
The NoName ransomware gang has been making an attempt to construct a popularity for greater than three years focusing on small and medium-sized companies worldwide with its encryptors and will now be working as a RansomHub affiliate.
The gang makes use of customized instruments often known as the Spacecolon malware household, and deploys them after getting access to a community via brute-force strategies in addition to exploiting older vulnerabilities like EternalBlue (CVE-2017-0144) or ZeroLogon (CVE-2020-1472).
In newer assaults NoName makes use of the ScRansom ransomware, which changed the Scarab encryptor. Moreover, the menace actor tried to make a reputation by experimenting with the leaked LockBit 3.0 ransomware builder, creating the same information leak web site, and utilizing comparable ransom notes.
ScRansom ransomware
Cybersecurity firm ESET tracks the NoName gang as CosmicBeetle and has been monitoring its actions since 2023, with the emergence of the ScRansom, a Delphi-based file-encrypting malware.
In a report at the moment, the researchers be aware that though ScRansom (a part of the Spacecolon malware household) isn’t as refined as different threats on the ransomware scene, it’s a menace that continues to evolve.
The malware helps partial encryption with completely different velocity modes to permit attackers some versatility, and in addition options an ‘ERASE’ mode that replaces file contents with a continuing worth, making them unrecoverable.
ScRansom can encrypt information throughout all drives, together with mounted, distant, and detachable media, and permits the operator to find out what file extensions to focus on via a customizable record.
Earlier than launching the encryptor, ScRansom kills an inventory of processes and companies on the Home windows host, together with Home windows Defender, the Quantity Shadow Copy, SVCHost, RDPclip, LSASS, and processes related to VMware instruments.
ESET notes that ScRansom’s encryption scheme is fairly sophisticated, utilizing a combo of AES-CTR-128 and RSA-1024, and an additional AES key generated to guard the general public key.
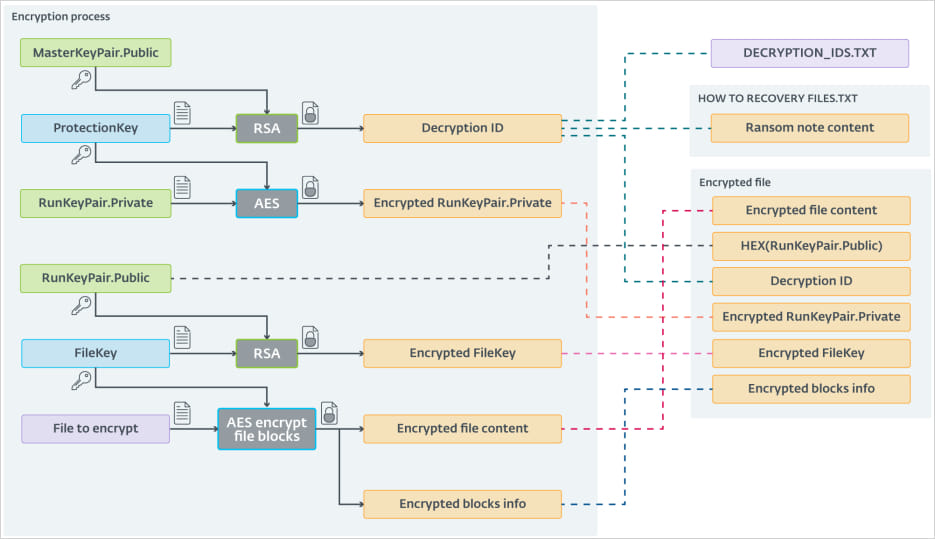
Supply: ESET
Nevertheless, the multi-step course of that entails a number of key exchanges generally introduces errors which will result in failure to decrypt the information even when utilizing the proper keys.
Additionally, if the ransomware is executed a second time on the identical gadget, or in a community of a number of distinct programs, new units of distinctive keys and sufferer IDs shall be generated, making the decryption course of fairly complicated.
One case that ESET highlights is of a sufferer that acquired 31 decryption IDs and AES ProtectionKeys after paying ScRansom, and so they have been nonetheless unable to recuperate all of the encrypted information.
NoName has been utilizing brute pressure to achieve entry to networks however the menace actor additionally exploits a number of vulnerabilities which are extra more likely to be current in SMB environments:
• CVE-2017-0144 (aka EternalBlue),
• CVE-2023-27532 (a vulnerability in a Veeam Backup & Replication element)
• CVE-2021-42278 and CVE-2021-42287 (AD privilege escalation vulnerabilities) via noPac
• CVE-2022-42475 (a vulnerability in FortiOS SSL-VPN)
• CVE-2020-1472 (aka Zerologon)
A latest report from Pure7, a cybersecurity firm in Turkey, additionally mentions that CVE-2017-0290 has additionally been exploited in NoName assaults via a batch file (DEF1.bat) that makes adjustments in Home windows Registry to disable Home windows Defender options, companies, or duties.
NoName deploying RansomHub instruments
NoName’s ascension to the standing of RansomHub affiliate was preceded by a set of strikes displaying the gang’s dedication to the ransomware enterprise. Since ScRansom was not a longtime identify on the scene, the gang determined to take a distinct strategy to extend its visibility.
In September 2023, CosmicBeetle arrange an extortion web site on the darkish net branded ‘NONAME,’ which was a modified copy of the LockBit information leak web site (DLS) that included victims truly compromised by LockBit, not ScRansom, the researchers found after checking on a number of DLS-tracking companies.
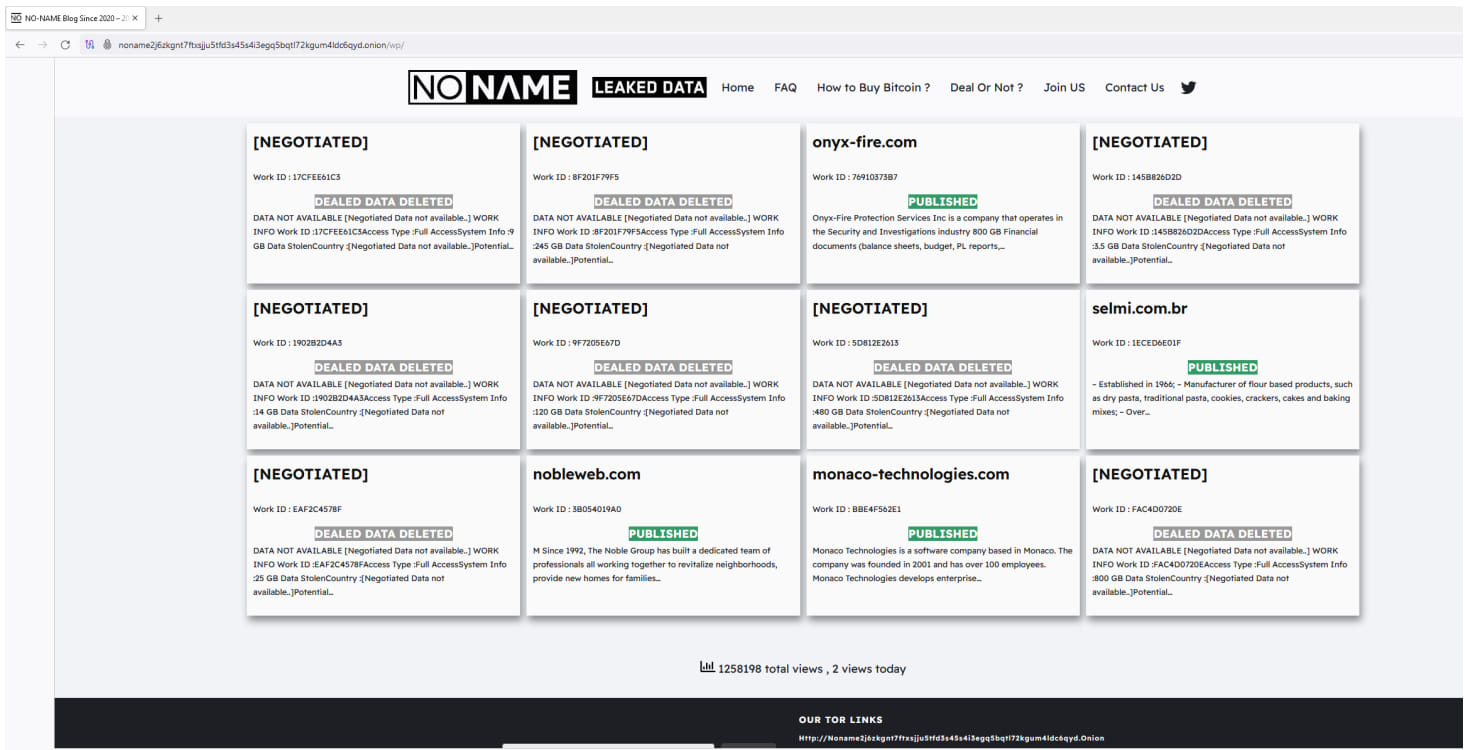
Supply: ESET
In November 2023, the menace actor stepped up its impersonation effort by registering the area lockbitblog[.]information and branding the DLS with the LockBit theme and emblem.
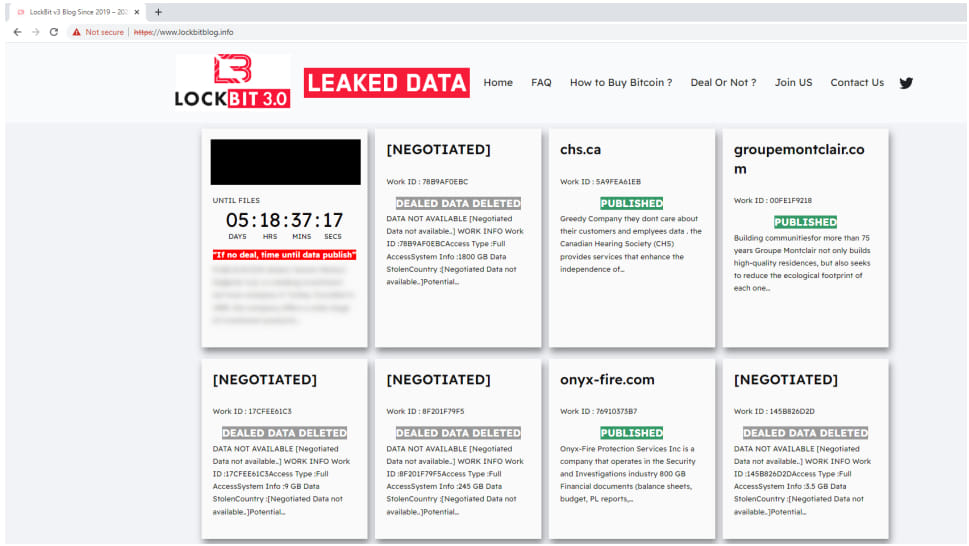
Supply: ESET
The researchers additionally found some latest assaults the place a LockBit pattern was deployed however the ransom be aware had a sufferer ID that they’d already linked to CosmicBeetle. Moreover, the toolset within the incident overlapped with the malware attributed to the CosmicBeetle/NoName menace actor.
Whereas investigating a ransomware incident that began in early June with a failed ScRansom deployment, ESET researchers discovered that the menace actor executed on the identical machine lower than per week later RansomHub’s EDR killer, a instrument that permits privilege escalation and disabling safety brokers by deploying a reputable, weak driver on focused units.
Two days later, on June 10, the hackers executed the RansomHub ransomware on the compromised machine.
The researchers be aware the strategy for extracting the EDR killer, which was typical of CosmicBeetle and never a RansomHub affiliate.
Since there aren’t any public leaks of the RansomHub code or its builder, ESET researchers “consider with medium confidence that CosmicBeetle enrolled itself as a brand new RansomHub affiliate.”
Though the affiliation with RanssomHub isn’t sure, ESET says that the ScRansom encrypter is beneath energetic growth. Mixed with the change from ScRansom to LockBit, it signifies that CosmicBeetle isn’t displaying any indicators of giving up.
