
UK’s Nationwide Cyber Safety Centre (NCSC) has revealed an evaluation of a Linux malware named “Pigmy Goat” created to backdoor Sophos XG firewall units as a part of not too long ago disclosed assaults by Chinese language risk actors.
Final week, Sophos revealed a sequence of reviews dubbed “Pacific Rim” that detailed five-year assaults by Chinese language risk actors on edge networking units.
One of many customized malware utilized in these assaults is a rootkit that intently impersonated Sophos product file naming conventions.
The malware, which is designed for compromising community units, options superior persistence, evasion, and distant entry mechanisms and has a relatively complicated code construction and execution paths.
Though the NCSC report doesn’t attribute the noticed exercise to identified risk actors, it underlines comparable methods, ways, and procedures (TTPs) to the “Castletap” malware, which Mandiant has related to a Chinese language nation-state actor.
Sophos has additionally disclosed the identical malware in its Pacific Rim report, stating the rootkit was utilized in 2022 assaults linked to a Chinese language risk actor generally known as “Tstark.”
“X-Ops recognized two copies of libsophos.so, each deployed utilizing CVE-2022-1040 — one on a high-level authorities system and the opposite on a know-how associate to the identical authorities division,” shared Sophos.
A goat within the firewall
The ‘Pygmy Goat’ malware is an x86-32 ELF shared object (‘libsophos.so’) offering risk actors with backdoor entry to Linux-based networking units such because the Sophos XG firewalls.
It makes use of the LD_PRELOAD surroundings variable to load its payload into the SSH daemon (sshd), permitting it to hook into the daemon’s capabilities and override the settle for operate, which processes incoming connections.
Pygmy Goat displays SSH site visitors for a particular sequence of “magic bytes” within the first 23 bytes of every bundle.
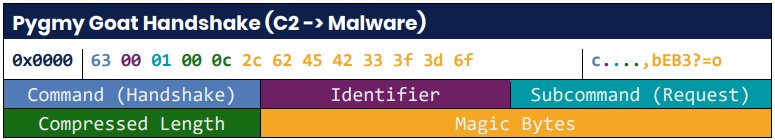
Supply: NCSC
As soon as that sequence is discovered, the connection is recognized as a backdoor session, and the malware redirects it to an inner Unix socket (/tmp/.sshd.ipc) to determine communication with its Command and Management (C2).
The malware additionally listens on a uncooked ICMP socket, ready for packets with an AES-encrypted payload that holds IP and port info for C2 communication, which triggers a connect-back try over TLS.
Supply: NCSC
Pygmy Goat communicates with the C2 over TLS, utilizing an embedded certificates mimicking Fortinet’s “FortiGate” CA, a possible cowl for mixing into community environments the place Fortinet units are widespread.
When an SSH connection is established, a faux handshake with pre-set responses is triggered to create a false picture of legitimacy on community displays.
The C2 server can ship Pygmy Goat instructions for execution on the system, together with the next:
- Open both a /bin/sh or /bin/csh shell.
- Begin capturing community site visitors through libpcap, forwarding outcomes to C2.
- Handle cron duties utilizing BusyBox to schedule actions when the actor is not actively related.
- Use the EarthWorm open-source toolkit to determine a SOCKS5 reverse proxy, permitting C2 site visitors to traverse the community unseen.
Detection and protection
The NCSC report comprises file hashes and YARA and Snort guidelines that detect the magic byte sequences and pretend SSH handshake, so defenders can use them to catch Pygmy Goat exercise early on.
Moreover, handbook checks for /lib/libsophos.so, /tmp/.sshd.ipc, /tmp/.fgmon_cli.ipc, /var/run/sshd.pid, and /var/run/goat.pid, can reveal an an infection.
Additionally it is advisable to arrange monitoring for encrypted payloads in ICMP packets and use of ‘LD_PRELOAD’ within the surroundings of the ‘ssdh’ course of, which is uncommon conduct which will point out Pygmy Goat exercise.
