
A brand new ransomware household referred to as ‘Ymir’ has been noticed within the wild, encrypting programs that have been beforehand compromised by the RustyStealer infostealer malware.
RustyStealer is a recognized malware household first documented in 2021, however its look with ransomware demonstrates one other instance of the latest development of cybercrime operations working collectively.
In keeping with Kaspersky researchers who found Ymir throughout an incident response, the novel ransomware pressure is notable for its in-memory execution, use of the African Lingala language in a code remark, use of PDF recordsdata as ransom notes, and its extension configuration choices.
Though Kaspersky has discovered proof that Ymir connects to exterior servers that may facilitate knowledge exfiltration, the ransomware doesn’t characteristic such a functionality.
BleepingComputer has confirmed that the ransomware operation launchedin July 2024, when it began attacking firms worldwide.
Ymir follows RustyStealer infections
Kaspersky’s evaluation revealed that Rusty stealer had infiltrated a number of programs inside the focused infrastructure two days earlier than Ymir’s deployment.
RustyStealer, basically a credential-harvesting device, enabled attackers to realize unauthorized entry to programs by compromising reputable high-privilege accounts helpful in lateral motion.
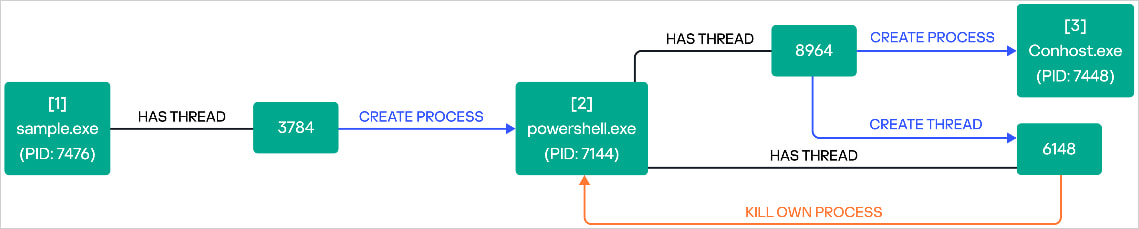
Lateral motion throughout the community was facilitated utilizing instruments like Home windows Distant Administration (WinRM) and PowerShell for distant management. On the identical time, the attackers additionally put in instruments like Course of Hacker and Superior IP Scanner.
Subsequent, they executed scripts related to the SystemBC malware and established covert channels, presumably for knowledge exfiltration or command execution, with the attackers’ infrastructure.
After solidifying the foothold and presumably additionally stealing knowledge utilizing RustyStealer, Ymir ransomware was dropped as the ultimate payload.
Ymir is a novel Home windows ransomware pressure that operates totally from reminiscence, leveraging capabilities like ‘malloc,’ ‘memove,’ and ‘memcmp,’ to evade detection.
Upon launch, it performs system reconnaissance by getting the system date and time, figuring out operating processes, and checking the system uptime, which may also help decide whether or not it runs on a sandbox.
Subsequent, it skips file extensions based mostly on a hardcoded record to keep away from rendering the system unbootable.
Ymir makes use of the ChaCha20 stream cipher, a complicated and quick encryption algorithm, to encrypt recordsdata on the sufferer’s system.
Encrypted recordsdata are appended with a random extension, like “.6C5oy2dVr6,” and a ransom notice named “INCIDENT_REPORT.pdf” is generated from the “.knowledge” part of the Ymir binary in all directories containing encrypted recordsdata.

Supply: BleepingComputer
The ransomware can even modify the Home windows Registry “legalnoticecaption” worth to indicate an extortion demand earlier than a consumer logs in to an encrypted gadget.
The ransom notice claims that knowledge was stolen from the sufferer’s system, and Kaspersky hypothesizes that this might need occurred utilizing instruments deployed previous to Ymir.
Lastly, Ymir scans the system for the presence of PowerShell and leverages it to delete its executable to evade identification and evaluation.
Supply: Kaspersky
Ymir has not established an information leak web site but, but it surely could possibly be that the risk actors have simply began accumulating sufferer knowledge.
Kaspersky warns that Ymir’s use of knowledge stealers as entry brokers might rapidly make this new ransomware household a widespread risk.
