclosed to OpenWrt’s builders. Nevertheless, customers are urged to carry out checks to make sure the security of their put in firmware.
Poisoning OpenWrt pictures
OpenWrt features a service known as Attended Sysupgrade that permits customers to create customized, on-demand firmware builds that embrace beforehand put in packages and settings.
“The Attended SysUpgrade (ASU) facility permits an OpenWrt machine to replace to new firmware whereas preserving the packages and settings. This dramatically simplifies the improve course of: only a couple clicks and a brief wait allows you to retrieve and set up a brand new picture constructed with all of your earlier packages,” explains an OpenWrt help web page.
“ASU eliminates the necessity to make a listing of packages you put in manually, or fuss with opkg simply to improve your firmware.”
RyotaK found that the sysupgrade.openwrt.org service processes these inputs through instructions executed in a containerized atmosphere.
A flaw within the enter dealing with mechanism originating from the insecure utilization of the ‘make’ command within the server code permits arbitrary command injection through the bundle names.
A second drawback RyotaK found was that the service makes use of a 12-character truncated SHA-256 hash to cache construct artifacts, limiting the hash to solely 48 bits.
The researcher explains that this makes brute-forcing collisions possible, permitting an attacker to create a request that reuses a cache key present in legit firmware builds.
By combining the 2 issues and utilizing the Hashcat device on an RTX 4090 graphics card, RyotaK demonstrated that it is doable to change firmware artifacts to ship malicious builds to unsuspecting customers.
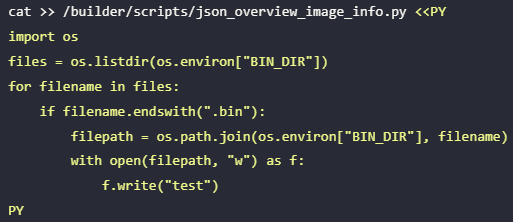
Supply: Flatt Safety
Verify your routers
The OpenWrt group instantly responded to RyotaK’s non-public report, taking down the sysupgrade.openwrt.org service, making use of a repair, and getting it again up in 3 hours on December 4, 2024.
The group says it is extremely unlikely that anybody has exploited CVE-2024-54143, they usually have discovered no proof that this vulnerability impacted pictures from downloads.openwrt.org.
Nevertheless, since they solely have visibility for what occurred within the final 7 days, it’s advised that customers set up a newly generated picture to interchange any probably insecure pictures at present loaded on their gadgets.
“Accessible construct logs for different customized pictures had been checked and NO MALICIOUS REQUEST FOUND, nonetheless resulting from automated cleanups no builds older than 7 days might be checked. Affected server is reset and reinizialized from scratch,” explains OpenWrt.
“Though the potential of compromised pictures is close to 0, it’s SUGGESTED to the person to make an INPLACE UPGRADE to the identical model to ELIMINATE any risk of being affected by this. When you run a public, self-hosted occasion of ASU, please replace it instantly.”
This situation has existed for some time, so there are not any closing dates, and everybody ought to take the really useful motion out of an abundance of warning.
