In 2023, 63% of firms had been victims of ransomware, in response to Sophos.. At a time once we hear extra usually than ever about this menace within the international media, it ought to be famous that ransomwares usually are not new, however at the moment gaining a variety of reputation amongst cybercriminals.
As we speak, all kinds of private and non-private organizations are attacked. Nonetheless, for cybercriminals essentially the most appropriate targets are these with poor IT hygiene, in fruitful sectors or whose exercise continuance is vital. Very often, public organizations’ cyberdefense budgets usually are not tailored to the criticality of the knowledge they deal with. Thus, they’re notably affected by threats reminiscent of ransomwares.
When the criticality of some gadgets is underestimated, as it’s usually the case with smartphones and tablets, hackers’ entry is facilitated.
Evolution of ransomwares
Two new tendencies have emerged. On the one hand, it has been noticed that ransomwares are sometimes used as a part of large-scale assaults, generally ready months upfront and concentrating on rigorously chosen firms or public establishments (vital sector, excessive added worth…). Certified as Massive Sport Searching, these onslaughts are sometimes carried out by groups of hackers who’ve extra monetary and/or human sources than the typical.
The second pattern is the alternative of the primary. It’s the widespread of Ransomware-as-a-Service affords on the darkish net, aimed toward individuals with little IT information and on the lookout for a easy and quick method to launch assaults. The Jigsaw ransomware, for instance, is bought for about 3,000 {dollars} on cybercriminal boards. RaaS is obtainable on a subscription foundation and generally affords a administration platform like several SaaS resolution to observe assaults. A lot much less highly effective than Massive Sport Searching, RaaS often targets people or small companies, randomly.
How can a ransomware infiltrate your system?
An infection methodology
To deploy a ransomware on a corporation’s data system, cybercriminals use fleets of computer systems, smartphones or tablets. Usually, they use phishing and software program vulnerabilities.
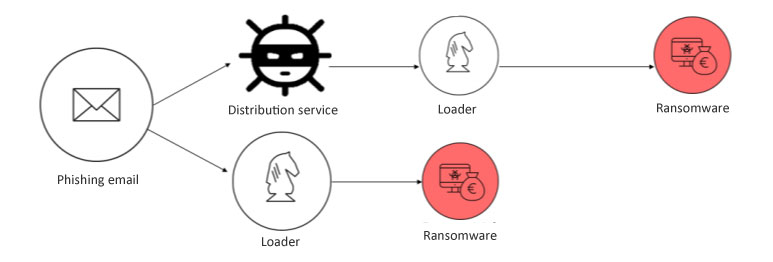
Phishing electronic mail
Operable on a big scale at no cost, electronic mail is a favoured method to unfold ransomwares. A examine performed by Pradeo reveals that 34% of workers click on on the hyperlink introduced in phishing makes an attempt despatched by textual content message (electronic mail, SMS or by way of messaging functions).
Malicious or hijacked net web page
Some web sites mimic recognized firm pages or show a false window to entice Web customers to obtain a program, for instance, claiming a safety flaw within the OS or a required replace. This system is definitely a malware.
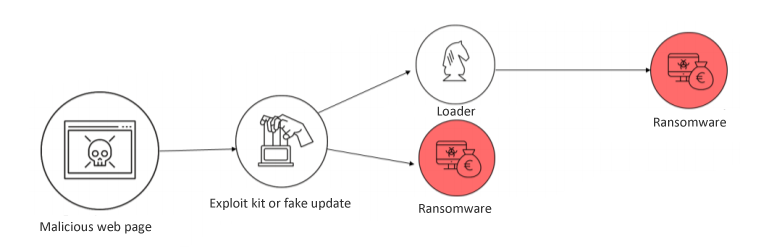
Vulnerabilities exploitation
- Server: Some community vulnerabilities might be exploited to unfold malware. Per week in the past, the banking system in India fell sufferer to it.
- Software program: Safety holes in softwares can facilitate entry to company information. For instance, the democratization of VPN companies makes them a goal of alternative and a few are victims of brute drive assaults to acquire directors’ credentials.
Encryption and ransom demand
When put in on a system linked to an data system, ransomwares quarantine safety and distant administration packages, after which encrypt native and distant information, linked disks, and many others. As soon as this step is accomplished, a ransom is requested.
Usually, hackers demand to be contacted inside a given timeframe. Past that deadline, the encrypted data is erased, bought or revealed on-line.
Nonetheless, even when the fee is made (usually in cryptocurrency, due to this fact untraceable), the group will not be certain to get well all of its information. To have an order of magnitude, the quantity of a ransom ranges from a couple of thousand euros for a person, and varies between 200,000 and 10 million {dollars} for the DarkSide and WastedLocker ransomwares.
Heavy penalties
Monetary losses
Ransomwares are meant to extort cash. When they’re trapped, organizations face a dilemma: ought to we pay the ransom? No matter their reply is, they should face monetary losses associated to an premature shutdown of their exercise, an entire clean-up of their data system, investigations to determine the supply of the assault, penalties from information safety authorities, and many others…
Information leaks
Throughout a ransomware assault and whatever the response of the sufferer, information leakage is inevitable. Even when the ransom is paid and the information is restored, the stolen data often finally ends up on the black market.
Compelled shutdown
A cyberattack usually renders the pc system inoperable. It might probably decelerate and even paralyze the exercise of the affected group. In some sectors, this results in appreciable monetary losses, in others, reminiscent of within the healthcare sector and notably in hospitals, it instantly jeopardizes sufferers’ security.
Picture damages
When a corporation falls sufferer to ransomware, or every other assault resulting in information leakage, it’s troublesome to maintain it quiet. Generally, the laws requires (in most international locations) to inform such incidents to the federal government company answerable for information safety. The media protection of a safety breach has severe penalties on a model picture, which may trigger a lack of confidence from stakeholders: prospects, companions, buyers, and many others.
Forestall ransomware from exploiting your cell fleet to contaminate your data system, defend your cell gadgets with Pradeo Safety.
