Researchers are growing a robotic exoskeleton platform that would overcome the restrictions of treadmills used in the course of the rehabilitation of the various stroke survivors who’ve issues strolling.
Greater than 80% of stroke sufferers can lose regular operate in a single leg, which impacts their pure gait, growing the chance of falling and stopping them from partaking in sure actions – maybe resulting in a extra sedentary way of life and its related well being points.
Coaching a affected person’s physique to appropriate asymmetrical gait is an important part of rehabilitation efforts, and we have seen numerous robotic exoskeletons used at the side of treadmills over time. However there’s room for enchancment.
“The final word purpose of gait rehabilitation is to not enhance strolling on a treadmill – it’s to enhance locomotor operate overground,” stated Meghan Huber, senior creator of a examine from the College of Massachusetts Amherst. “With this in thoughts, our focus is to develop strategies of gait rehabilitation that translate to practical enhancements in real-world contexts.”
Impressed by the success of split-belt treadmills, the workforce has managed develop a hip exoskeleton system that mimics the actions of side-by-side belts shifting at totally different speeds to amplify gait asymmetry to reinforce motor studying.
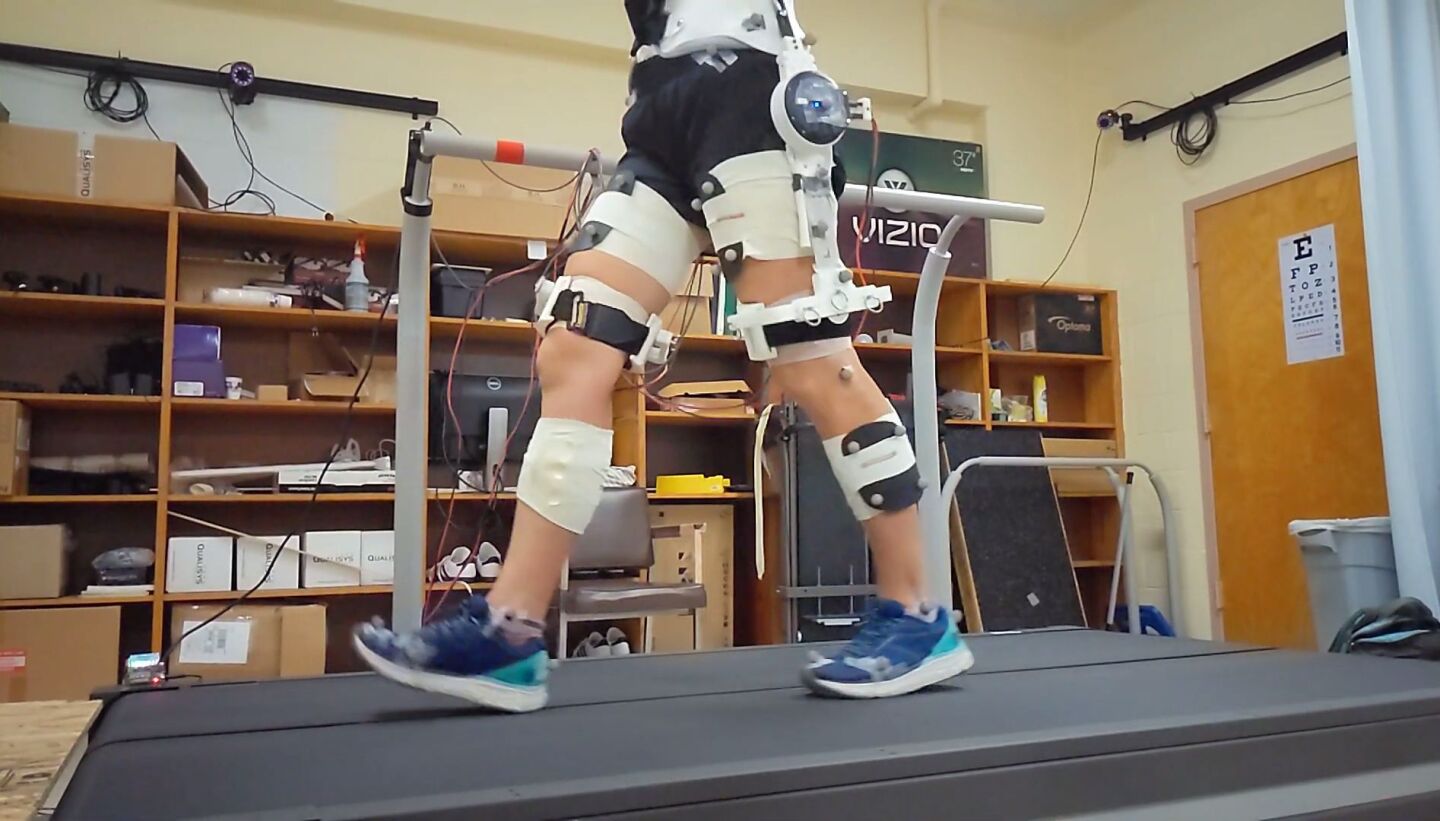
College of Massachusetts Amherst
The compact exoskeleton in query is a customized creation from the Human Robotic Techniques Laboratory at Amherst, which is worn across the waist and secured to the consumer’s thighs. An actuator at every hip joint gives the limb-moving torque whereas a Raspberry Pi 4 controls the present.
The proof of idea was programmed to imitate the performance of a split-belt treadmill by making use of resistive forces at one hip whereas the opposite is handled to assistive forces, altering gait symmetry within the course of. It was examined on simply over a dozen wholesome volunteers, with the workforce discovering that the system “elicited adaptation in spatiotemporal and kinetic gait measures just like split-belt treadmill coaching.”
Although energy and processing throughout this examine have been off-device, the workforce is now shifting to develop a conveyable setup for overground settings, within the hope of future medical purposes.
“A transportable exoskeleton provides quite a few medical advantages,” stated lead creator of the examine, Banu Abdikadirova. “Such a tool may be seamlessly built-in into the every day lives of persistent stroke survivors, providing an accessible option to enhance coaching time, which is essential for enhancing strolling. It will also be used throughout early intervention in hospitals for improved practical outcomes.”
A paper on the event has been revealed in IEEE Transactions on Neural Techniques and Rehabilitation Engineering.
Supply: College of Massachusetts Amherst
